Section 5.2.notebook
... Examples: 7. A heptagon has exterior angles of 90, 48, 54, 72 and the rest of the angles are congruent. What are the missing angles? ...
... Examples: 7. A heptagon has exterior angles of 90, 48, 54, 72 and the rest of the angles are congruent. What are the missing angles? ...
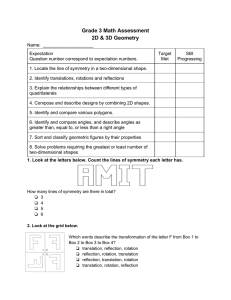
Summative – Geometry Grade 3 Summative for geometry Grade 3.
... Question number correspond to expectation numbers. ...
... Question number correspond to expectation numbers. ...
Trig/Math Anal - cloudfront.net
... 13. Two observers 1600 m apart on a straight road measure the angles of elevation of a helicopter hovering over the road between them. If these angles are 32.0 and 50.5 , how high is the helicopter? ...
... 13. Two observers 1600 m apart on a straight road measure the angles of elevation of a helicopter hovering over the road between them. If these angles are 32.0 and 50.5 , how high is the helicopter? ...
Geometry CP - Chapter 1 Review
... mXYZ and mXYW ? 29. ABC and DEF are supplementary angles. The measure of DEF is twenty degrees less ...
... mXYZ and mXYW ? 29. ABC and DEF are supplementary angles. The measure of DEF is twenty degrees less ...
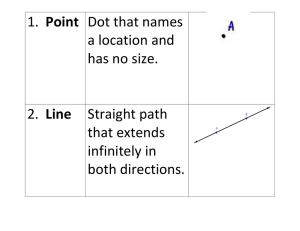
Triangles and Angles
... Triangles • Triangle-figure formed by 3 segments joining 3 noncollinear pts. • Triangles are named by these three pts (ΔQRS) ...
... Triangles • Triangle-figure formed by 3 segments joining 3 noncollinear pts. • Triangles are named by these three pts (ΔQRS) ...
Euler angles
The Euler angles are three angles introduced by Leonhard Euler to describe the orientation of a rigid body. To describe such an orientation in 3-dimensional Euclidean space three parameters are required. They can be given in several ways, Euler angles being one of them; see charts on SO(3) for others. Euler angles are also used to describe the orientation of a frame of reference (typically, a coordinate system or basis) relative to another. They are typically denoted as α, β, γ, or φ, θ, ψ.Euler angles represent a sequence of three elemental rotations, i.e. rotations about the axes of a coordinate system. For instance, a first rotation about z by an angle α, a second rotation about x by an angle β, and a last rotation again about z, by an angle γ. These rotations start from a known standard orientation. In physics, this standard initial orientation is typically represented by a motionless (fixed, global, or world) coordinate system; in linear algebra, by a standard basis.Any orientation can be achieved by composing three elemental rotations. The elemental rotations can either occur about the axes of the fixed coordinate system (extrinsic rotations) or about the axes of a rotating coordinate system, which is initially aligned with the fixed one, and modifies its orientation after each elemental rotation (intrinsic rotations). The rotating coordinate system may be imagined to be rigidly attached to a rigid body. In this case, it is sometimes called a local coordinate system. Without considering the possibility of using two different conventions for the definition of the rotation axes (intrinsic or extrinsic), there exist twelve possible sequences of rotation axes, divided in two groups: Proper Euler angles (z-x-z, x-y-x, y-z-y, z-y-z, x-z-x, y-x-y) Tait–Bryan angles (x-y-z, y-z-x, z-x-y, x-z-y, z-y-x, y-x-z). Tait–Bryan angles are also called Cardan angles; nautical angles; heading, elevation, and bank; or yaw, pitch, and roll. Sometimes, both kinds of sequences are called ""Euler angles"". In that case, the sequences of the first group are called proper or classic Euler angles.