Neuron Function
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
Nervous System
... • travels down axon one small segment at a time • As soon as action potential moves on, the previous section undergoes refractory period – Sodium gates cannot reopen – Prevents retrograde transmission – During this time sodium-potassium pump restores ions to original positions ...
... • travels down axon one small segment at a time • As soon as action potential moves on, the previous section undergoes refractory period – Sodium gates cannot reopen – Prevents retrograde transmission – During this time sodium-potassium pump restores ions to original positions ...
Exam - (canvas.brown.edu).
... T F 8. The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is made up in part by the axons of neurons in the hypothalamus destined for the visceromotor nuclei of the cranial nerves. T F 9. The spinal component of the spinal accessory nerve (11th cranial nerve) innervates the larynx. T F 10. Confocal microscopy ...
... T F 8. The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is made up in part by the axons of neurons in the hypothalamus destined for the visceromotor nuclei of the cranial nerves. T F 9. The spinal component of the spinal accessory nerve (11th cranial nerve) innervates the larynx. T F 10. Confocal microscopy ...
Fig. 6.1
... between the cells. • The distance from motor cortex in the brain to the toe muscle = 2meters. • 2meters / 20micrometers cells = 100,000 cells • Assume that inside a cell electrical signal is transmitted instantaneously • Delay between cells = 1millisecond • Total transmission time = 100,000 x 1ms = ...
... between the cells. • The distance from motor cortex in the brain to the toe muscle = 2meters. • 2meters / 20micrometers cells = 100,000 cells • Assume that inside a cell electrical signal is transmitted instantaneously • Delay between cells = 1millisecond • Total transmission time = 100,000 x 1ms = ...
Nervous System - The Beat@KUMC
... Consists of the brain and spinal cord Gathers information from our surrounding environment and interprets it Controls much of the activity in the body Contains all of the higher mental functions like thinking and ...
... Consists of the brain and spinal cord Gathers information from our surrounding environment and interprets it Controls much of the activity in the body Contains all of the higher mental functions like thinking and ...
Begin Nervous system
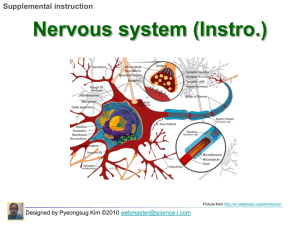
... In action potential, repolarization Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com ...
... In action potential, repolarization Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com ...
Nervous System Development
... •At about the time a child reaches puberty the “pruning” process kicks in, and streamlines the networks to about 500 trillion connections. •This pruning isn’t a random process. The synapses which have been used repeatedly tend to remain. Those which haven’t been used often enough are eliminated. ...
... •At about the time a child reaches puberty the “pruning” process kicks in, and streamlines the networks to about 500 trillion connections. •This pruning isn’t a random process. The synapses which have been used repeatedly tend to remain. Those which haven’t been used often enough are eliminated. ...
Axons break in animals lacking β-spectrin
... Defects were also rare in β-spectrin mutant embryos (fraction of neurons with defects: wild type = 1.3%; unc-70(s1502) = 3.1%; P = 0.31 in a two-tailed Fisher’s exact test). However, β-spectrin mutant animals accumulated defects with time. At hatching, the percentage of neurons with defects had incr ...
... Defects were also rare in β-spectrin mutant embryos (fraction of neurons with defects: wild type = 1.3%; unc-70(s1502) = 3.1%; P = 0.31 in a two-tailed Fisher’s exact test). However, β-spectrin mutant animals accumulated defects with time. At hatching, the percentage of neurons with defects had incr ...
File
... Depolarization is stopped When the membrane voltage reaches 35 mV, the inactivation gates close in response to depolarization and the sodium ions can’t enter the cell anymore. The Na+ can only come in during a brief period when both activation and inactivation ...
... Depolarization is stopped When the membrane voltage reaches 35 mV, the inactivation gates close in response to depolarization and the sodium ions can’t enter the cell anymore. The Na+ can only come in during a brief period when both activation and inactivation ...
1 - Kvalley Computers and Internet
... Distinguish between resting potential and action potential. (What chemical actions create the neuron’s resting potential? What chemical changes cause the action potential?) ...
... Distinguish between resting potential and action potential. (What chemical actions create the neuron’s resting potential? What chemical changes cause the action potential?) ...
Nervous System
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
C2 - The Biological Perspective
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
Chapter 3
... • (negative inside/positive outside) = resting potential • Neurons are selectively permeable (usually blocking POSITIVELY charged sodium ions until given the signal to fire • Depolarization occurs when neurons allow sodium ions inside causing neurological firing ...
... • (negative inside/positive outside) = resting potential • Neurons are selectively permeable (usually blocking POSITIVELY charged sodium ions until given the signal to fire • Depolarization occurs when neurons allow sodium ions inside causing neurological firing ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... identify: nucleus, prominent nucleolus, and many Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substance) = RER. o A network of fine threads called neurofibrils extends into the axons and supports them. ...
... identify: nucleus, prominent nucleolus, and many Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substance) = RER. o A network of fine threads called neurofibrils extends into the axons and supports them. ...
The cells of the nervous system
... • The presynaptic knob contains many mitochondria to provide ATP for synthesis of neurotransmitters. • When a nerve impulse passes through a neuron and reaches the end of the axon (known as the axon terminal), many vesicles containing neurotransmitters are stimulated. ...
... • The presynaptic knob contains many mitochondria to provide ATP for synthesis of neurotransmitters. • When a nerve impulse passes through a neuron and reaches the end of the axon (known as the axon terminal), many vesicles containing neurotransmitters are stimulated. ...
Biological Neurons and Neural Networks, Artificial Neurons
... electrical pulses (i.e. spikes or action potentials). ...
... electrical pulses (i.e. spikes or action potentials). ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Chapter 10 - Nervous System I
... peripheral nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body. C. The nervous system provides sensory, integrative, and motor functions to the body. 9.2 General Functions of the Nervous System (p. 215) A. Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerv ...
... peripheral nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body. C. The nervous system provides sensory, integrative, and motor functions to the body. 9.2 General Functions of the Nervous System (p. 215) A. Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerv ...
Neurons and Glial Cells
... Like other cells, each neuron has a cell body (or soma) that contains a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other cellular components. ...
... Like other cells, each neuron has a cell body (or soma) that contains a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other cellular components. ...
nerve_pharmacy_(mana..
... phosphate ions) cannot leave the cell. • 3. very small amount of Na+ diffuses into the cell down its conc gradient. The mb only slightly permeable to Na+. (through Na+ leak channels). • 4. Na+-K+ pump maintain conc gradients of K+, and Na+ between the two sides of the mb. ...
... phosphate ions) cannot leave the cell. • 3. very small amount of Na+ diffuses into the cell down its conc gradient. The mb only slightly permeable to Na+. (through Na+ leak channels). • 4. Na+-K+ pump maintain conc gradients of K+, and Na+ between the two sides of the mb. ...
Neurons and Nervous Systems
... In a chemical synapse neurotransmitters from a presynaptic cell bind to receptors in a postsynaptic cell. The synaptic cleft—about 25 nanometers wide—separates the cells. ...
... In a chemical synapse neurotransmitters from a presynaptic cell bind to receptors in a postsynaptic cell. The synaptic cleft—about 25 nanometers wide—separates the cells. ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.