Principles of Extracellular Single
... widely used. Metal electrodes are most commonly used in microelectrode recordings in humans. The choice of electrode invariably involves several compromises (Table 2–1). A material sufficiently rugged to pass through neural tissues is an obvious requirement. Metal electrodes can generally penetrate ...
... widely used. Metal electrodes are most commonly used in microelectrode recordings in humans. The choice of electrode invariably involves several compromises (Table 2–1). A material sufficiently rugged to pass through neural tissues is an obvious requirement. Metal electrodes can generally penetrate ...
The quantitative single-neuron modeling competition | SpringerLink
... data and model spike trains and α = 1/[1 − 2 ν∆] is a factor that normalizes the coincidence factor Γ to a maximum of 1. Γ = 0 implies that the prediction is not better than chance level. Γ =1 implies that the prediction by the model is optimal. The overall aim is to maximize Γ averaged across all t ...
... data and model spike trains and α = 1/[1 − 2 ν∆] is a factor that normalizes the coincidence factor Γ to a maximum of 1. Γ = 0 implies that the prediction is not better than chance level. Γ =1 implies that the prediction by the model is optimal. The overall aim is to maximize Γ averaged across all t ...
Molecular heterogeneity of central synapses: afferent and target
... regulated by cellular domain (Fig. 1f). Some aspects of synaptic composition are determined by synapse location on the cell, and this in turn can be determined intrinsic features of the neuron. Thus certain domains of axons or dendrites are permissive or instructive for specific classes or features ...
... regulated by cellular domain (Fig. 1f). Some aspects of synaptic composition are determined by synapse location on the cell, and this in turn can be determined intrinsic features of the neuron. Thus certain domains of axons or dendrites are permissive or instructive for specific classes or features ...
Nerve Muscle Physiology
... • Dendrites of cerebral cortex and cerebellar cortex show knobby projections called dendritic spine • May be absent if present may be one or many in number • Conduct impulses towards the cell body • Generate local potential not action potential as well as integrate activity • Has Nissl granules and ...
... • Dendrites of cerebral cortex and cerebellar cortex show knobby projections called dendritic spine • May be absent if present may be one or many in number • Conduct impulses towards the cell body • Generate local potential not action potential as well as integrate activity • Has Nissl granules and ...
Nerve Muscle Physiology
... • Dendrites of cerebral cortex and cerebellar cortex show knobby projections called dendritic spine • May be absent if present may be one or many in number • Conduct impulses towards the cell body • Generate local potential not action potential as well as integrate activity • Has Nissl granules and ...
... • Dendrites of cerebral cortex and cerebellar cortex show knobby projections called dendritic spine • May be absent if present may be one or many in number • Conduct impulses towards the cell body • Generate local potential not action potential as well as integrate activity • Has Nissl granules and ...
Prenatal morphine exposure alters the layer II/III pyramidal neurons
... dendrites growth and the synapse maturation on the dendrites (Leite et al., 2005; Matsuzaki, 2007). Therefore, the changes in the neurons morphology are somewhat indicative of alterations in pyramidal neurons excitability. In our study, morphine exposure was found to have the effect of decreasing to ...
... dendrites growth and the synapse maturation on the dendrites (Leite et al., 2005; Matsuzaki, 2007). Therefore, the changes in the neurons morphology are somewhat indicative of alterations in pyramidal neurons excitability. In our study, morphine exposure was found to have the effect of decreasing to ...
Neurological Control of Movement. Chapter 3.
... that membrane and can cause depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolarization (inhibition), depending on the specific neurotransmitter and the receptors to which ...
... that membrane and can cause depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolarization (inhibition), depending on the specific neurotransmitter and the receptors to which ...
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic
... of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization ...
... of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization ...
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... postsynaptic currents indicated in Fig. 1), the setting of extracellular current and return current will not be instantaneous, and there will be a transient time during which charges will accumulate in the postsynaptic region. During this transient time, Kirchhoff’s current rule does not apply (the ...
... postsynaptic currents indicated in Fig. 1), the setting of extracellular current and return current will not be instantaneous, and there will be a transient time during which charges will accumulate in the postsynaptic region. During this transient time, Kirchhoff’s current rule does not apply (the ...
Synaptic reverberation underlying mnemonic persistent activity
... realistic models of cortical neurons and synapses22–27. Figure 2 illustrates the biophysics of an attractor network. In an object-working-memory model by Amit and Brunel22, subpopulations of neurons are selective to different object stimuli. When the strength of excitatory connections between neuron ...
... realistic models of cortical neurons and synapses22–27. Figure 2 illustrates the biophysics of an attractor network. In an object-working-memory model by Amit and Brunel22, subpopulations of neurons are selective to different object stimuli. When the strength of excitatory connections between neuron ...
nerves
... http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/Michael.Gregory/files/Bio% 20102/Bio%20102%20lectures/nervous%20system/neuron6.gif ...
... http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/Michael.Gregory/files/Bio% 20102/Bio%20102%20lectures/nervous%20system/neuron6.gif ...
Recognition by Variance: Learning Rules for Spatiotemporal Patterns
... start with. Bressloff and Taylor (1992) introduced a two layer model of timesummating neurons, which can be viewed as a discrete-time single neuron model with an exponentially decaying response function for the inputs. This model solves the first problem mentioned above by adding the temporal memor ...
... start with. Bressloff and Taylor (1992) introduced a two layer model of timesummating neurons, which can be viewed as a discrete-time single neuron model with an exponentially decaying response function for the inputs. This model solves the first problem mentioned above by adding the temporal memor ...
Electrophysiology - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... Threshold is 10-15 mV depolarized (ie. –55 to –60 mV) All or none response – Once membrane reaches threshold, amplitude is independent of strength of initiating stimulus – Action potential cannot be summed ...
... Threshold is 10-15 mV depolarized (ie. –55 to –60 mV) All or none response – Once membrane reaches threshold, amplitude is independent of strength of initiating stimulus – Action potential cannot be summed ...
input output - Brian Nils Lundstrom
... Our goal was to consider inputs that fluctuate randomly in time as a model for realistic neuronal inputs, and to discover how the transformation from input to output depends on statistical characteristics of the input. We considered this transformation for the cases in which the stimulus statistics ...
... Our goal was to consider inputs that fluctuate randomly in time as a model for realistic neuronal inputs, and to discover how the transformation from input to output depends on statistical characteristics of the input. We considered this transformation for the cases in which the stimulus statistics ...
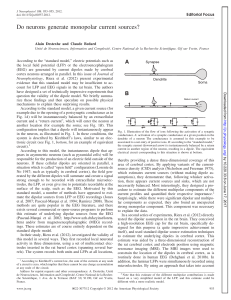
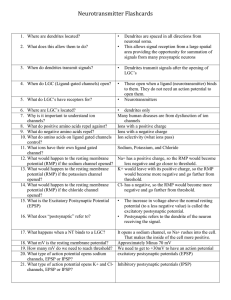
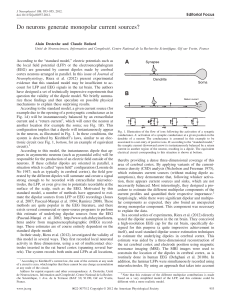
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... 145. When a person is detoxing from alcohol abuse, what medicine is given, what symptom does it prevent, and how does the medicine work (what is its mechanism of action)? 146. What two neurotransmitters are inhibitory? 147. Alcohol stimulates what 2 neurotransmitters? 148. What effect does alcohol h ...
... 145. When a person is detoxing from alcohol abuse, what medicine is given, what symptom does it prevent, and how does the medicine work (what is its mechanism of action)? 146. What two neurotransmitters are inhibitory? 147. Alcohol stimulates what 2 neurotransmitters? 148. What effect does alcohol h ...
Ch. 13 Nervous System Cells Textbook
... capillaries of the brain. Astrocytes have recently been called “stars of the nervous system” because of all of the many important functions they perform. Astrocytes actually “feed” the neurons by picking up glucose from the blood, converting it to lactic acid, and passing it along to the neurons to ...
... capillaries of the brain. Astrocytes have recently been called “stars of the nervous system” because of all of the many important functions they perform. Astrocytes actually “feed” the neurons by picking up glucose from the blood, converting it to lactic acid, and passing it along to the neurons to ...
Chapter 2
... and sodium ions out of the cell, resulting in a net negative charge within the cell and contributing to the membrane potential. Receptors are protein molecules that respond to specific chemical stimuli, typically by causing the opening of associated channels. The most abundant ions in extracellular ...
... and sodium ions out of the cell, resulting in a net negative charge within the cell and contributing to the membrane potential. Receptors are protein molecules that respond to specific chemical stimuli, typically by causing the opening of associated channels. The most abundant ions in extracellular ...
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... postsynaptic currents indicated in Fig. 1), the setting of extracellular current and return current will not be instantaneous, and there will be a transient time during which charges will accumulate in the postsynaptic region. During this transient time, Kirchhoff’s current rule does not apply (the ...
... postsynaptic currents indicated in Fig. 1), the setting of extracellular current and return current will not be instantaneous, and there will be a transient time during which charges will accumulate in the postsynaptic region. During this transient time, Kirchhoff’s current rule does not apply (the ...
Document
... characterize excitatory and inhibitory motor neurons in the human gastric sling and clasp fibers, their location, structure, responses, and how they affect that area of the body and potential complications that may arise there. Often times, there is a discrepancy with the cell signaling that takes p ...
... characterize excitatory and inhibitory motor neurons in the human gastric sling and clasp fibers, their location, structure, responses, and how they affect that area of the body and potential complications that may arise there. Often times, there is a discrepancy with the cell signaling that takes p ...
Which Model to Use for the Liquid State Machine?
... work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational performance for various neuron models. The integrate-and-fire, resonate-and-fire, FitzHugh-Nagumo, Morris-Lecar, both versions of Hindmarsh-Rose and Izikevich’s neural models are examined and assessed. Beata J. Grzyb and Eris ...
... work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational performance for various neuron models. The integrate-and-fire, resonate-and-fire, FitzHugh-Nagumo, Morris-Lecar, both versions of Hindmarsh-Rose and Izikevich’s neural models are examined and assessed. Beata J. Grzyb and Eris ...
Handout 1 - Porterville College Home
... 2. *Dopamine & __________________________ are opposites and work together Course Objective #6: Identify psychiatric disorders that appear to be related to the body’s inability to regulate the availability of neurotransmitters. A. Imbalance ______________________________________ B. ___________ dopa ...
... 2. *Dopamine & __________________________ are opposites and work together Course Objective #6: Identify psychiatric disorders that appear to be related to the body’s inability to regulate the availability of neurotransmitters. A. Imbalance ______________________________________ B. ___________ dopa ...
The Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter
... The nervous system is involved in receiving information about the environment around us (sensation) and generating responses to that information (motor responses). The nervous system can be divided into regions that are responsible for sensation (sensory functions) and for the response (motor functi ...
... The nervous system is involved in receiving information about the environment around us (sensation) and generating responses to that information (motor responses). The nervous system can be divided into regions that are responsible for sensation (sensory functions) and for the response (motor functi ...
Chapter 02 - Neurons and Glia
... to the axon terminals; it is also taken up by axon terminals at the site of injection and transported retrogradely to the cells that project to the injected site.) 2) How is the HRP visualized? (By use of a chemical reaction.) 3) How do the herpes virus or rabies virus use retrograde transport to th ...
... to the axon terminals; it is also taken up by axon terminals at the site of injection and transported retrogradely to the cells that project to the injected site.) 2) How is the HRP visualized? (By use of a chemical reaction.) 3) How do the herpes virus or rabies virus use retrograde transport to th ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.