
Modeling Neural Mechanisms of Cognitive-Affective Interaction Abninder Litt () Chris Eliasmith ()
... negative errors (Schultz, 2000). While this has indeed been observed within certain ranges, the capacity of dopamine to work alone in this manner has recently been questioned. Daw, Kakade and Dayan (2002) argue that low baseline firing rates make a dopamine-only scheme unsuitable for computing highl ...
... negative errors (Schultz, 2000). While this has indeed been observed within certain ranges, the capacity of dopamine to work alone in this manner has recently been questioned. Daw, Kakade and Dayan (2002) argue that low baseline firing rates make a dopamine-only scheme unsuitable for computing highl ...
Neural correlates of decision processes
... view that RT is occupied by formally distinct stages of processing [43]. Determining the relative contributions of successive stochastic processes to RT poses both technical and conceptual challenges. For example, questions remain as to whether the transformations within and the transmission between ...
... view that RT is occupied by formally distinct stages of processing [43]. Determining the relative contributions of successive stochastic processes to RT poses both technical and conceptual challenges. For example, questions remain as to whether the transformations within and the transmission between ...
Neural Network
... Objectives As you read these words you are using a complex biological neural network. You have a highly interconnected set of 1011 neurons to facilitate your reading, breathing, motion and thinking. In the artificial neural network, the neurons are not biological. They are extremely simple abstract ...
... Objectives As you read these words you are using a complex biological neural network. You have a highly interconnected set of 1011 neurons to facilitate your reading, breathing, motion and thinking. In the artificial neural network, the neurons are not biological. They are extremely simple abstract ...
Central Nervous System
... - has four lobes that receive and store information and are responsible for giving signals for voluntary movement. ...
... - has four lobes that receive and store information and are responsible for giving signals for voluntary movement. ...
Ch 11 lec 1
... Impulsive violence may be consequence of faulty emotional regulation…in frustrating situations we can usually calm ourselves down…probably due to the vmPFC ...
... Impulsive violence may be consequence of faulty emotional regulation…in frustrating situations we can usually calm ourselves down…probably due to the vmPFC ...
BSc_ ZOOA_Part-I
... Field trips to any locations suitable for watching animals in their natural habitats and natural moods as much intensively as possible (for example, watching surface swimming insects in a stream or pond, ants and other insects foraging on ground and in the plants, grazing herbivores in a forest patc ...
... Field trips to any locations suitable for watching animals in their natural habitats and natural moods as much intensively as possible (for example, watching surface swimming insects in a stream or pond, ants and other insects foraging on ground and in the plants, grazing herbivores in a forest patc ...
The Nervous System - Christian Fenger Academy High School
... 5. bruiselike injury to the brain Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. ...
... 5. bruiselike injury to the brain Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. ...
Enlightenment - The Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science
... results when using a light-activated activity block compared to a pharmocological block (19). When tetrodotoxin (TTX) was injected to inactivate the CA1 region of the hippocampus, a timedependent affect on memory retrieval in a contextual fear conditioning task was found: when injected before traini ...
... results when using a light-activated activity block compared to a pharmocological block (19). When tetrodotoxin (TTX) was injected to inactivate the CA1 region of the hippocampus, a timedependent affect on memory retrieval in a contextual fear conditioning task was found: when injected before traini ...
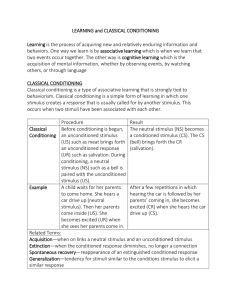
LEARNING and Classical Conditioning
... Learning is the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information and behaviors. One way we learn is by associative learning which is when we learn that two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing even ...
... Learning is the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information and behaviors. One way we learn is by associative learning which is when we learn that two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing even ...
Introduction to the physiology of perception
... The connection between environmental stimuli and perception • The nervous system is the part of the body that sends information about external stimuli to the brain • The nervous system consists of special type of cell called neuron or ...
... The connection between environmental stimuli and perception • The nervous system is the part of the body that sends information about external stimuli to the brain • The nervous system consists of special type of cell called neuron or ...
2008 Unit 3 Biological Bases of Behavior
... in the pons and midbrain innervate most of the brain (as the Locus coeruleus neurons do) Part of the ascending reticular activation system Implicated in mood and emotional behavior Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior ...
... in the pons and midbrain innervate most of the brain (as the Locus coeruleus neurons do) Part of the ascending reticular activation system Implicated in mood and emotional behavior Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior ...
Fig. 48.1 Peripheral nervous system
... – Sensory receptors a responsive to external and internal stimuli. • Such sensory input is conveyed to integration centers. Where in the input is interpreted and associated with a response. ...
... – Sensory receptors a responsive to external and internal stimuli. • Such sensory input is conveyed to integration centers. Where in the input is interpreted and associated with a response. ...
Thalamus & Hypothalamus
... sexual activity, food & water intake, aggression • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
... sexual activity, food & water intake, aggression • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
Biology and Behavior
... The human nervous system is involved in thinking, dreaming, feeling, moving and much more. It is working while we are active, still, awake, or asleep, is involved in how we react to the world, how we learning, remember, and also regulates our internal functions. Ex: when we learn something new, the ...
... The human nervous system is involved in thinking, dreaming, feeling, moving and much more. It is working while we are active, still, awake, or asleep, is involved in how we react to the world, how we learning, remember, and also regulates our internal functions. Ex: when we learn something new, the ...
3._Biological_Basis_of_Behavior_objectives
... at a minimum, be able to provide thorough answers for the following objectives without looking at any resources. Any additional material covered in your assigned reading and notes should also be reviewed. Study BEYOND RECOGNITION! 1. Be able to state the definition of biological psychology. 2. Ident ...
... at a minimum, be able to provide thorough answers for the following objectives without looking at any resources. Any additional material covered in your assigned reading and notes should also be reviewed. Study BEYOND RECOGNITION! 1. Be able to state the definition of biological psychology. 2. Ident ...
Document
... 1) Sensory neurons: detect stimuli and transmit signals to the brain and the spinal cord 2) Interneurons: receive signals from sensory neurons and relay them within the brain and spinal cord 3) Motor neurons: pass messages from the nervous system to the other tissues in the body, such as muscles ...
... 1) Sensory neurons: detect stimuli and transmit signals to the brain and the spinal cord 2) Interneurons: receive signals from sensory neurons and relay them within the brain and spinal cord 3) Motor neurons: pass messages from the nervous system to the other tissues in the body, such as muscles ...
Connecting cortex to machines: recent advances in brain interfaces
... its interface to the user to elicit a percept (such as touch or vision). The use of these inputs and outputs is determined by the individual through the voluntary interplay between percept and desired action. ...
... its interface to the user to elicit a percept (such as touch or vision). The use of these inputs and outputs is determined by the individual through the voluntary interplay between percept and desired action. ...
[pdf]
... ‘attention’. A variety of attention-related modulatory effects on neural processing across the visual system have been demonstrated, such as increases in baseline activity [1], increases in response gain of neurons that selectively respond to an attended feature or location [2,3], as well as shifts ...
... ‘attention’. A variety of attention-related modulatory effects on neural processing across the visual system have been demonstrated, such as increases in baseline activity [1], increases in response gain of neurons that selectively respond to an attended feature or location [2,3], as well as shifts ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... activations as if it had been performed by oneself. • The MNS helps to understand actions of others, modeling their behavior via embodied simulation of their actions, intentions, and emotions. ...
... activations as if it had been performed by oneself. • The MNS helps to understand actions of others, modeling their behavior via embodied simulation of their actions, intentions, and emotions. ...
Nature 402
... following damage to the dorsal part of mPFC. • Amygdala is required for both the acquisition and expression of learned fear responses(freezing). ...
... following damage to the dorsal part of mPFC. • Amygdala is required for both the acquisition and expression of learned fear responses(freezing). ...
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... Neurons are grouped together in complex networks that make the largest computer seem like a child’s toy. The nervous system is composed of something on the order of 100 billion neurons, about as many as the number of stars in our galaxy. Each neuron can receive messages from or transmit messages to ...
... Neurons are grouped together in complex networks that make the largest computer seem like a child’s toy. The nervous system is composed of something on the order of 100 billion neurons, about as many as the number of stars in our galaxy. Each neuron can receive messages from or transmit messages to ...
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... Neurons are grouped together in complex networks that make the largest computer seem like a child’s toy. The nervous system is composed of something on the order of 100 billion neurons, about as many as the number of stars in our galaxy. Each neuron can receive messages from or transmit messages to ...
... Neurons are grouped together in complex networks that make the largest computer seem like a child’s toy. The nervous system is composed of something on the order of 100 billion neurons, about as many as the number of stars in our galaxy. Each neuron can receive messages from or transmit messages to ...
Neuroethology

Neuroethology is the evolutionary and comparative approach to the study of animal behavior and its underlying mechanistic control by the nervous system. This interdisciplinary branch of behavioral neuroscience endeavors to understand how the central nervous system translates biologically relevant stimuli into natural behavior. For example, many bats are capable of echolocation which is used for prey capture and navigation. The auditory system of bats is often cited as an example for how acoustic properties of sounds can be converted into a sensory map of behaviorally relevant features of sounds. Neuroethologists hope to uncover general principles of the nervous system from the study of animals with exaggerated or specialized behaviors.As its name implies, neuroethology is a multidisciplinary field composed of neurobiology (the study of the nervous system) and ethology (the study of behavior in natural conditions). A central theme of the field of neuroethology, delineating it from other branches of neuroscience, is this focus on natural behavior. Natural behaviors may be thought of as those behaviors generated through means of natural selection (i.e. finding mates, navigation, locomotion, predator avoidance) rather than behaviors in disease states, or behavioral tasks that are particular to the laboratory.

















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008855303_1-42c5934975f83fadb4141440e1a86c3f-300x300.png)




