Document
... • Ventral horns—somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots • Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) –sympathetic neurons • Dorsal root (spinal) gangia—contain cell bodies of sensory neurons ...
... • Ventral horns—somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots • Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) –sympathetic neurons • Dorsal root (spinal) gangia—contain cell bodies of sensory neurons ...
94. Hippocampus
... Of the layers of the hippocampus, there are 3 layers, which are well recognizable even in hematoxyline-eosine stained specimens. First is the alveus hippocampi, which is formed by the efferens axons of the hippocampus. Gradually emerging from the hippocampus these axons also form the fimbria and the ...
... Of the layers of the hippocampus, there are 3 layers, which are well recognizable even in hematoxyline-eosine stained specimens. First is the alveus hippocampi, which is formed by the efferens axons of the hippocampus. Gradually emerging from the hippocampus these axons also form the fimbria and the ...
ch.6
... seems to have its own separate and private sensations; its own perceptions; its own concepts; and its own impulses to act. . . . ...
... seems to have its own separate and private sensations; its own perceptions; its own concepts; and its own impulses to act. . . . ...
Chapter 15 - Las Positas College
... A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a system of motor neurons that innervate the smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands of the body; the ANS is the general visceral motor division of the peripheral nervous system. (p. 459, Fig. 15.1) B. Basic points of comparison between the autonomic and so ...
... A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a system of motor neurons that innervate the smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands of the body; the ANS is the general visceral motor division of the peripheral nervous system. (p. 459, Fig. 15.1) B. Basic points of comparison between the autonomic and so ...
Joshua Khani - Giant Axonal Neuropathy
... auditory cortex MRI show white matter abnormalities Moderate to complete reduction of nerve conduction velocity ...
... auditory cortex MRI show white matter abnormalities Moderate to complete reduction of nerve conduction velocity ...
Renal system
... skin and cartilage. It concentrates the sound and aids in localization of its origin. Auditory canal is a channel leading from the pinna to the tympanic membrane. Tympanic membrane is flexible and moves in response to variations in air pressure. Tensor tympani muscle changes the degree of tension ap ...
... skin and cartilage. It concentrates the sound and aids in localization of its origin. Auditory canal is a channel leading from the pinna to the tympanic membrane. Tympanic membrane is flexible and moves in response to variations in air pressure. Tensor tympani muscle changes the degree of tension ap ...
2013 Action Potential Modeling in PYTHON
... respect to the extracellular space. This tends to draw positively charged K+ ions back in to the cell and, as a result, the diffusion force will eventually be opposed and balanced by an electrical force[1]. At electrochemical equilibrium, this is called the resting membrane potential of the cell. T ...
... respect to the extracellular space. This tends to draw positively charged K+ ions back in to the cell and, as a result, the diffusion force will eventually be opposed and balanced by an electrical force[1]. At electrochemical equilibrium, this is called the resting membrane potential of the cell. T ...
Theme 6. Vision
... action potentials as well as those mediating the fast and slow afterhyperpolarizations. (3p) ...
... action potentials as well as those mediating the fast and slow afterhyperpolarizations. (3p) ...
Chapter 3—The Brain and Behavior
... The midbrain is involved in the relay of information between the brain and the hindbrain and forebrain. A midbrain structure called the reticular formation is involved in stereotyped patterns of behavior. The highest region of the brain is called the forebrain. A forebrain structure that plays impo ...
... The midbrain is involved in the relay of information between the brain and the hindbrain and forebrain. A midbrain structure called the reticular formation is involved in stereotyped patterns of behavior. The highest region of the brain is called the forebrain. A forebrain structure that plays impo ...
- Orange Coast College
... efferent pathway. 1st neuron has its cell body in gray matter of brain or spinal cord. ...
... efferent pathway. 1st neuron has its cell body in gray matter of brain or spinal cord. ...
Sacrificing America On The Altar Of Mediocrity
... information to the prefrontal cortex helps to bring a pleasurable feeling when solving problems. This connection can be surgically severed to treat or cure some emotional disorders. Unfortunately, the limbic system is tremendously impacted by use and abuse of substances like alcohol, nicotine, and o ...
... information to the prefrontal cortex helps to bring a pleasurable feeling when solving problems. This connection can be surgically severed to treat or cure some emotional disorders. Unfortunately, the limbic system is tremendously impacted by use and abuse of substances like alcohol, nicotine, and o ...
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Reflexes
... Paravertebral Ganglia •although the chains receive input form only the thoracolumbar regions, they extend from the cervical to the sacral cord •usually there are 3 cervical (superior, middle, inferior), 11 thoracic, 4 lumbar, 4 sacral, and 1 coccygeal •In the thoracolumbar region, each paravertebra ...
... Paravertebral Ganglia •although the chains receive input form only the thoracolumbar regions, they extend from the cervical to the sacral cord •usually there are 3 cervical (superior, middle, inferior), 11 thoracic, 4 lumbar, 4 sacral, and 1 coccygeal •In the thoracolumbar region, each paravertebra ...
Opposite rheological properties of neuronal microcompartments
... We hypothesized that specific cytoskeletal organization within neuronal microcompartments may lead to distinct rheological properties that potentiate a greater vulnerability of axons to injury. To test this, we combined micropatterning with magnetic tweezers to apply local stresses to individual mic ...
... We hypothesized that specific cytoskeletal organization within neuronal microcompartments may lead to distinct rheological properties that potentiate a greater vulnerability of axons to injury. To test this, we combined micropatterning with magnetic tweezers to apply local stresses to individual mic ...
Physio lecture 9 Membrane and Action Potentials
... abundant outside of cell, more guys inside room. After class, guys want to leave, they can use the door. Ladies want to get into the room, but to get in, they have to come under the crack of the door. Not likely to get in. Sodium does not have leak channels, which are created by integral proteins. P ...
... abundant outside of cell, more guys inside room. After class, guys want to leave, they can use the door. Ladies want to get into the room, but to get in, they have to come under the crack of the door. Not likely to get in. Sodium does not have leak channels, which are created by integral proteins. P ...
File
... General chemoreceptors transmit information about the total solute concentration of a solution, while specific chemoreceptors respond to specific types of molecules. ○ Osmoreceptors in the mammalian brain are general receptors that detect changes in the solute concentration of the blood and stimulat ...
... General chemoreceptors transmit information about the total solute concentration of a solution, while specific chemoreceptors respond to specific types of molecules. ○ Osmoreceptors in the mammalian brain are general receptors that detect changes in the solute concentration of the blood and stimulat ...
A comparision of Hodgkin-Huxley and soliton neural theories
... Reversal potentials and conductances are empirical parameters. So, it is demonstrated that the neurons transmit information by firing and propagating electrical action potentials along their axons. Usually, motor neurons possess a myelin sheath around their axons acting as an insulator and enhancing ...
... Reversal potentials and conductances are empirical parameters. So, it is demonstrated that the neurons transmit information by firing and propagating electrical action potentials along their axons. Usually, motor neurons possess a myelin sheath around their axons acting as an insulator and enhancing ...
RETICULAR FORMATION
... • Cranial nerve reflexes • Central pattern generators • Cerebellum input & output • Gaze centers within brainstem ...
... • Cranial nerve reflexes • Central pattern generators • Cerebellum input & output • Gaze centers within brainstem ...
2605_lect9
... themselves with others cells and form structures • Cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs): – Aid both migration and aggregation – CAMs recognize and adhere to molecules ...
... themselves with others cells and form structures • Cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs): – Aid both migration and aggregation – CAMs recognize and adhere to molecules ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to Physiology of Perception
... been set equal to 1.0. However, the relative sensitivities of the rods and the cones depend on the conditions of adaptation: the cones are more sensitive in the light, and the rods are more sensitive in the dark. ...
... been set equal to 1.0. However, the relative sensitivities of the rods and the cones depend on the conditions of adaptation: the cones are more sensitive in the light, and the rods are more sensitive in the dark. ...
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... General chemoreceptors transmit information about the total solute concentration of a solution, while specific chemoreceptors respond to specific types of molecules. ○ Osmoreceptors in the mammalian brain are general receptors that detect changes in the solute concentration of the blood and stimulat ...
... General chemoreceptors transmit information about the total solute concentration of a solution, while specific chemoreceptors respond to specific types of molecules. ○ Osmoreceptors in the mammalian brain are general receptors that detect changes in the solute concentration of the blood and stimulat ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy
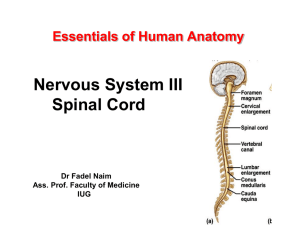
... – contains neurons whose axons form the cervical spinal nerves (8) ...
... – contains neurons whose axons form the cervical spinal nerves (8) ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy Nervous System III Spinal Cord The
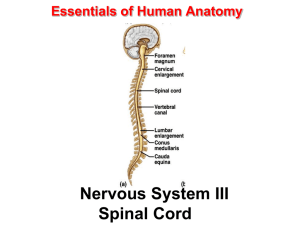
... – contains neurons whose axons form the cervical spinal nerves (8) ...
... – contains neurons whose axons form the cervical spinal nerves (8) ...
This Week in The Journal
... same odorant receptor converge onto two isofunctional columns in the olfactory bulb. Paired isofunctional columns are connected by tufted cell axons, which synapse on GABAergic granule neurons. After a postnatal refinement period during which intrabulbar projections narrow to the width of a single g ...
... same odorant receptor converge onto two isofunctional columns in the olfactory bulb. Paired isofunctional columns are connected by tufted cell axons, which synapse on GABAergic granule neurons. After a postnatal refinement period during which intrabulbar projections narrow to the width of a single g ...
Nerve Fiber Classification Nerve fibers are classified according to:
... G-protein activation works by controlling production of second messengers such as cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, diacylglycerol, or Ca++ which open or close ion channels or activate kinase enzymes that initiate an enzymatic ...
... G-protein activation works by controlling production of second messengers such as cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, diacylglycerol, or Ca++ which open or close ion channels or activate kinase enzymes that initiate an enzymatic ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.