Nervous System - APBio
... • 3. When threshold is met, membrane is in rising phase • 4. The Na+ channels close and K+ channels open- falling phase • 5. Because more K+ are open than usual, the membrane potential is more neg – undershoot • 6. More K+ close returning the potential to normal ...
... • 3. When threshold is met, membrane is in rising phase • 4. The Na+ channels close and K+ channels open- falling phase • 5. Because more K+ are open than usual, the membrane potential is more neg – undershoot • 6. More K+ close returning the potential to normal ...
Roman German VS Chernyshenko, scientific supervisor ML Isakova
... of people, no matter how deeply they are into science. Let’s touch one of many implementations of AI which knows how to recognize faces, helps you with weather prediction and understands your handwriting better than you do. According to Wikipedia definition, an artificial neural network, often just ...
... of people, no matter how deeply they are into science. Let’s touch one of many implementations of AI which knows how to recognize faces, helps you with weather prediction and understands your handwriting better than you do. According to Wikipedia definition, an artificial neural network, often just ...
chapter 15 sensory, motor, and integrative systems
... d. is due to the generation of nerve impulses in severed neurons after amputation of a limb 7. Which of the following is true concerning voluntary motor impulses? a. They are carried from the motor cortex to skeletal muscle by somatic afferent neurons b. Impulses originate in the somatosensory corte ...
... d. is due to the generation of nerve impulses in severed neurons after amputation of a limb 7. Which of the following is true concerning voluntary motor impulses? a. They are carried from the motor cortex to skeletal muscle by somatic afferent neurons b. Impulses originate in the somatosensory corte ...
Lecture 6C
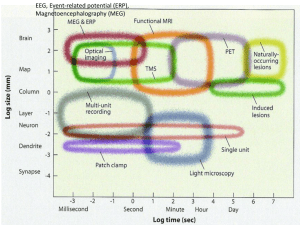
... This method provides high resolution radioactive labeling of active neurons. The physical pattern of active neurons (right panel, darker pixels correspond to greater neuronal activity) is clearly a geometrical representation of the pattern physically laid-out on the cortex. This experiment clearly d ...
... This method provides high resolution radioactive labeling of active neurons. The physical pattern of active neurons (right panel, darker pixels correspond to greater neuronal activity) is clearly a geometrical representation of the pattern physically laid-out on the cortex. This experiment clearly d ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... means of directed communication links, each with associated weight. ...
... means of directed communication links, each with associated weight. ...
System Introduction to Sensory Physiology: Sensory- Motor
... 11.! Efferent Control! 13.! Higher level processing for perception (what you ! ...
... 11.! Efferent Control! 13.! Higher level processing for perception (what you ! ...
Lecture 7 Neurons
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
The Nervous System
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
Seminar in Neuroscience Why Corticospinal Motor Neurons Are Important For
... circuitry. Their unique ability to collect, integrate, translate and transmit the brain's input to the spinal cord targets allow them to function as the spokesperson for the cerebral cortex for the initiation and modulation of voluntary movement. CSMN vulnerability and progressive degeneration is ke ...
... circuitry. Their unique ability to collect, integrate, translate and transmit the brain's input to the spinal cord targets allow them to function as the spokesperson for the cerebral cortex for the initiation and modulation of voluntary movement. CSMN vulnerability and progressive degeneration is ke ...
topic 6.5 Neurons
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Lecture slides from 2007
... Skeletal Joints Joints can rotate along: •One axis (knee) •Two axes (wrist) •Three axes (hip) ...
... Skeletal Joints Joints can rotate along: •One axis (knee) •Two axes (wrist) •Three axes (hip) ...
Chapter Two Part One - K-Dub
... Like a gun, it either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... Like a gun, it either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
Chapter Two Part One PPT - K-Dub
... Like a gun, it either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... Like a gun, it either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (PART II): THE TRAFFIC CONTROL
... directly to the ventral horn motor neurons. In addition, the cortex sends the planned movements to subcortical structures such as the thalamus, basal nuclei, and cerebellum. The subcortical structures finetune and coordinate the movement plan, send information down the spinal cord, and correct the o ...
... directly to the ventral horn motor neurons. In addition, the cortex sends the planned movements to subcortical structures such as the thalamus, basal nuclei, and cerebellum. The subcortical structures finetune and coordinate the movement plan, send information down the spinal cord, and correct the o ...
Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across synaptic cleft where they can bind with receptor sites on postsynaptic end to influence electrical response in neuron • If number of excitatory postsynaptic events is large enough, ...
... Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across synaptic cleft where they can bind with receptor sites on postsynaptic end to influence electrical response in neuron • If number of excitatory postsynaptic events is large enough, ...
mspn1a
... Question 1: Spinal Cord Organization: Draw a basic cross section of the spinal cord depicting the regions of white and gray matter (e.g., top diagram on page 3 of Spinal Cord I handout). Then label the following regions. Also, in a few sentences describe what you would find in the given region. a. V ...
... Question 1: Spinal Cord Organization: Draw a basic cross section of the spinal cord depicting the regions of white and gray matter (e.g., top diagram on page 3 of Spinal Cord I handout). Then label the following regions. Also, in a few sentences describe what you would find in the given region. a. V ...
BCH 450 Nervous Tissues
... Largest part of the human brain. Controls thinking, speech, vision, hearing and all voluntary acts ...
... Largest part of the human brain. Controls thinking, speech, vision, hearing and all voluntary acts ...
big
... Neurons and Glia are the two major cell types that make up the nervous system Neurons transmit messages from cell to cell – Sensory neurons transform stimuli (e.g. light, sound, or joint position) into messages sent to other neurons – Interneurons integrate information from many cells; particular in ...
... Neurons and Glia are the two major cell types that make up the nervous system Neurons transmit messages from cell to cell – Sensory neurons transform stimuli (e.g. light, sound, or joint position) into messages sent to other neurons – Interneurons integrate information from many cells; particular in ...
The Nervous System - chemistrywithmrsmorton
... 3. CNS integration center 4. Motor neuron 5. Effector organ – muscle or gland ...
... 3. CNS integration center 4. Motor neuron 5. Effector organ – muscle or gland ...