Gated Channels
... • APs appear to jump rapidly from node to node Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • APs appear to jump rapidly from node to node Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
embj201593518-sup-0001
... vibratome. Four sections per mouse containing the whole hippocampus were post-fixed in 2% osmium tetroxide (OsO4) for 2 h. They were then rinsed, dehydrated, and embedded in Durcupan (Durcupan, Fluka). Serial semi-thin sections (1 µm) were cut with a diamond knife and stained with 1% Toluidine blue. ...
... vibratome. Four sections per mouse containing the whole hippocampus were post-fixed in 2% osmium tetroxide (OsO4) for 2 h. They were then rinsed, dehydrated, and embedded in Durcupan (Durcupan, Fluka). Serial semi-thin sections (1 µm) were cut with a diamond knife and stained with 1% Toluidine blue. ...
resting membrane potential
... Figure 7.4 Functional classes of neurons. Afferent neurons originate in the periphery with sensory or visceral receptors. The peripheral axons of afferent neurons are part of the peripheral nervous system, but the axon terminals are located in the central nervous system, where they communicate with ...
... Figure 7.4 Functional classes of neurons. Afferent neurons originate in the periphery with sensory or visceral receptors. The peripheral axons of afferent neurons are part of the peripheral nervous system, but the axon terminals are located in the central nervous system, where they communicate with ...
Action potential - Scranton Prep Biology
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
... – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
Nancy A. O`Rourke Nicholas C. Weiler Kristina D
... known about synapse diversity. Mass spectrometry-based proteomic studies typically require the pooling of heterogeneous synaptic populations, and thus do not inform us about differences in the molecular composition of single synapses. Thus far, only a few proteomic studies have analyzed different sy ...
... known about synapse diversity. Mass spectrometry-based proteomic studies typically require the pooling of heterogeneous synaptic populations, and thus do not inform us about differences in the molecular composition of single synapses. Thus far, only a few proteomic studies have analyzed different sy ...
ppt - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
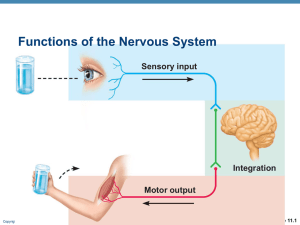
... • Neural communication depends on the anatomical components that connect individual neurons (structure) and the process of transmitting information (function). Both aspects affect the overall performance of the system. ...
... • Neural communication depends on the anatomical components that connect individual neurons (structure) and the process of transmitting information (function). Both aspects affect the overall performance of the system. ...
Lecture 15
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
The tetrapartite synapse_ Extracellular matrix remodeling
... Willcocks and McNally, 2013), and a second from the infralimbic cortex (IL) with terminals in the nucleus accumbens shell (NAshell) that promotes extinction of drug seeking for cocaine or alcohol (Gass et al., 2014; Peters et al., 2008; Stefanik et al., 2013a), but not heroin (Millan et al., 2011; P ...
... Willcocks and McNally, 2013), and a second from the infralimbic cortex (IL) with terminals in the nucleus accumbens shell (NAshell) that promotes extinction of drug seeking for cocaine or alcohol (Gass et al., 2014; Peters et al., 2008; Stefanik et al., 2013a), but not heroin (Millan et al., 2011; P ...
File
... a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus Brain Sensory neuron (incoming information) ...
... a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus Brain Sensory neuron (incoming information) ...
I Can Quit Anytime I Want by William D. Rogers Ball State University
... “Wow! I had no idea. He must feel miserable a lot of the time,” exclaimed Ashley. Sheila responded, “That’s one of the ironies of all this. He uses the drug to feel good, but overall it has the opposite effect. He probably feels lousy if the drug is not in his system!” ...
... “Wow! I had no idea. He must feel miserable a lot of the time,” exclaimed Ashley. Sheila responded, “That’s one of the ironies of all this. He uses the drug to feel good, but overall it has the opposite effect. He probably feels lousy if the drug is not in his system!” ...
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... The nature of the cellular basis of learning and memory remains an oftendiscussed, but elusive problem in neurobiology. A popular model for the physiological mechanisms underlying learning and memory postulates that memories are stored by alterations in the strength of neuronal connections within th ...
... The nature of the cellular basis of learning and memory remains an oftendiscussed, but elusive problem in neurobiology. A popular model for the physiological mechanisms underlying learning and memory postulates that memories are stored by alterations in the strength of neuronal connections within th ...
OTTO LOEWI
... idea that the transmission should be electrical, just like the propagation wave along the axon. It was actually making sense to imagine electrical synapses. Unfortunately there were three important arguments against such simple picture of the nervous system. The first is the unidirectional flow of i ...
... idea that the transmission should be electrical, just like the propagation wave along the axon. It was actually making sense to imagine electrical synapses. Unfortunately there were three important arguments against such simple picture of the nervous system. The first is the unidirectional flow of i ...
Abstract Background Preliminary Data Hypothesis
... active zone of excitatory neurons in the CA3 region. I expect to see a rescue of size, accumulation and docking of vesicles in the active zone of excitatory synapses in IGF2 treated FGF22KO mice and cultures. In the future I will assess the dependence of FGF22 effects on IGF2 ...
... active zone of excitatory neurons in the CA3 region. I expect to see a rescue of size, accumulation and docking of vesicles in the active zone of excitatory synapses in IGF2 treated FGF22KO mice and cultures. In the future I will assess the dependence of FGF22 effects on IGF2 ...
Calcium-activated chloride channels: a new target to
... Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the cellular mechanisms of spike-frequency adaptation via ANO2 channel. The repetitive ...
... Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the cellular mechanisms of spike-frequency adaptation via ANO2 channel. The repetitive ...
Neural Networks
... glia (greek: “glue”) cells in the central nervous tissue of vertebrates. The function of glia is not understood in full detail, but their active role in signal transduction in the brain is probably small. Electrical and chemical synapses allow for excitatory or inhibitory stimulation. They most ofte ...
... glia (greek: “glue”) cells in the central nervous tissue of vertebrates. The function of glia is not understood in full detail, but their active role in signal transduction in the brain is probably small. Electrical and chemical synapses allow for excitatory or inhibitory stimulation. They most ofte ...
The Role of Neurotrophins in Neurotransmitter Release
... Schulz and others 1994), as well as the coefficient of variation of evoked EPSCs, another robust indicator of presynaptic properties, such as neurotransmitter release probability (Pr) and the number of release sites (Lessmann and Heumann 1998; Berninger and others 1999; Schinder and others 2000). Sy ...
... Schulz and others 1994), as well as the coefficient of variation of evoked EPSCs, another robust indicator of presynaptic properties, such as neurotransmitter release probability (Pr) and the number of release sites (Lessmann and Heumann 1998; Berninger and others 1999; Schinder and others 2000). Sy ...
pharm chapter 8 [3-16
... Cellular Organization of the Nervous System Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic ...
... Cellular Organization of the Nervous System Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic ...
membrane potential
... Formation of the Resting Potential K and Na play an essential role in forming the resting potential In most neurons, the concentration of K is highest inside the cell, while the concentration of Na is highest outside the cell Sodium-potassium pumps use the energy of ATP to maintain these ...
... Formation of the Resting Potential K and Na play an essential role in forming the resting potential In most neurons, the concentration of K is highest inside the cell, while the concentration of Na is highest outside the cell Sodium-potassium pumps use the energy of ATP to maintain these ...
Eagleman Ch 9. Memory
... This type of ionotropic glutamate receptor is important for early stages of LTP. This receptor is not active under normal conditions, because the channel is blocked by a magnesium ion. If the cell is repeatedly depolarized, the change in membrane voltage causes the magnesium ion leave the channe ...
... This type of ionotropic glutamate receptor is important for early stages of LTP. This receptor is not active under normal conditions, because the channel is blocked by a magnesium ion. If the cell is repeatedly depolarized, the change in membrane voltage causes the magnesium ion leave the channe ...
The Nervous System - Valhalla High School
... chemical/electrical message. The message travels as an electrical signal, originating in the cell body and sent along the axon. The myelin sheath helps increase the speed the impulse travels. The message reaches the axon terminals which causes a release of chemical neurotransmitters. chemicals are r ...
... chemical/electrical message. The message travels as an electrical signal, originating in the cell body and sent along the axon. The myelin sheath helps increase the speed the impulse travels. The message reaches the axon terminals which causes a release of chemical neurotransmitters. chemicals are r ...
Neurotransmission: “Muscle Messages”
... May be reproduced for non-profit educational use only. Please credit source. ...
... May be reproduced for non-profit educational use only. Please credit source. ...
Biology 231
... Na+/K+ pumps pump Na+ out of neuron (high Na+ concentration outside neuron) K+ positive Na+ balanced by negative Clpump K+ into neuron (high K+ concentration inside neuron) positive K+ balanced by negative protein molecules Neuron has different permeability to ions K+ permeability is 50-100 times gr ...
... Na+/K+ pumps pump Na+ out of neuron (high Na+ concentration outside neuron) K+ positive Na+ balanced by negative Clpump K+ into neuron (high K+ concentration inside neuron) positive K+ balanced by negative protein molecules Neuron has different permeability to ions K+ permeability is 50-100 times gr ...
ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Measuring Action potential
... - if there is no conductive path from two points that have a voltage potential between them (e.g. a potential difference applied to two metal plates in air), charge will accumulate at the two points. - If 1 volt potential between two plates causes an accumulation of 1 coulomb of charge (i.e. 1 coulo ...
... - if there is no conductive path from two points that have a voltage potential between them (e.g. a potential difference applied to two metal plates in air), charge will accumulate at the two points. - If 1 volt potential between two plates causes an accumulation of 1 coulomb of charge (i.e. 1 coulo ...
State-dependent computations - Frankfurt Institute for Advanced
... of neurons A′ will respond to the second (but identical) stimulus — thus providing information about the inter-stimulus interval. It is important to stress that short-term synaptic plasticity is but one of many time-dependent neuronal properties that have the potential to provide a memory of the rec ...
... of neurons A′ will respond to the second (but identical) stimulus — thus providing information about the inter-stimulus interval. It is important to stress that short-term synaptic plasticity is but one of many time-dependent neuronal properties that have the potential to provide a memory of the rec ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.