Autonomic Nervous System
... neurons, preganglionic axons are small-diameter, myelinated, relatively slowly conducting B fibers.) (The axons of the postganglionic neurons are mostly unmyelinated C fibers and terminate on the visceral effectors.) • Neurotransmitters: Autonomic nerves release NT that may be excitatory or inhibito ...
... neurons, preganglionic axons are small-diameter, myelinated, relatively slowly conducting B fibers.) (The axons of the postganglionic neurons are mostly unmyelinated C fibers and terminate on the visceral effectors.) • Neurotransmitters: Autonomic nerves release NT that may be excitatory or inhibito ...
Target neuron prespecification in the olfactory map of Drosophila
... to estimate the binaural FTRFs. In fact, matching the levels of these very different types of auditory stimuli would pose dif®cult technical problems. However, to allow a post hoc comparison between the sound levels used during the FTRF measurement and the SRF mapping we estimated the level of the V ...
... to estimate the binaural FTRFs. In fact, matching the levels of these very different types of auditory stimuli would pose dif®cult technical problems. However, to allow a post hoc comparison between the sound levels used during the FTRF measurement and the SRF mapping we estimated the level of the V ...
Cerebellum
... from cortical motor areas about the intended motor command and on feedback from the spinal cord and periphery, which provides details about the evolving movement. These inputs allow the spinoocerebellum to correct for deviations from the intended movement. The Cerebrocerebellum Coordinates the Plann ...
... from cortical motor areas about the intended motor command and on feedback from the spinal cord and periphery, which provides details about the evolving movement. These inputs allow the spinoocerebellum to correct for deviations from the intended movement. The Cerebrocerebellum Coordinates the Plann ...
49-Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... quadriceps in this reflex as an example, propose a model for regulation of smooth muscle activity in the esophagus during the swallowing reflex (see Figure 41.10, p. 884). ...
... quadriceps in this reflex as an example, propose a model for regulation of smooth muscle activity in the esophagus during the swallowing reflex (see Figure 41.10, p. 884). ...
Multiple sites of spike initiation in a single dendritic
... afferents project to the same neuropilar areas and, therefore, probably terminate on the same dendritic branch of a given postsynaptic cell. We have to date not performed this experiment using homolateral pairs of roots which terminate in disparate neuropilar areas. Unlike the dendritic spikes obser ...
... afferents project to the same neuropilar areas and, therefore, probably terminate on the same dendritic branch of a given postsynaptic cell. We have to date not performed this experiment using homolateral pairs of roots which terminate in disparate neuropilar areas. Unlike the dendritic spikes obser ...
Responses to Odors Mapped in Snail Tentacle and Brain by [14C]
... variations in response that support the hypothesis of a spatial code for odor quality (Stewart et al., 1979; Jourdan et al., 1980; Kauer, 1980; Mackay-Sim and Kubie, 1981; Nathan and Moulton, 1981). In the present study, odor-dependent variations in neural response were investigated using both quali ...
... variations in response that support the hypothesis of a spatial code for odor quality (Stewart et al., 1979; Jourdan et al., 1980; Kauer, 1980; Mackay-Sim and Kubie, 1981; Nathan and Moulton, 1981). In the present study, odor-dependent variations in neural response were investigated using both quali ...
PDF
... preserved even after training (p = 0.03, permutation test; Figure 2A), suggesting that olfactory conditioning operates on top of the individually variable base valence of a scent. Individually trained flies exhibited many of the characteristics seen in population learning (Tully and Quinn, 1985). Fi ...
... preserved even after training (p = 0.03, permutation test; Figure 2A), suggesting that olfactory conditioning operates on top of the individually variable base valence of a scent. Individually trained flies exhibited many of the characteristics seen in population learning (Tully and Quinn, 1985). Fi ...
Studies of the Role of the Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation
... burst neurons in head-restrained monkeys, and (2) reversible inactivation techniques confirmed the traditional view of the importance of PPRF in the control of horizontal eye movements. Reversible inactivation of neurons in the vicinity of identified short-lead burst neurons produced dramatic reduct ...
... burst neurons in head-restrained monkeys, and (2) reversible inactivation techniques confirmed the traditional view of the importance of PPRF in the control of horizontal eye movements. Reversible inactivation of neurons in the vicinity of identified short-lead burst neurons produced dramatic reduct ...
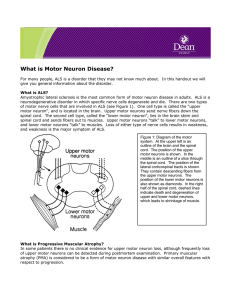
What is Motor Neuron
... neuron involvement. However, most patients who initially have only upper motor neuron signs eventually develop lower motor neuron signs and go to have ALS. Thus, to be certain that a patient has PLS they must be followed for 3-4 years to be certain that lower motor neuron signs do not develop. PLS h ...
... neuron involvement. However, most patients who initially have only upper motor neuron signs eventually develop lower motor neuron signs and go to have ALS. Thus, to be certain that a patient has PLS they must be followed for 3-4 years to be certain that lower motor neuron signs do not develop. PLS h ...
Document
... C. Functions of the Spinal Cord 1. The spinal cord has two major functions: a. Transmit impulses to and from the brain b. House spinal reflexes. 2. Tracts carrying sensory information to the brain are called ascending tracts; descending tracts carry motor information from the brain. ...
... C. Functions of the Spinal Cord 1. The spinal cord has two major functions: a. Transmit impulses to and from the brain b. House spinal reflexes. 2. Tracts carrying sensory information to the brain are called ascending tracts; descending tracts carry motor information from the brain. ...
The neuronal structure of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in the
... presynaptic to presynaptic dendrites of GLN interneurons, and these presynaptic dendrites establish synaptic contacts with the relay (projection) neurons [8]. This relay is gated and can be suppressed by activity among local inhibitory interneurons that use GABA as a neurotransmitter [28]. There is ...
... presynaptic to presynaptic dendrites of GLN interneurons, and these presynaptic dendrites establish synaptic contacts with the relay (projection) neurons [8]. This relay is gated and can be suppressed by activity among local inhibitory interneurons that use GABA as a neurotransmitter [28]. There is ...
Cortical region interactions and the functional role of apical
... Figure 3: Illustrations of three possible ways in which the stimulation (‘a’ or ‘b’) received by each dendrite could affect learning of synaptic weights (‘w’). The functions ‘f’, ‘g’ and ‘h’ could potentially take numerous alternative forms. Various functions (both linear and nonlinear) have been em ...
... Figure 3: Illustrations of three possible ways in which the stimulation (‘a’ or ‘b’) received by each dendrite could affect learning of synaptic weights (‘w’). The functions ‘f’, ‘g’ and ‘h’ could potentially take numerous alternative forms. Various functions (both linear and nonlinear) have been em ...
Synapse
... vesicles containing neurotransmitters and both are released simultaneously by the action potential that reaches the synaptic ...
... vesicles containing neurotransmitters and both are released simultaneously by the action potential that reaches the synaptic ...
An Integrate-and-fire Model of Prefrontal Cortex Neuronal Activity during Performance of Goal-directed
... 1998), so we will commonly refer to sensory information from the environment as ‘state’. We will refer to motor output as ‘actions’ and to the desired goal as ‘reward’. However, this model does not focus on the temporal difference learning rule (Sutton, 1988), a rule that uses the difference between ...
... 1998), so we will commonly refer to sensory information from the environment as ‘state’. We will refer to motor output as ‘actions’ and to the desired goal as ‘reward’. However, this model does not focus on the temporal difference learning rule (Sutton, 1988), a rule that uses the difference between ...
Survival of cultured hippocampal neurons upon hypoxia
... campal cultures in hypoxic condition death of 30% of non-treated neurons was observed. In cultures containing high GBP concentrations:100 μM and 300 μM, two-fold higher number of nerve cells remained viable as compared to control cultures without drug. Neuroprotective properties of GBP were describe ...
... campal cultures in hypoxic condition death of 30% of non-treated neurons was observed. In cultures containing high GBP concentrations:100 μM and 300 μM, two-fold higher number of nerve cells remained viable as compared to control cultures without drug. Neuroprotective properties of GBP were describe ...
Dorsal spinal cord stimulation obtunds the capacity of intrathoracic
... After waiting for at least 5 minutes, the artery that perfused the identified sensory field was occluded 3-4 times. That is, the ventral descending or circumflex coronary artery was occluded individually for 30 seconds – depending on which vessels perfused its identified sensory field. At least 5 mi ...
... After waiting for at least 5 minutes, the artery that perfused the identified sensory field was occluded 3-4 times. That is, the ventral descending or circumflex coronary artery was occluded individually for 30 seconds – depending on which vessels perfused its identified sensory field. At least 5 mi ...
Neuroembryology of Neural Tube Defects
... infant lumbar myeloschisis The open spinal cord (arrow) is covered by a delicate, semitransparent membrane. ...
... infant lumbar myeloschisis The open spinal cord (arrow) is covered by a delicate, semitransparent membrane. ...
Basic functional neuroanatomy
... with pathological findings, either after death or in images of the living brain. Many disorders affecting the cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum are diagnosed in this way, working from the assumption that particular functions are carried out in localized regions of the central nervous system. 2 ...
... with pathological findings, either after death or in images of the living brain. Many disorders affecting the cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum are diagnosed in this way, working from the assumption that particular functions are carried out in localized regions of the central nervous system. 2 ...
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... Cell bodies of neurons which receive afferent information from spinal nerves and send it toward the brain Cell bodies of neurons which receive efferent information from the brain and send it to smooth myocytes, cardiac myocytes, and glands (autonomic motor innervation) ...
... Cell bodies of neurons which receive afferent information from spinal nerves and send it toward the brain Cell bodies of neurons which receive efferent information from the brain and send it to smooth myocytes, cardiac myocytes, and glands (autonomic motor innervation) ...
Chapter 18
... 4. The anterior rami of spinal nerves, except for thoracic nerves T2-T12, form networks on both right and left sides of the body that are called plexuses; emerging from the plexuses are nerves that bear names which often describe the general regions they serve or the routes that they follow. 5. The ...
... 4. The anterior rami of spinal nerves, except for thoracic nerves T2-T12, form networks on both right and left sides of the body that are called plexuses; emerging from the plexuses are nerves that bear names which often describe the general regions they serve or the routes that they follow. 5. The ...
PPT - UCLA Health
... • There are positive effects of electrical stimulation on auditory brain stem nuclei, midbrain and auditory cortex. • Results suggest that there is a critical period or at least age-related plasticity for the developing auditory cortex ...
... • There are positive effects of electrical stimulation on auditory brain stem nuclei, midbrain and auditory cortex. • Results suggest that there is a critical period or at least age-related plasticity for the developing auditory cortex ...
CHAPTER 2 THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM
... capable of producing Action Potentials (Figure 2.4). Such excitable membranes besides generating action potentials are able to transmit them along their surfaces. Thus the Action Potential is the signal which is transmitted from one part of the nerve or muscle cell to another. An Action Potential tr ...
... capable of producing Action Potentials (Figure 2.4). Such excitable membranes besides generating action potentials are able to transmit them along their surfaces. Thus the Action Potential is the signal which is transmitted from one part of the nerve or muscle cell to another. An Action Potential tr ...




![Responses to Odors Mapped in Snail Tentacle and Brain by [14C]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017009313_1-932f7069dbfdd3fd3915bbe942d02b0f-300x300.png)