Exam 5 Objectives Bio241
... 1. Identify and describe the types of cells found in the nervous system including neurons (sensory, motor, and association/interneurons), and glia (microglia, astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cell, and satellite cells). Know the function(s) of each cell in the nervous system 2. ...
... 1. Identify and describe the types of cells found in the nervous system including neurons (sensory, motor, and association/interneurons), and glia (microglia, astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cell, and satellite cells). Know the function(s) of each cell in the nervous system 2. ...
Brain and Neuron Quiz Key
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
Chapter 12 Notes Part 1 File
... A single process extending from the axon hillock Axon collaterals (side branches) Sometimes covered by a fatty layer called a myelin sheath Conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body of the neuron Distal tips of axons are telodendria, each of which terminates in a synaptic knob – Thicker diamet ...
... A single process extending from the axon hillock Axon collaterals (side branches) Sometimes covered by a fatty layer called a myelin sheath Conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body of the neuron Distal tips of axons are telodendria, each of which terminates in a synaptic knob – Thicker diamet ...
UNIT 2: Internal geological agents
... are grouped in the sense organs ans their main characteristics are: - Are very specific for every type of stimulus. - They are stimulated as long as the stimulus exceeds a threshold of excitation. -They can suffer adaptation if the stimulus is persistent (do not respond). - A very intense stimulus c ...
... are grouped in the sense organs ans their main characteristics are: - Are very specific for every type of stimulus. - They are stimulated as long as the stimulus exceeds a threshold of excitation. -They can suffer adaptation if the stimulus is persistent (do not respond). - A very intense stimulus c ...
General histology of nervous system
... • 2 cell types: – Nerve cells (neurons) • receive or transmit impulses • interconnections (at least 1000 each) ...
... • 2 cell types: – Nerve cells (neurons) • receive or transmit impulses • interconnections (at least 1000 each) ...
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... Protection of the CNS • Blood-brain barrier – What is It? A tight network of capillary beds that are both SELECTIVE - Keeps some things out and other allows other things in. DIRECTIONAL - Moves INTO the brain not OUT OF the brain – How Does it Work? Acts as a successively smaller filters to keep su ...
... Protection of the CNS • Blood-brain barrier – What is It? A tight network of capillary beds that are both SELECTIVE - Keeps some things out and other allows other things in. DIRECTIONAL - Moves INTO the brain not OUT OF the brain – How Does it Work? Acts as a successively smaller filters to keep su ...
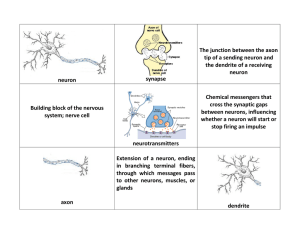
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... cross the synaptic gaps between neurons, influencing whether a neuron will start or stop firing an impulse ...
... cross the synaptic gaps between neurons, influencing whether a neuron will start or stop firing an impulse ...
Chapter 29 Nervous and Endocrine System
... from the axon and transmit impulse across synapse by binding to receptor sites on dendrite of adjacent neuron Impulses are self-propagating, like dominos ...
... from the axon and transmit impulse across synapse by binding to receptor sites on dendrite of adjacent neuron Impulses are self-propagating, like dominos ...
Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
... They are called neurons And there are just three types Sensory is the first has receptors They respond to stimuli Association's in brain and spinal cord Interpreting the info and passing on To move the motor neurons carry to the body Bring it to the glands Bring it to the muscles...oh oh oh oh oh Ne ...
... They are called neurons And there are just three types Sensory is the first has receptors They respond to stimuli Association's in brain and spinal cord Interpreting the info and passing on To move the motor neurons carry to the body Bring it to the glands Bring it to the muscles...oh oh oh oh oh Ne ...
Ch. 48 - Ltcconline.net
... 3. cell body houses nucleus and most cytoplasmic organelles. 4. 2 types of fibers project from cell body a. axons (Greek for axle) - on many neurons is a single fiber; where it joins cell body = axon hillock 1. conduct signals toward another neuron or toward an effector a. many axons are long- may s ...
... 3. cell body houses nucleus and most cytoplasmic organelles. 4. 2 types of fibers project from cell body a. axons (Greek for axle) - on many neurons is a single fiber; where it joins cell body = axon hillock 1. conduct signals toward another neuron or toward an effector a. many axons are long- may s ...
The Nervous System - Appoquinimink High School
... potassium in ions in again bringing the charge back to negative. This is called REPOLARIZATION ...
... potassium in ions in again bringing the charge back to negative. This is called REPOLARIZATION ...
Chapter 3 - Morgan Community College
... concentration of ions different inside & outside extracellular fluid rich in Na+ and Cl cytosol full of K+, organic phosphate & amino acids membrane permeability differs for Na+ and K+ 50-100 greater permeability for K+ inward flow of Na+ can’t keep up with outward flow of K+ Na+/K+ pu ...
... concentration of ions different inside & outside extracellular fluid rich in Na+ and Cl cytosol full of K+, organic phosphate & amino acids membrane permeability differs for Na+ and K+ 50-100 greater permeability for K+ inward flow of Na+ can’t keep up with outward flow of K+ Na+/K+ pu ...
1 MCB3210F NAME EXAM 1A SECTION CELLS, TISSUES
... 35. T-F? Temporal summation occurs when a nerve stimulates another nerve with two sequential EPSP’s. T 36. An inhibitory neurotransmitter reduces excitation of postsynaptic nerves by A) preventing binding of excitatory neurotransmitters to their receptors B) depolarizing presynaptic nerves C) hyperp ...
... 35. T-F? Temporal summation occurs when a nerve stimulates another nerve with two sequential EPSP’s. T 36. An inhibitory neurotransmitter reduces excitation of postsynaptic nerves by A) preventing binding of excitatory neurotransmitters to their receptors B) depolarizing presynaptic nerves C) hyperp ...
Exam
... 35. T-F? Temporal summation occurs when a nerve stimulates another nerve with two sequential EPSP’s. T 36. An inhibitory neurotransmitter reduces excitation of postsynaptic nerves by A) preventing binding of excitatory neurotransmitters to their receptors B) depolarizing presynaptic nerves C) hyperp ...
... 35. T-F? Temporal summation occurs when a nerve stimulates another nerve with two sequential EPSP’s. T 36. An inhibitory neurotransmitter reduces excitation of postsynaptic nerves by A) preventing binding of excitatory neurotransmitters to their receptors B) depolarizing presynaptic nerves C) hyperp ...
Nervous Systems (ch. 48 & 49) Sum13
... 1) Frontal: Primary motor area; complex reasoning 2) Parietal: Primary sensory area 3) Temporal: Primary auditory and olfactory areas ...
... 1) Frontal: Primary motor area; complex reasoning 2) Parietal: Primary sensory area 3) Temporal: Primary auditory and olfactory areas ...
Chapter 6 - TeacherWeb
... * dendrites – a nerve fiber in the neuron that caries impulses towards the neuron’s cell body * axon – a nerve fiber in the neuron that carries impulses away from the cell body * the nerve impulse travels into the dendrite then down the axon ...
... * dendrites – a nerve fiber in the neuron that caries impulses towards the neuron’s cell body * axon – a nerve fiber in the neuron that carries impulses away from the cell body * the nerve impulse travels into the dendrite then down the axon ...
Chapter 13 - Nervous Tissue
... specialized to detect stimuli and transmit the information to CNS. They begin in any organ in the body, but end in the brain or spinal cord. ...
... specialized to detect stimuli and transmit the information to CNS. They begin in any organ in the body, but end in the brain or spinal cord. ...
Lecture #19 - Suraj @ LUMS
... thirst, hunger, body temperature, water balance, and blood pressure. • The midbrain and pons are also part of the unconscious brain. • The thalamus serves as a central relay point for incoming nervous messages, acts as a switching center for nerve messages • The cerebellum is the second largest part ...
... thirst, hunger, body temperature, water balance, and blood pressure. • The midbrain and pons are also part of the unconscious brain. • The thalamus serves as a central relay point for incoming nervous messages, acts as a switching center for nerve messages • The cerebellum is the second largest part ...
CHAPTER 11 Nervous Tissue - Austin Community College
... Epithelial cells that line ventricles and central cavities of brain and spinal cord-secrete CSF Ciliated to circulate CSF ...
... Epithelial cells that line ventricles and central cavities of brain and spinal cord-secrete CSF Ciliated to circulate CSF ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.