Strategies for drug delivery through the blood
... • Protects the brain from “foreign substances” in the blood that my injure the brain • Protects the brain from hormones and neurotransmitters in the rest of the body • Maintains a constant environment for the brain ...
... • Protects the brain from “foreign substances” in the blood that my injure the brain • Protects the brain from hormones and neurotransmitters in the rest of the body • Maintains a constant environment for the brain ...
THE BASAL GANGLIA
... The most frequent disease affecting the basal ganglia is Parkinson’s disease (PD). Typically, voluntary movements are hard mo initiate (akinesia) and they are slower and smaller than normal (bradykinesia). The akinesia also leads to a conspicuous lack of facial movements (mask like face). In additio ...
... The most frequent disease affecting the basal ganglia is Parkinson’s disease (PD). Typically, voluntary movements are hard mo initiate (akinesia) and they are slower and smaller than normal (bradykinesia). The akinesia also leads to a conspicuous lack of facial movements (mask like face). In additio ...
Nervous System - Academic Computer Center
... There are two main types of neurotransmitter receptors: channel-linked receptors mediate direct transmitter action and result in brief, localized changes; and G proteinlinked receptors mediate indirect transmitter action resulting in slow, persistent, and ...
... There are two main types of neurotransmitter receptors: channel-linked receptors mediate direct transmitter action and result in brief, localized changes; and G proteinlinked receptors mediate indirect transmitter action resulting in slow, persistent, and ...
Symptoms: visual disturbances, ______, loss of
... ii. Pons- Connect higher brain centers and the spinal cord, Relay impulses between the motor cortex and the cerebellum iii. Medulla oblongata- Autonomic reflex centers, adjusts force and rate of heart contraction, adjusts blood vessel diameter for blood pressure regulation, generate respiratory rhyt ...
... ii. Pons- Connect higher brain centers and the spinal cord, Relay impulses between the motor cortex and the cerebellum iii. Medulla oblongata- Autonomic reflex centers, adjusts force and rate of heart contraction, adjusts blood vessel diameter for blood pressure regulation, generate respiratory rhyt ...
Lab #7: Nerve Pathways and Somatosensory Physiology
... phasic receptors. Other sensors, however, show little sensory adaptation with continuous stimulation, and continue to generate action potentials at a constant rate as long as the stimulus is applied. These sensors are called tonic receptors. Somatosensory receptors, like all sensory receptors, funct ...
... phasic receptors. Other sensors, however, show little sensory adaptation with continuous stimulation, and continue to generate action potentials at a constant rate as long as the stimulus is applied. These sensors are called tonic receptors. Somatosensory receptors, like all sensory receptors, funct ...
ben_slides1
... Calcium and sodium ions to enter into the cell, depolarizing the ORN Calcium-dependent Chlorine channels contribute to depolarization as well ...
... Calcium and sodium ions to enter into the cell, depolarizing the ORN Calcium-dependent Chlorine channels contribute to depolarization as well ...
Movement
... Disorders of the Motor Neurons. a) Myasthenia Gravis: The immune system progressively attacks acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. This leads to progressive muscle weakness and rapid fatigue apparent after short periods of exercise. Drugs such as Physostigmine (an acetylcholine agonis ...
... Disorders of the Motor Neurons. a) Myasthenia Gravis: The immune system progressively attacks acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. This leads to progressive muscle weakness and rapid fatigue apparent after short periods of exercise. Drugs such as Physostigmine (an acetylcholine agonis ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... • Integrates and interprets sensory information and initiates voluntary movements • Has taken over many of the midbrain functions in lower vertebrates • Six layers • Isocortex (outer layer) is necessary for cognition and higher brain functions • More folded in more advanced mammals • Gyri – folds • ...
... • Integrates and interprets sensory information and initiates voluntary movements • Has taken over many of the midbrain functions in lower vertebrates • Six layers • Isocortex (outer layer) is necessary for cognition and higher brain functions • More folded in more advanced mammals • Gyri – folds • ...
NOTES FOR CHAPTER 13
... e. effector (muscle or gland) A stimulus is received by a _________________________, which initiates an impulse in the __________________________. The impulse travels through the sensory neuron to the spinal cord and transmits it to the __________________________. This neuron passes the impulse to t ...
... e. effector (muscle or gland) A stimulus is received by a _________________________, which initiates an impulse in the __________________________. The impulse travels through the sensory neuron to the spinal cord and transmits it to the __________________________. This neuron passes the impulse to t ...
SHH - bthsresearch
... • Differentiation into various regions of the CNS • Happens in 3 ways, simultaneously – Gross anatomical changes - bulging and constriction of Neural tube to form chambers of brain and Spinal Cord – Tissue-level Changes - Cells rearrange into functional regions of the brain – Cellular-level Changes ...
... • Differentiation into various regions of the CNS • Happens in 3 ways, simultaneously – Gross anatomical changes - bulging and constriction of Neural tube to form chambers of brain and Spinal Cord – Tissue-level Changes - Cells rearrange into functional regions of the brain – Cellular-level Changes ...
Chapter 6
... Physical site of the stimulated receptor Acuity - precision of stimulus location Greater receptive field size and overlap decreases acuity Lateral inhibition increases acuity Intensity Stronger stimuli result in higher frequency of receptor potentials leading to a higher frequency of action potentia ...
... Physical site of the stimulated receptor Acuity - precision of stimulus location Greater receptive field size and overlap decreases acuity Lateral inhibition increases acuity Intensity Stronger stimuli result in higher frequency of receptor potentials leading to a higher frequency of action potentia ...
Olfactory network dynamics and the coding of multidimensional
... • Sparse, synthetic representations are useful, but they eliminate the detail and segmentability of a representation (Gestalt). This is consistent with behavioural and psychophysical observations in olfactory ...
... • Sparse, synthetic representations are useful, but they eliminate the detail and segmentability of a representation (Gestalt). This is consistent with behavioural and psychophysical observations in olfactory ...
Document
... Parasympathetic responses sometimes refered to as the REST-AND-DIGEST STATE. Almost all visceral targets receive both sympathetic & parasympathetic neuronal inputs. Enteric nervous system Enteric neurons form plexuses that surround and extend along the length of the gut, including stomach, small and ...
... Parasympathetic responses sometimes refered to as the REST-AND-DIGEST STATE. Almost all visceral targets receive both sympathetic & parasympathetic neuronal inputs. Enteric nervous system Enteric neurons form plexuses that surround and extend along the length of the gut, including stomach, small and ...
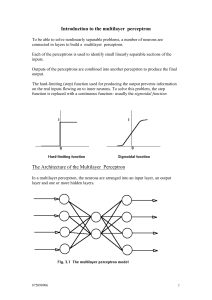
Introduction to the multilayer perceptron
... Learning Difficulties in Multilayer Perceptrons Occasionally, the multilayer perceptron fails to settle into the global minimum of the energy surface and instead find itself in one of the local minima. This is due to the gradient descent strategy followed. A number of alternative approaches can be t ...
... Learning Difficulties in Multilayer Perceptrons Occasionally, the multilayer perceptron fails to settle into the global minimum of the energy surface and instead find itself in one of the local minima. This is due to the gradient descent strategy followed. A number of alternative approaches can be t ...
AP Ch. 2 vocab
... consists of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems the brain and spinal cord the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body neural "cables" containing many axons bundled axons, which are part of the peripheral nervous system c ...
... consists of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems the brain and spinal cord the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body neural "cables" containing many axons bundled axons, which are part of the peripheral nervous system c ...
Ch 2 Physiology - Texas A&M University
... schematically shown as a1 a2 a3 a4 The firing rate of neuron B is determined by the activation sent by neurons a1-a4. B ...
... schematically shown as a1 a2 a3 a4 The firing rate of neuron B is determined by the activation sent by neurons a1-a4. B ...
nervous system divisions cns, pns 1
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
The Nervous System
... 1. What part of the brain do you use to do your math homework? 2. What part of the brain do you mostly use to create a drawing? 3. What part of the brain helps a basketball player maintain her balance while driving for a lay-up? 4. What part of the body protects the spinal cord? To which body system ...
... 1. What part of the brain do you use to do your math homework? 2. What part of the brain do you mostly use to create a drawing? 3. What part of the brain helps a basketball player maintain her balance while driving for a lay-up? 4. What part of the body protects the spinal cord? To which body system ...
Sonia Gasparini, PhD Degrees Assistant Professor of Cell Biology & Anatomy and
... the direct involvement of the entorhinal cortex in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy and schizophrenia. In particular, layer V neurons, being the main target of processed outputs leaving the hippocampal formation and sending their axons to cortical reg ...
... the direct involvement of the entorhinal cortex in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy and schizophrenia. In particular, layer V neurons, being the main target of processed outputs leaving the hippocampal formation and sending their axons to cortical reg ...
Ch.10
... • groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other • interneurons work together to perform a common function • each pool receives input from other neurons • each pool generates output to other neurons ...
... • groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other • interneurons work together to perform a common function • each pool receives input from other neurons • each pool generates output to other neurons ...