AP Music Theory Syllabus
... Attend concerts of all types of music; analyze the concert for all musical elements. Expectations of Students 1. Students will participate in all classroom discussions and activities. 2. Students will complete all assigned exercises and readings. 3. Students will keep and maintain a Music Theory not ...
... Attend concerts of all types of music; analyze the concert for all musical elements. Expectations of Students 1. Students will participate in all classroom discussions and activities. 2. Students will complete all assigned exercises and readings. 3. Students will keep and maintain a Music Theory not ...
How Music Works
... During the Baroque period, composers needed to make alterations in these pure tunings to allow modulations to more distant keys. Various new systems were developed that alter some intervals from pure ratios and are called mean-tone temperaments. Mean-tone systems in general make more commonly-used i ...
... During the Baroque period, composers needed to make alterations in these pure tunings to allow modulations to more distant keys. Various new systems were developed that alter some intervals from pure ratios and are called mean-tone temperaments. Mean-tone systems in general make more commonly-used i ...
Master Your Theory Grade 1
... A FLAT b is another kind of accidental. It lowers a note by a semitone. D flat is a semitone below D (D flat is another name for the black note between C and D) E flat is a semitone below E (E flat is the same note as D sharp on a keyboard). ...
... A FLAT b is another kind of accidental. It lowers a note by a semitone. D flat is a semitone below D (D flat is another name for the black note between C and D) E flat is a semitone below E (E flat is the same note as D sharp on a keyboard). ...
Scales and temperaments: the fivefold way
... We saw in the last chapter that for notes played on conventional instruments, where partials occur at integer multiples of the fundamental frequency, intervals corresponding to frequency ratios expressable as a ratio of small integers are favored as consonant. In this chapter, we shall investigate Q ...
... We saw in the last chapter that for notes played on conventional instruments, where partials occur at integer multiples of the fundamental frequency, intervals corresponding to frequency ratios expressable as a ratio of small integers are favored as consonant. In this chapter, we shall investigate Q ...
Is Relative Pitch Specific to Pitch?
... We began our study with the classic paradigm used by Dowling and his colleagues (Dowling, 1978; Dowling & Fujitani, 1970) to demonstrate the importance of the melodic contour. They presented subjects with a randomly generated five-note melody, followed by a second five-note melody that was transpose ...
... We began our study with the classic paradigm used by Dowling and his colleagues (Dowling, 1978; Dowling & Fujitani, 1970) to demonstrate the importance of the melodic contour. They presented subjects with a randomly generated five-note melody, followed by a second five-note melody that was transpose ...
Lesson UUU: The Major Scale Introduction: The
... The major scale, one of the most important building blocks of tonal music, consists of seven distinct pitch classes called scale degrees arranged in a specific pattern. It begins and ends with the most important pitch, the keynote (or tonic), by which we name the scale. Each pitch letter name is use ...
... The major scale, one of the most important building blocks of tonal music, consists of seven distinct pitch classes called scale degrees arranged in a specific pattern. It begins and ends with the most important pitch, the keynote (or tonic), by which we name the scale. Each pitch letter name is use ...
Lesson_UUU_-_The_Maj..
... The major scale, one of the most important building blocks of tonal music, consists of seven distinct pitch classes called scale degrees arranged in a specific pattern. It begins and ends with the most important pitch, the keynote (or tonic), by which we name the scale. Each pitch letter name is use ...
... The major scale, one of the most important building blocks of tonal music, consists of seven distinct pitch classes called scale degrees arranged in a specific pattern. It begins and ends with the most important pitch, the keynote (or tonic), by which we name the scale. Each pitch letter name is use ...
Notation in the Works of Luciano Berio
... The first section, since it incorporates this ostinato, has nothing written for the fingers on the second staff line. The second section drops the ostinato and indicates points along the ...
... The first section, since it incorporates this ostinato, has nothing written for the fingers on the second staff line. The second section drops the ostinato and indicates points along the ...
abstract - eThesis
... The studies that compose this dissertation analyze a selection of pieces of early post-tonal music (by Debussy, Scriabin, Schoenberg, Berg, and Webern) on the basis of the notion of prolongation. They also discuss extensively the theoretical principles of post-tonal prolongation and, to some extent, ...
... The studies that compose this dissertation analyze a selection of pieces of early post-tonal music (by Debussy, Scriabin, Schoenberg, Berg, and Webern) on the basis of the notion of prolongation. They also discuss extensively the theoretical principles of post-tonal prolongation and, to some extent, ...
A permutational triadic approach to jazz harmony and the chord
... creatures with the capacity to create—and from this capacity has flowed the sweet songs of sorrow and joy that have allowed man to cope with his environment and many different situations. Jazz speaks for life. The Blues tell a story of life’s difficulties, and if you think for a moment, you will rea ...
... creatures with the capacity to create—and from this capacity has flowed the sweet songs of sorrow and joy that have allowed man to cope with his environment and many different situations. Jazz speaks for life. The Blues tell a story of life’s difficulties, and if you think for a moment, you will rea ...
(1) Sound and Music
... The set of all musical notes is called the Chromatic Scale, a name which comes from the Greek word chr獽a, meaning color. In this sense, chromatic scale means 'notes of all colors'. Colors, in fact, are also made up from different frequencies, those of light waves. Because notes repeat in each octav ...
... The set of all musical notes is called the Chromatic Scale, a name which comes from the Greek word chr獽a, meaning color. In this sense, chromatic scale means 'notes of all colors'. Colors, in fact, are also made up from different frequencies, those of light waves. Because notes repeat in each octav ...
pdf - Santa Fe Institute
... canonical tuning systems. We adopt a similar approach here, assuming a fixed number of “discrete” [Burns and Ward p. 243] pitches for a tuning system. While musics vary widely in the numbers of named pitches in use, having a fixed number of pitches offers practical and cognitive advantages. The most ...
... canonical tuning systems. We adopt a similar approach here, assuming a fixed number of “discrete” [Burns and Ward p. 243] pitches for a tuning system. While musics vary widely in the numbers of named pitches in use, having a fixed number of pitches offers practical and cognitive advantages. The most ...
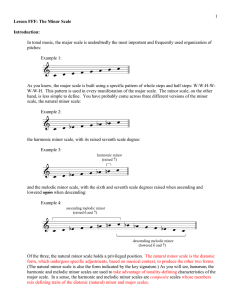
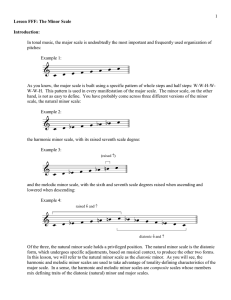
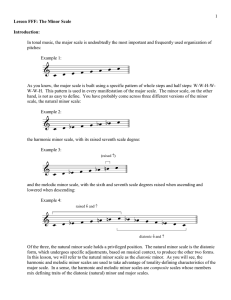
Lesson_CCC_-_The_Min..
... their leading-tone adjusted forms, although both appear in other functional roles in a minor key (discussed in lesson XXX). Listen again to Example 6 and then compare it to Example 7. Which version of the V chord has a stronger pull back to tonic? The addition of a leading tone gives Example 7 gives ...
... their leading-tone adjusted forms, although both appear in other functional roles in a minor key (discussed in lesson XXX). Listen again to Example 6 and then compare it to Example 7. Which version of the V chord has a stronger pull back to tonic? The addition of a leading tone gives Example 7 gives ...
A Theory of Tonal Hierarchies in Music
... music, but also they may be especially important there. This is because music does not provide fixed reference tones except as determined by the music itself. Thus, unlike other domains in which cognitive reference points are defined independently of the category (red is perceptually red whether it ...
... music, but also they may be especially important there. This is because music does not provide fixed reference tones except as determined by the music itself. Thus, unlike other domains in which cognitive reference points are defined independently of the category (red is perceptually red whether it ...
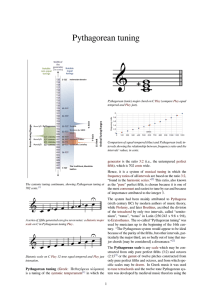
Pythagorean tuning
... In the formulas, the ratios 3:2 or 2:3 represent an ascending or descending perfect fifth (i.e. an increase or decrease in frequency by a perfect fifth), while 2:1 or 1:2 represent an ascending or descending octave. The major scale based on C, obtained from this tuning is:[5] In equal temperament, pai ...
... In the formulas, the ratios 3:2 or 2:3 represent an ascending or descending perfect fifth (i.e. an increase or decrease in frequency by a perfect fifth), while 2:1 or 1:2 represent an ascending or descending octave. The major scale based on C, obtained from this tuning is:[5] In equal temperament, pai ...
Arithmetic and music in twelve easy steps
... Musical sounds are caused by regular vibrations in the air. The number of vibrations per second causing any particular note is the frequency of that note in units of Hertz (Hz). For example, the modern standard of orchestral pitch is established by defining the note A above middle C to have a freque ...
... Musical sounds are caused by regular vibrations in the air. The number of vibrations per second causing any particular note is the frequency of that note in units of Hertz (Hz). For example, the modern standard of orchestral pitch is established by defining the note A above middle C to have a freque ...
Prolongation of Seventh Chords in Tonal Music, by Yosef Goldenberg
... Schenker’s normative view, of course, was that the seventh chord is not an independent harmony; like any other dissonance (or rather, untransformed dissonance), its prolongation is prohibited—though dissonance at one level could of course receive consonant harmonic support at another. However, which ...
... Schenker’s normative view, of course, was that the seventh chord is not an independent harmony; like any other dissonance (or rather, untransformed dissonance), its prolongation is prohibited—though dissonance at one level could of course receive consonant harmonic support at another. However, which ...
Composing In the Flesh: Perceptually
... dissonance. The degree of roughness of an interval or chord depends on the extent to which it has spectral components within the same critical band. The critical band is related to the smallest frequency difference that will allow two pure tones to be perceptually identified as two autonomous tones ...
... dissonance. The degree of roughness of an interval or chord depends on the extent to which it has spectral components within the same critical band. The critical band is related to the smallest frequency difference that will allow two pure tones to be perceptually identified as two autonomous tones ...
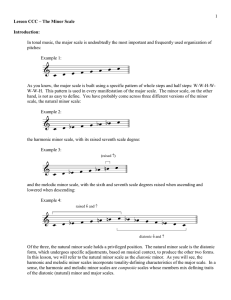
Lesson_CCC_-_The_Min..
... As you can hear, the presence of the leading tone in creates a stronger, satisfying sense of resolution at the arrival of tonic. The following example shows the triads built with the leading-tone adjusted harmonic minor scale: Example 11: ...
... As you can hear, the presence of the leading tone in creates a stronger, satisfying sense of resolution at the arrival of tonic. The following example shows the triads built with the leading-tone adjusted harmonic minor scale: Example 11: ...
Tone and Voice: A Derivation of the Rules of Voice
... we will examine compositional practice to determine whether composers typically write in a manner consistent with these additional rules. To foreshadow the results, we will see that voice-leading practices are indeed consistent with several nontraditional rules predicted by the perceptual principles ...
... we will examine compositional practice to determine whether composers typically write in a manner consistent with these additional rules. To foreshadow the results, we will see that voice-leading practices are indeed consistent with several nontraditional rules predicted by the perceptual principles ...
Full PDF - 2012 Book Archive
... 3.0/) license. See the license for more details, but that basically means you can share this book as long as you credit the author (but see below), don't make money from it, and do make it available to everyone else under the same terms. This book was accessible as of December 29, 2012, and it was d ...
... 3.0/) license. See the license for more details, but that basically means you can share this book as long as you credit the author (but see below), don't make money from it, and do make it available to everyone else under the same terms. This book was accessible as of December 29, 2012, and it was d ...
Lesson_UUU_-_The_Maj..
... spelled in ascending order and begins and ends on the keynote, the letter G is used twice (G and G#).” Response if incorrect: “Incorrect. This scale is spelled correctly: it begins and ends on the keynote and each intervening letter name is used once and only once. Try again.”] In this lesson, we wi ...
... spelled in ascending order and begins and ends on the keynote, the letter G is used twice (G and G#).” Response if incorrect: “Incorrect. This scale is spelled correctly: it begins and ends on the keynote and each intervening letter name is used once and only once. Try again.”] In this lesson, we wi ...
Lesson EEE: The Dominant Seventh Chord
... As you can hear, the presence of the leading tone in creates a stronger, satisfying sense of resolution at the arrival of tonic. The following example shows the triads built with the leading-tone adjusted harmonic minor scale: ...
... As you can hear, the presence of the leading tone in creates a stronger, satisfying sense of resolution at the arrival of tonic. The following example shows the triads built with the leading-tone adjusted harmonic minor scale: ...
Lesson_CCC_-_The_Min..
... As you can hear, the presence of the leading tone in creates a stronger, satisfying sense of resolution at the arrival of tonic. The following example shows the triads built with the leading-tone adjusted harmonic minor scale: ...
... As you can hear, the presence of the leading tone in creates a stronger, satisfying sense of resolution at the arrival of tonic. The following example shows the triads built with the leading-tone adjusted harmonic minor scale: ...
What are Musical Scales?
... "I believe that by the fifteenth century with the introduction of the bass voice line, harmony became more important than melody. The lowest voice was now the foundation for everything above it, usually three other voices. Rather than flowing in a horizontal, lyrical fashion, music, because of chord ...
... "I believe that by the fifteenth century with the introduction of the bass voice line, harmony became more important than melody. The lowest voice was now the foundation for everything above it, usually three other voices. Rather than flowing in a horizontal, lyrical fashion, music, because of chord ...