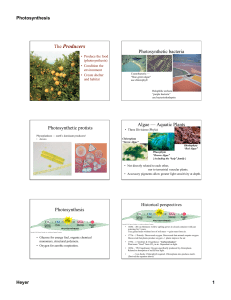
Light-independent reactions
... reactions involved do not need light to occur, and so technically can take place without light. However, the products (ATP and reduced NADP) of the light-dependent reactions are required, and so in practice, these reactions will not continue for very long without light, as the light-dependent stage ...
... reactions involved do not need light to occur, and so technically can take place without light. However, the products (ATP and reduced NADP) of the light-dependent reactions are required, and so in practice, these reactions will not continue for very long without light, as the light-dependent stage ...
Mitochondrial DNA
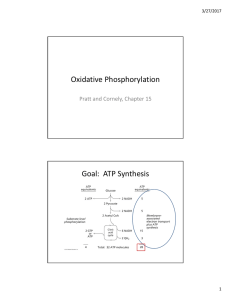
... – The high energy electrons are removed from NADH and FADH2, and passed through three protein complexes embedded in the inner membrane. – Each complex uses some of the electrons’ energy to pump H+ ions out of the matrix into the intermembrane space. – The final protein complex gives the electrons to ...
... – The high energy electrons are removed from NADH and FADH2, and passed through three protein complexes embedded in the inner membrane. – Each complex uses some of the electrons’ energy to pump H+ ions out of the matrix into the intermembrane space. – The final protein complex gives the electrons to ...
Lecture 6 Thurs 4-13-06
... The Plasma Membrane: 3. Mechanisms for transport of macromolecules, cont. B. Endocytosis, cont.: 3. Ubiquitin-mediated endoctyosis (UME): Ubiquitin: 76 aa protein that gets conjugated to substrate proteins Poly-ubiquitination targets proteins for degradation by proteasome. Mono-ubiquitination acts ...
... The Plasma Membrane: 3. Mechanisms for transport of macromolecules, cont. B. Endocytosis, cont.: 3. Ubiquitin-mediated endoctyosis (UME): Ubiquitin: 76 aa protein that gets conjugated to substrate proteins Poly-ubiquitination targets proteins for degradation by proteasome. Mono-ubiquitination acts ...
Neuronal Modeling
... The cytoplasm of most cells (including neurons) has an excess of negative ions over positive ions (due to active pumping of sodium ions out of the cell) By convention this is referred to as a negative membrane potential (inside minus outside) Typical resting potential is -50 mV ...
... The cytoplasm of most cells (including neurons) has an excess of negative ions over positive ions (due to active pumping of sodium ions out of the cell) By convention this is referred to as a negative membrane potential (inside minus outside) Typical resting potential is -50 mV ...
Ubiquinone
... have abnormally shaped mitochondria containing paracrystalline structures. • This lysyl-tRNA mutation is also one of the causes of adult-onset (type II) diabetes. ...
... have abnormally shaped mitochondria containing paracrystalline structures. • This lysyl-tRNA mutation is also one of the causes of adult-onset (type II) diabetes. ...
Cellular Respiration
... The movement of electrons from NADH and FADH2 occurs along an electron transport chain in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. The electrons end up in oxygen . ...
... The movement of electrons from NADH and FADH2 occurs along an electron transport chain in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. The electrons end up in oxygen . ...
15-25 kD
... – Class – Order – Family – Genus – Species • Traditional classification based upon traits: – Morphological – Behavioral ...
... – Class – Order – Family – Genus – Species • Traditional classification based upon traits: – Morphological – Behavioral ...
Membrane Proteins: Capturing the signal | eLife
... Ribosomes that are not building proteins destined for the endoplasmic reticulum do not recruit the SRP (shown in green). (2) Membrane proteins have hydrophobic segments (called transmembrane domains) that are eventually inserted into the membrane. Exposing these transmembrane domains in the aqueous ...
... Ribosomes that are not building proteins destined for the endoplasmic reticulum do not recruit the SRP (shown in green). (2) Membrane proteins have hydrophobic segments (called transmembrane domains) that are eventually inserted into the membrane. Exposing these transmembrane domains in the aqueous ...
Unit 2
... Peroxisomes function in a variety of metabolic processes that produce hydrogen peroxide as a waste product, then voncerts the peroxide to water. 9. Describe the structure & function of a mitochondrion Mitochondrion is the site of cellular respiration at the catabolic process that generates ATP by ex ...
... Peroxisomes function in a variety of metabolic processes that produce hydrogen peroxide as a waste product, then voncerts the peroxide to water. 9. Describe the structure & function of a mitochondrion Mitochondrion is the site of cellular respiration at the catabolic process that generates ATP by ex ...
Immunolocalization of maize transglutaminase and its substrates in
... The increase of TGase with chloroplast differentiation and its specific detection in the thylakoid appressed grana indicated that this enzyme might be related to the LHCII proteins of the antenna complex, which are localized in the same grana structures [12]. The 58 kDa band present in the lightexpo ...
... The increase of TGase with chloroplast differentiation and its specific detection in the thylakoid appressed grana indicated that this enzyme might be related to the LHCII proteins of the antenna complex, which are localized in the same grana structures [12]. The 58 kDa band present in the lightexpo ...
Unit 2
... 1. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells lack nuclei and membrane-enclosed organelles; bacteria are prokaryotes. All other organisms are made up of eukaryotic cells with membraneenclosed nuclei surrounded b cytoplasm, in which are suspended specialized organelles no ...
... 1. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells lack nuclei and membrane-enclosed organelles; bacteria are prokaryotes. All other organisms are made up of eukaryotic cells with membraneenclosed nuclei surrounded b cytoplasm, in which are suspended specialized organelles no ...
3.7 Cell Respiration
... Acetyl coA will combine with a molecule of oxaloacetate to form a 6-carbon molecule Citrate. Citrate will be decarboxylated (loses carbon, forms CO2) and oxidized (loses electrons) twice, releasing 2 CO2 and forming 2 NADH, and a 4-carbon molecule. This molecule will undergo substrate-level phosphor ...
... Acetyl coA will combine with a molecule of oxaloacetate to form a 6-carbon molecule Citrate. Citrate will be decarboxylated (loses carbon, forms CO2) and oxidized (loses electrons) twice, releasing 2 CO2 and forming 2 NADH, and a 4-carbon molecule. This molecule will undergo substrate-level phosphor ...
Appendices 1-5
... 10) ATP synthase, H+ transporting, F1 1 (Atp5a1), is a regulatory subunit in the production of ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. 11) ATP synthase, H+ transporting, F1 1 (Atp5c1), produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane, ...
... 10) ATP synthase, H+ transporting, F1 1 (Atp5a1), is a regulatory subunit in the production of ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. 11) ATP synthase, H+ transporting, F1 1 (Atp5c1), produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane, ...
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... a) The current (flow of electric charges carried by ions) can pass directly from the axon terminal to the second cell if their plasma membranes are connected by gap junctions which allow ions to flow between the cells. This is an electrical synapse; it is rare. b) The action potential can cause the ...
... a) The current (flow of electric charges carried by ions) can pass directly from the axon terminal to the second cell if their plasma membranes are connected by gap junctions which allow ions to flow between the cells. This is an electrical synapse; it is rare. b) The action potential can cause the ...
Chapter 7 - OnMyCalendar
... 1. Describe the structure of the cell membrane. 2. By what methods are substances transported across membranes? Fluid Mosaic Model The membrane is a fluid structure with various proteins embedded in or attached to a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids o Fluid = capable of flowing and easily ch ...
... 1. Describe the structure of the cell membrane. 2. By what methods are substances transported across membranes? Fluid Mosaic Model The membrane is a fluid structure with various proteins embedded in or attached to a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids o Fluid = capable of flowing and easily ch ...
Peptides - Alfred State College
... CHAPTER 3.2 and 3.3 Peptides, Proteins, and Working with Proteins Today’s Objectives: to understand • The structure and properties of peptides • The ionization behavior of and peptides • Various methods to characterize peptides and proteins ...
... CHAPTER 3.2 and 3.3 Peptides, Proteins, and Working with Proteins Today’s Objectives: to understand • The structure and properties of peptides • The ionization behavior of and peptides • Various methods to characterize peptides and proteins ...
Bacterial Physiology Lec-8 Catabolism: Tricarboxylic acid cycle
... Many bacteria have electron transport chains that can operate with exogenous electron acceptors other than O2. The major electron acceptors are nitrate , sulfate and CO2 but metals and a few organic molecules can also be reduced. Some bacteria can use nitrate as the electron acceptor at the end of t ...
... Many bacteria have electron transport chains that can operate with exogenous electron acceptors other than O2. The major electron acceptors are nitrate , sulfate and CO2 but metals and a few organic molecules can also be reduced. Some bacteria can use nitrate as the electron acceptor at the end of t ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... energy hill. • What happens to the energy of the electrons as it falls down the electron transport chain? • The energy is used to pump H+ against their gradient which then come back through ATP synthase to generate ATP ...
... energy hill. • What happens to the energy of the electrons as it falls down the electron transport chain? • The energy is used to pump H+ against their gradient which then come back through ATP synthase to generate ATP ...
Mock Exam 2 BY 123 - Cusic Supplemental Instruction
... 23. What class of enzyme is responsible for moving phosphate groups? a. Kinase b. Isomerase c. Dehydrogenase d. None of the above 24. What class of enzyme is responsible for the movement of electrons? a. Kinase b. Isomerase c. Dehydrogenase d. None of the above 25. What is reduced in the photosynth ...
... 23. What class of enzyme is responsible for moving phosphate groups? a. Kinase b. Isomerase c. Dehydrogenase d. None of the above 24. What class of enzyme is responsible for the movement of electrons? a. Kinase b. Isomerase c. Dehydrogenase d. None of the above 25. What is reduced in the photosynth ...
Comparative Proteomics Kit I: Protein Profiler Module
... • Traditional classification based upon traits: – Morphological – Behavioral ...
... • Traditional classification based upon traits: – Morphological – Behavioral ...
BioH_Cellular Respiration
... Each protein in the chain has a higher attraction for electrons than the one before it, causing electrons to be pulled “down” the chain. The last protein of the chain passes its electrons to oxygen, which also picks up a pair of H+ from the surroundings to form water (oxygen is the “final electron a ...
... Each protein in the chain has a higher attraction for electrons than the one before it, causing electrons to be pulled “down” the chain. The last protein of the chain passes its electrons to oxygen, which also picks up a pair of H+ from the surroundings to form water (oxygen is the “final electron a ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.