(580.422) Lecture 7, Synaptic Transmission
... An example is provided by the GIRK channel, which open when ACh is applied to a membrane patch. This is evident in the records below by increased “open” conductance states. The increase in open states occurs if the ACh is applied locally in the patch pipette (third trace) and not if ACh is applied t ...
... An example is provided by the GIRK channel, which open when ACh is applied to a membrane patch. This is evident in the records below by increased “open” conductance states. The increase in open states occurs if the ACh is applied locally in the patch pipette (third trace) and not if ACh is applied t ...
Ch 7
... during development. It is also the basis for rejection of foreign cells by the immune system. Cells recognize other cells by binding to surface molecules, often carbohydrates, on the plasma membrane. ...
... during development. It is also the basis for rejection of foreign cells by the immune system. Cells recognize other cells by binding to surface molecules, often carbohydrates, on the plasma membrane. ...
PharmacologyLec 1 Central nervous system pharmacology
... Central nervous system pharmacology There are two reasons why understanding the action of drugs act on the central nervous system, the first is that centrally acting drugs are of therapeutic importance,the second reason is that the CNS is functionally far more complex than any other system in the bo ...
... Central nervous system pharmacology There are two reasons why understanding the action of drugs act on the central nervous system, the first is that centrally acting drugs are of therapeutic importance,the second reason is that the CNS is functionally far more complex than any other system in the bo ...
ppt
... determining a neurotransmitter’s effect on the post-synaptic cell. 4. Compare the mechanisms of action and output of different neurotransmitters ...
... determining a neurotransmitter’s effect on the post-synaptic cell. 4. Compare the mechanisms of action and output of different neurotransmitters ...
Section 3.3 The Cell Membrane
... Some proteins extend through one or both phospholipid layers and help materials cross the membrane. Other proteins are key components of the cytoskeleton. Different cell types have different membrane proteins. Carbohydrates attached to membrane proteins serve as identification tags, enabling cel ...
... Some proteins extend through one or both phospholipid layers and help materials cross the membrane. Other proteins are key components of the cytoskeleton. Different cell types have different membrane proteins. Carbohydrates attached to membrane proteins serve as identification tags, enabling cel ...
Nervous System
... An IPSP is a local hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane and drives the neuron away from AP threshold. Neurotransmitter binding opens K+ or Cl– channels. ...
... An IPSP is a local hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane and drives the neuron away from AP threshold. Neurotransmitter binding opens K+ or Cl– channels. ...
Bacterial Systems for Assembly, Secretion and Targeted
... Type III system A battery of toxins of human enteropathogens, such as Yersiniae, Salmonellae and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, use this system to carry out the invasion of host intestinal epithelial cells (Fig. 1F). A Type III system is also used by Pseudomonas syringae and other plant pathogen ...
... Type III system A battery of toxins of human enteropathogens, such as Yersiniae, Salmonellae and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, use this system to carry out the invasion of host intestinal epithelial cells (Fig. 1F). A Type III system is also used by Pseudomonas syringae and other plant pathogen ...
The Neuron - Austin Community College
... Typically, a single synaptic interaction will not create a graded depolarization strong enough to migrate to the axon hillock and induce the firing of an AP However, a graded depolarization will bring the membrane potential closer to threshold. Thus, it’s often referred to as an excitatory postsynap ...
... Typically, a single synaptic interaction will not create a graded depolarization strong enough to migrate to the axon hillock and induce the firing of an AP However, a graded depolarization will bring the membrane potential closer to threshold. Thus, it’s often referred to as an excitatory postsynap ...
Researchers determine how part of the endoplasmic reticulum gets
... fly GTPase, atlastin, took care of both fusion and curvature stabilization, eliminating the need for a REEP or a reticulon. ...
... fly GTPase, atlastin, took care of both fusion and curvature stabilization, eliminating the need for a REEP or a reticulon. ...
Components and Structure
... of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate-linked head group. Cholesterol, another lipid composed of four fused carbon rings, is found alongside the phospholipids in the core of the membrane. The proportions of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates in the plasma membrane vary with cell type, but fo ...
... of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate-linked head group. Cholesterol, another lipid composed of four fused carbon rings, is found alongside the phospholipids in the core of the membrane. The proportions of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates in the plasma membrane vary with cell type, but fo ...
Lecture 19 Membranes 2: Membrane Proteins
... glycosidic bonds to specific Ser, Thr, and Asn residues) • Carbohydrates include ABO and MN blood group antigen-determining structures. • Extracellular part of protein also receptor for influenza virus binding to cells • C-terminal portion on cytosolic side of membrane, interacts with cytoskeletal p ...
... glycosidic bonds to specific Ser, Thr, and Asn residues) • Carbohydrates include ABO and MN blood group antigen-determining structures. • Extracellular part of protein also receptor for influenza virus binding to cells • C-terminal portion on cytosolic side of membrane, interacts with cytoskeletal p ...
to the complete text
... The above data have made p24 proteins strong candidates to act as coat receptors. In contrast, their putative role as cargo receptors is less clear. Although in yeast several lines of evidence support a role for them in selective sorting [19••,27], a direct interaction with cargo molecules remains t ...
... The above data have made p24 proteins strong candidates to act as coat receptors. In contrast, their putative role as cargo receptors is less clear. Although in yeast several lines of evidence support a role for them in selective sorting [19••,27], a direct interaction with cargo molecules remains t ...
h-Barrel membrane protein folding and structure viewed through the
... The h-barrel is a transmembrane structural motif commonly encountered in bacterial outer membrane proteins and pore-forming toxins (PFTs). a-Hemolysin (aHL) is a cytotoxin secreted by Staphylococcus aureus that assembles from a water-soluble monomer to form a membrane-bound heptameric h-barrel on th ...
... The h-barrel is a transmembrane structural motif commonly encountered in bacterial outer membrane proteins and pore-forming toxins (PFTs). a-Hemolysin (aHL) is a cytotoxin secreted by Staphylococcus aureus that assembles from a water-soluble monomer to form a membrane-bound heptameric h-barrel on th ...
What is “membrane potential”
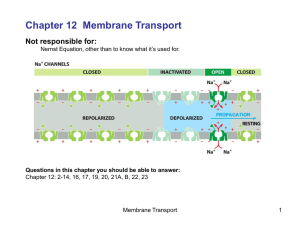
... Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
... Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
Shedding light on the translocation pore
... of the nascent transmembrane region while it is still in an aqueous environment, followed by its transfer into the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. For some multispanning integral membrane proteins, such recognition and transfer would have to occur as many as ten times. Any aqueous translocatio ...
... of the nascent transmembrane region while it is still in an aqueous environment, followed by its transfer into the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. For some multispanning integral membrane proteins, such recognition and transfer would have to occur as many as ten times. Any aqueous translocatio ...
Mass Spectrometry-Based Analysis Of Membrane Proteins Derived
... carried out using density gradient ultracentrifugation for the enrichment of membrane proteins that were digested using the standard protocol with an extra washing step with 1% FA. When compared to the traditional fractionation approach, density gradient ultracentrifugation was able to identify more ...
... carried out using density gradient ultracentrifugation for the enrichment of membrane proteins that were digested using the standard protocol with an extra washing step with 1% FA. When compared to the traditional fractionation approach, density gradient ultracentrifugation was able to identify more ...
aminoacyl-tRNA
... • Most lysosomal, membrane and secretary proteins have a N-terminal signal sequence that directs them for translocation into the lumen of the ER. • These signal sequences ranging in length from 13 to 36 residues have the following features: a highly hydrophobic stretch of 10 to 15 residues forms the ...
... • Most lysosomal, membrane and secretary proteins have a N-terminal signal sequence that directs them for translocation into the lumen of the ER. • These signal sequences ranging in length from 13 to 36 residues have the following features: a highly hydrophobic stretch of 10 to 15 residues forms the ...
Constitutive cycling: a general mechanism to regulate cell surface
... tyrosine-based sorting motif (YDSI) although other endocytotic motifs may be present in the C terminus.(26–29) There is also evidence for a role for AP-2 in the trafficking of Hþ –KþATPase. The beta subunit of this enzyme has in its N terminus a highly conserved tyrosine-based motif that is similar ...
... tyrosine-based sorting motif (YDSI) although other endocytotic motifs may be present in the C terminus.(26–29) There is also evidence for a role for AP-2 in the trafficking of Hþ –KþATPase. The beta subunit of this enzyme has in its N terminus a highly conserved tyrosine-based motif that is similar ...
Membranous Structures of the Cell The Cell Membrane
... pathways constitutive and regulated. Some proteins are secreted continuously by the cells that make them. Secretion of mucus by goblet cells in the small intestine is a specific example. In this case, exocytosis follows the constitutive pathway, which is present in all cells. In other cells, macromo ...
... pathways constitutive and regulated. Some proteins are secreted continuously by the cells that make them. Secretion of mucus by goblet cells in the small intestine is a specific example. In this case, exocytosis follows the constitutive pathway, which is present in all cells. In other cells, macromo ...
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... membrane spreads to nearby regions of the membrane, causing them to depolarize then repolarize. This, in turn, stimulates regions a little further out to depolarize and repolarize, so these events spread away from the original location. ...
... membrane spreads to nearby regions of the membrane, causing them to depolarize then repolarize. This, in turn, stimulates regions a little further out to depolarize and repolarize, so these events spread away from the original location. ...
Chapt. 10: Protein Sorting, Transport: Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi
... Mannose-6-PO4, binds Mannose-6-PO4 receptors in trans Golgi membrane Mannose-6-PO4 receptors span the Golgi membrane, binding sites for cytosolic adaptor proteins, which bind clathrin Clathrin-coated vesicles have many destinations; different adaptors Fig. 10.37 ...
... Mannose-6-PO4, binds Mannose-6-PO4 receptors in trans Golgi membrane Mannose-6-PO4 receptors span the Golgi membrane, binding sites for cytosolic adaptor proteins, which bind clathrin Clathrin-coated vesicles have many destinations; different adaptors Fig. 10.37 ...
ppt
... Mannose-6-PO4, binds Mannose-6-PO4 receptors in trans Golgi membrane Mannose-6-PO4 receptors span the Golgi membrane, binding sites for cytosolic adaptor proteins, which bind clathrin Clathrin-coated vesicles have many destinations; different adaptors Fig. 10.37 ...
... Mannose-6-PO4, binds Mannose-6-PO4 receptors in trans Golgi membrane Mannose-6-PO4 receptors span the Golgi membrane, binding sites for cytosolic adaptor proteins, which bind clathrin Clathrin-coated vesicles have many destinations; different adaptors Fig. 10.37 ...
mitochondria
... across/into the thylakoid membrane 1. Sec pathway: uses components that are homolog to the Sec proteins in bacteria which mediate the translocation across the bacterial plasma membrane 2. SRP-like pathway: uses the homolog of the signal recognition particle, or SRP 3. TAT pathway: twin arginine tran ...
... across/into the thylakoid membrane 1. Sec pathway: uses components that are homolog to the Sec proteins in bacteria which mediate the translocation across the bacterial plasma membrane 2. SRP-like pathway: uses the homolog of the signal recognition particle, or SRP 3. TAT pathway: twin arginine tran ...
SNARE (protein)

SNARE proteins (an acronym derived from ""SNAP (Soluble NSF Attachment Protein) REceptor"") are a large protein superfamily consisting of more than 60 members in yeast and mammalian cells. The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate vesicle fusion, that is, the fusion of vesicles with their target membrane bound compartments (such as a lysosome). The best studied SNAREs are those that mediate docking of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane in neurons. These SNAREs are the targets of the bacterial neurotoxins responsible for botulism and tetanus.