Balance_notes
... One row inner hair cells, 3 rows outer hair cells. All hair cells have stereocilia (“hairs”) sticking out of their tops (apical ends) into the endolymph-filled space between hair cells & tectorial membrane. Afferent nerve fibers connect to basal end of hair cells. Incoming sound causes BM vibrat ...
... One row inner hair cells, 3 rows outer hair cells. All hair cells have stereocilia (“hairs”) sticking out of their tops (apical ends) into the endolymph-filled space between hair cells & tectorial membrane. Afferent nerve fibers connect to basal end of hair cells. Incoming sound causes BM vibrat ...
E4 - Neurotransmitters and Synapses - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... E.g. this Neuron needs a 2 more “+” than “-” before it can generate an action potential. ...
... E.g. this Neuron needs a 2 more “+” than “-” before it can generate an action potential. ...
Psychology Chapter 3
... Brain Scans and Type Medical Note: A CT Scan (or CAT Scan) and an MRI operate differently and are better suited for different types of diagnoses. An MRI suited for examining soft tissue, (e.g. ligament and tendon injury, spinal cord injury, brain tumors etc.) while a CT scan is better suited for b ...
... Brain Scans and Type Medical Note: A CT Scan (or CAT Scan) and an MRI operate differently and are better suited for different types of diagnoses. An MRI suited for examining soft tissue, (e.g. ligament and tendon injury, spinal cord injury, brain tumors etc.) while a CT scan is better suited for b ...
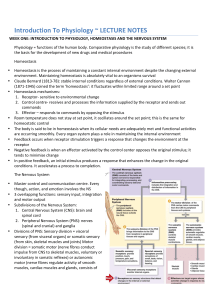
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... division = somatic motor (nerve fibres conduct impulse from CNS to skeletal muscles, voluntary or involuntary in somatic reflexes) or autonomic motor (nerve fibres regulate activity of smooth muscles, cardiac ...
... division = somatic motor (nerve fibres conduct impulse from CNS to skeletal muscles, voluntary or involuntary in somatic reflexes) or autonomic motor (nerve fibres regulate activity of smooth muscles, cardiac ...
Dr. Begay`s Notes from Pharm I
... • Psychoactive drugs: those drugs that alter cognition, behavior, and emotions by changing the functioning of the brain. • Psychopharmacology: the study of the use, mechanisms, and effects of drugs that act on the brain and subsequently ...
... • Psychoactive drugs: those drugs that alter cognition, behavior, and emotions by changing the functioning of the brain. • Psychopharmacology: the study of the use, mechanisms, and effects of drugs that act on the brain and subsequently ...
A. Normal OD development - Molecular and Cell Biology
... Criteria for neurotrophins to function as molecular signals in synaptic plasticity: 1) expressed in the right places and at the right times 2) expression and secretion are activity-dependent 3) regulate aspects of neuronal function 4) For competitive plasticity, the amount of ...
... Criteria for neurotrophins to function as molecular signals in synaptic plasticity: 1) expressed in the right places and at the right times 2) expression and secretion are activity-dependent 3) regulate aspects of neuronal function 4) For competitive plasticity, the amount of ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 5.1 Intracellular recording of the
... potentials propagate in unmyelinated axons through the depolarization of adjacent regions of membrane. In the illustrated axon, region 2 is undergoing depolarization during the generation of the action potential, whereas region 3 has already generated the action potential and is now hyperpolarized. ...
... potentials propagate in unmyelinated axons through the depolarization of adjacent regions of membrane. In the illustrated axon, region 2 is undergoing depolarization during the generation of the action potential, whereas region 3 has already generated the action potential and is now hyperpolarized. ...
AI_Connectionism_Excel
... • Cell references can be used in formulas as well. This feature shows the power of spreadsheets. • For example, suppose the cell B7 contains the value 8 and the cell C7 has the value 100. We can enter a value in another cell, say D8, to multiply cell B7 by C7. • The cell in D8 would then hold the fo ...
... • Cell references can be used in formulas as well. This feature shows the power of spreadsheets. • For example, suppose the cell B7 contains the value 8 and the cell C7 has the value 100. We can enter a value in another cell, say D8, to multiply cell B7 by C7. • The cell in D8 would then hold the fo ...
Physiologic basis of EMG/NCS or what constitutes a waveform?
... membrane capacitor discharge and then alteration of proteins to turn on Na activation channels. This process can be slow. • Hence unmyelinated nerve conducts slowly = 10-15 m/sec. ...
... membrane capacitor discharge and then alteration of proteins to turn on Na activation channels. This process can be slow. • Hence unmyelinated nerve conducts slowly = 10-15 m/sec. ...
Nervous System
... Key question#1: What are the major parts of the nervous system and there jobs? Stimuli, homeostasis, neurons, denterites, axons, and impulses. The job for the stimuli brings responses to your body. The homeostasis controls your breathing, heart rate, and digestion. The neurons carry messages to the ...
... Key question#1: What are the major parts of the nervous system and there jobs? Stimuli, homeostasis, neurons, denterites, axons, and impulses. The job for the stimuli brings responses to your body. The homeostasis controls your breathing, heart rate, and digestion. The neurons carry messages to the ...
Neural Development
... • Presence of tissue that is developing triggers the development of another tissue • Notochord (mesoderm) ectoderm neural plate folds in and closes neural tube elongates into brain and spinal cord • Closure of neural tube happens in stagesbrain forms before caudal (tail) area closes ...
... • Presence of tissue that is developing triggers the development of another tissue • Notochord (mesoderm) ectoderm neural plate folds in and closes neural tube elongates into brain and spinal cord • Closure of neural tube happens in stagesbrain forms before caudal (tail) area closes ...
1) Propagated electrical signals - UW Canvas
... Ions pass through a gated aqueous pore. The voltage sensor regulates the gate. ...
... Ions pass through a gated aqueous pore. The voltage sensor regulates the gate. ...
Psychology - Bideford College Sixth Form
... This assignment will be checked on the first day of class for a completion grade. An open note quiz over the material will also be given. All work should be hand written or typed onto the assignment. This can be printed off in school or at home. If you have any questions that arise over the summer, ...
... This assignment will be checked on the first day of class for a completion grade. An open note quiz over the material will also be given. All work should be hand written or typed onto the assignment. This can be printed off in school or at home. If you have any questions that arise over the summer, ...
Learning Objectives
... 8. Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9. Distinguish between gated and ungated ion channels and among ligand-gated ion channels and voltage-gated ion channels. 10. Define a graded potential and explain how it is different from a resting potential or a ...
... 8. Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9. Distinguish between gated and ungated ion channels and among ligand-gated ion channels and voltage-gated ion channels. 10. Define a graded potential and explain how it is different from a resting potential or a ...
Simplified view of how a neuron sends a signal
... match head enough (the threshold). And when the match head does ignite, it does so explosively and completely: an "all or nothing" response.} The neuron, too, does not respond to an inadequate stimulus; but when its threshold is met, it's resting potential is converted into an action potential compl ...
... match head enough (the threshold). And when the match head does ignite, it does so explosively and completely: an "all or nothing" response.} The neuron, too, does not respond to an inadequate stimulus; but when its threshold is met, it's resting potential is converted into an action potential compl ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 The Central Nervous
... nervous system (CNS), the autonomic nervous system (ANS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. Both the peripheral nervous system and the autonomic nervous system carry information to and from the central nervous system. The ce ...
... nervous system (CNS), the autonomic nervous system (ANS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. Both the peripheral nervous system and the autonomic nervous system carry information to and from the central nervous system. The ce ...
New Insights into Neuron-Glia Communication
... (18) or by astrocytes activating an intervening function at different places. This implies subinhibitory neuron in the synaptic circuit (19). In stantial involvement of astrocytes with inforeach case, imaging techniques reveal that the mation processing in the brain. rise in cytoplasmic Ca2⫹ concent ...
... (18) or by astrocytes activating an intervening function at different places. This implies subinhibitory neuron in the synaptic circuit (19). In stantial involvement of astrocytes with inforeach case, imaging techniques reveal that the mation processing in the brain. rise in cytoplasmic Ca2⫹ concent ...
ppt file
... external part of the cord. It is made up of myelinated axons. These carry signals up and down the axis of the spinal cord, and make it white. • Gray matter forms the butterfly shaped inner core of the cord. It is made up of neuron cell bodies, dendrites and synapses. Here neurotransmission takes pla ...
... external part of the cord. It is made up of myelinated axons. These carry signals up and down the axis of the spinal cord, and make it white. • Gray matter forms the butterfly shaped inner core of the cord. It is made up of neuron cell bodies, dendrites and synapses. Here neurotransmission takes pla ...
Chapter 7: Nervous System
... toward the cell body. Many, short Axons move neural impulses away from the cell body. One, can be long. Come from the axon hillock. Can branch off (collateral branch). Have many axon terminals ...
... toward the cell body. Many, short Axons move neural impulses away from the cell body. One, can be long. Come from the axon hillock. Can branch off (collateral branch). Have many axon terminals ...
Neurons
... Largely the result of negatively charged organic molecules within the cell. Limited diffusion of positively charged inorganic ions. Electrochemical gradients of Na+ and K+. ...
... Largely the result of negatively charged organic molecules within the cell. Limited diffusion of positively charged inorganic ions. Electrochemical gradients of Na+ and K+. ...
TEACHER`S GUIDE
... Exocytosis—When an impulse arrives at the terminal, the vesicles fuse with the terminal membrane and release the neurotransmitters within them into the synaptic cleft (space). G Proteins—Proteins that help receptors such as dopamine or THC receptors to activate or inhibit the enzyme adenyl cyclase a ...
... Exocytosis—When an impulse arrives at the terminal, the vesicles fuse with the terminal membrane and release the neurotransmitters within them into the synaptic cleft (space). G Proteins—Proteins that help receptors such as dopamine or THC receptors to activate or inhibit the enzyme adenyl cyclase a ...
Spinal nerves 1
... abdominal muscles • sensory: skin on anterior and lateral aspect of thorax and abdomen, pleura parietalis, ...
... abdominal muscles • sensory: skin on anterior and lateral aspect of thorax and abdomen, pleura parietalis, ...
solutions - Berkeley MCB
... a. Rods hyperpolarize to light, while cones depolarize to light b. Cones do not use the effector enzyme phosphodiesterase c. Cones and rods use different types of opsins d. Only cones contain retinal 2) The optic disk is a “blind spot” in the visual field because: This is where the retinal ganglion ...
... a. Rods hyperpolarize to light, while cones depolarize to light b. Cones do not use the effector enzyme phosphodiesterase c. Cones and rods use different types of opsins d. Only cones contain retinal 2) The optic disk is a “blind spot” in the visual field because: This is where the retinal ganglion ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not conve ...
... dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not conve ...
Unit 3 "Cliff Notes" Review
... •Threshold–you can push the handle a little bit, but it won’t flush until you push the handle past a certain point (this corresponds to the level of excitatory neurotransmitters that a neuron must absorb before it will fire) •Resting potential–the toilet is waiting to fire, and the water in the tank ...
... •Threshold–you can push the handle a little bit, but it won’t flush until you push the handle past a certain point (this corresponds to the level of excitatory neurotransmitters that a neuron must absorb before it will fire) •Resting potential–the toilet is waiting to fire, and the water in the tank ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.