SM-718: Artificial Intelligence and Neural Networks Credits: 4 (2-1-2)
... Introduction to artificial intelligence, History of AI, production system, Problem solving: Characteristics of production systems, Study and comparison of breadth first search and depth first search. Techniques, other Search Techniques like hill Climbing, Best first Search. A* algorithm, AO* algorit ...
... Introduction to artificial intelligence, History of AI, production system, Problem solving: Characteristics of production systems, Study and comparison of breadth first search and depth first search. Techniques, other Search Techniques like hill Climbing, Best first Search. A* algorithm, AO* algorit ...
PDF
... - image understanding (computer vision) B) Reasoning and Planning - modeling the external world - problem solving, planning, and decision making - ability to deal with unexpected problems, uncertainty C) Learning and Adaptation - we are continuously learning and adapting - Also: we want systems that ...
... - image understanding (computer vision) B) Reasoning and Planning - modeling the external world - problem solving, planning, and decision making - ability to deal with unexpected problems, uncertainty C) Learning and Adaptation - we are continuously learning and adapting - Also: we want systems that ...
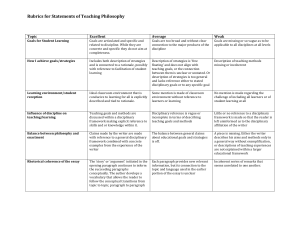
Rubrics for Statements of Teaching Philosophy
... Description of strategies is ‘free floating’ and does not align with teaching goals, or the connection between them is unclear or unstated. Or description of strategies is too general and lacks referenc ...
... Description of strategies is ‘free floating’ and does not align with teaching goals, or the connection between them is unclear or unstated. Or description of strategies is too general and lacks referenc ...
Humanism, when applied to psychology and learning
... as biological reductionism, in which human beings are reduced to only their physical parts. They also differ from psychoanalysis in that they do not believe that humans are controlled by their unconscious. According to the Association for Humanistic Psychology, neither of these psychological movemen ...
... as biological reductionism, in which human beings are reduced to only their physical parts. They also differ from psychoanalysis in that they do not believe that humans are controlled by their unconscious. According to the Association for Humanistic Psychology, neither of these psychological movemen ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... Artificial Intelligence : is a science that has defined its goal as making machines do things that would require intelligence if done by humans. Intelligence : is ability to learn and understand to solve problems and to make decisions. A machine is thought intelligent if it can achieve human level p ...
... Artificial Intelligence : is a science that has defined its goal as making machines do things that would require intelligence if done by humans. Intelligence : is ability to learn and understand to solve problems and to make decisions. A machine is thought intelligent if it can achieve human level p ...
Lecture Notes
... • The true error (errorD(h)) of hypothesis h with respect to target function f and distribution D is the probability that h will misclassify an instance drawn at random according to D – errorD(h)=Prx in D[f(x)≠h(x)] ...
... • The true error (errorD(h)) of hypothesis h with respect to target function f and distribution D is the probability that h will misclassify an instance drawn at random according to D – errorD(h)=Prx in D[f(x)≠h(x)] ...
Scoring Rubric
... The nervous system is a critical system that sends signals throughout the body to coordinate movements and actions. It allows communication throughout your body and contains the brain, spinal cord and a large network of nerves. In total, your nervous system is made of 85 billion nerve cells called n ...
... The nervous system is a critical system that sends signals throughout the body to coordinate movements and actions. It allows communication throughout your body and contains the brain, spinal cord and a large network of nerves. In total, your nervous system is made of 85 billion nerve cells called n ...
Machine Learning: An Overview - SRI Artificial Intelligence Center
... Basic Idea: Use knowledge of what is relevant to infer new properties about a new instance. • form of deductive learning • learns a new general rule that explains observations • does not create knowledge outside logical content of prior knowledge and observations ...
... Basic Idea: Use knowledge of what is relevant to infer new properties about a new instance. • form of deductive learning • learns a new general rule that explains observations • does not create knowledge outside logical content of prior knowledge and observations ...
PhD proposal - Sophia
... The PhD thesis takes place in the context of Pulsar team’s current work on automatic interpretation of videos for the recognition of human behaviors. This topic is relatively new and very active in the scientific community. The PULSAR team has been working for more than 12 years in video understandi ...
... The PhD thesis takes place in the context of Pulsar team’s current work on automatic interpretation of videos for the recognition of human behaviors. This topic is relatively new and very active in the scientific community. The PULSAR team has been working for more than 12 years in video understandi ...
Perception and behavior (vision, robotic, NLP, bionics …) not
... Artificial Intelligence Bo Yuan, Ph.D. Professor Shanghai Jiaotong University ...
... Artificial Intelligence Bo Yuan, Ph.D. Professor Shanghai Jiaotong University ...
Learning how to Learn Learning Algorithms: Recursive Self
... algorithm, adaptive Levin search, and incremental self-improvement. Machine Learning 28:105-130, 1997. (Based on 3.) 7. J. Schmidhuber. Gödel machines: Fully Self-Referential Optimal Universal SelfImprovers. In Artificial General Intelligence, p. 119-226, 2006. (Based on TR of 2003.) 8. T. Schaul ...
... algorithm, adaptive Levin search, and incremental self-improvement. Machine Learning 28:105-130, 1997. (Based on 3.) 7. J. Schmidhuber. Gödel machines: Fully Self-Referential Optimal Universal SelfImprovers. In Artificial General Intelligence, p. 119-226, 2006. (Based on TR of 2003.) 8. T. Schaul ...
Learning how to Learn Learning Algorithms: Recursive Self
... Given f:X→Y and x∈X, search proofs to find program q that provably computes f(z) for all z∈X within time bound tq(z); spend most time on f(x)-computing q with best current bound ...
... Given f:X→Y and x∈X, search proofs to find program q that provably computes f(z) for all z∈X within time bound tq(z); spend most time on f(x)-computing q with best current bound ...
Intelligent Systems in Nanjing University
... combining global and local characteristics, by which a 3D model is first segmented into several meaningful parts, and then representative 3D feature descriptors are extracted from those parts. ...
... combining global and local characteristics, by which a 3D model is first segmented into several meaningful parts, and then representative 3D feature descriptors are extracted from those parts. ...
Knowledge Management Process–Perspective on e
... From a learning administration point of view, learners require experiencing the procedures of information cooperation, trade, sharing, securing, creation, dissemination, scattering, stockpiling and personalization; keeping in mind the end goal of acquire learning. Information administration devices ...
... From a learning administration point of view, learners require experiencing the procedures of information cooperation, trade, sharing, securing, creation, dissemination, scattering, stockpiling and personalization; keeping in mind the end goal of acquire learning. Information administration devices ...
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
... Artificial intelligence (AI) is concerned with the use of computers in tasks that are normally considered to require knowledge, perception, reasoning, learning, understanding and similar cognitive abilities. There are two important ways how to implement intelligence from the computational point of v ...
... Artificial intelligence (AI) is concerned with the use of computers in tasks that are normally considered to require knowledge, perception, reasoning, learning, understanding and similar cognitive abilities. There are two important ways how to implement intelligence from the computational point of v ...
Document
... application of something previously learned to a new problem or in a new context, is difficult at any age. ...
... application of something previously learned to a new problem or in a new context, is difficult at any age. ...
Learning of Compositional Hierarchies By Data-Driven Chunking Karl Pfleger
... discrete, finite alphabet, and where the data is potentially unbounded in both directions, not organized into a set of strings with definite beginnings and ends. Unlike some chunking systems, our chunking is purely data-driven in the sense that only the data, and its underlying statistical regularit ...
... discrete, finite alphabet, and where the data is potentially unbounded in both directions, not organized into a set of strings with definite beginnings and ends. Unlike some chunking systems, our chunking is purely data-driven in the sense that only the data, and its underlying statistical regularit ...
2013-11-18-CS10-L20-..
... • All of these applications are tough because they require: – Knowing about context – Uncertainty about input – Intensive computations ...
... • All of these applications are tough because they require: – Knowing about context – Uncertainty about input – Intensive computations ...
Presentation
... • Bi : state abstraction function which maps state s in the original MDP into an abstract state in Mi • Ai : The set of subtasks that can be called by Mi • Gi : Termination predicate ...
... • Bi : state abstraction function which maps state s in the original MDP into an abstract state in Mi • Ai : The set of subtasks that can be called by Mi • Gi : Termination predicate ...
Improving the Design and Discovery of Dynamic in Sequential Decision-Making
... In recent years, we have investigated algorithmic methods for automatically discovering and optimizing sequential treatments for chronic and life-threatening diseases. In this talk I will discuss two aspects of this work, first the problem of efficiently collecting data to learn good sequential trea ...
... In recent years, we have investigated algorithmic methods for automatically discovering and optimizing sequential treatments for chronic and life-threatening diseases. In this talk I will discuss two aspects of this work, first the problem of efficiently collecting data to learn good sequential trea ...
Die assesseringsproses
... BETWEEN TWO POINTS. • In the first case it indicates the learner’s ability to synthesis previous knowledge into one diagram where as in the second outcome learners should be able to apply their previous knowledge in connecting the two points. When using active verbs identify the context in which the ...
... BETWEEN TWO POINTS. • In the first case it indicates the learner’s ability to synthesis previous knowledge into one diagram where as in the second outcome learners should be able to apply their previous knowledge in connecting the two points. When using active verbs identify the context in which the ...
Socio-environmental Agents
... – Sociological Theory: rich, difficult to unambiguously relate to any specific case – Statistical and experimental: Valid but impossible to extend to future ...
... – Sociological Theory: rich, difficult to unambiguously relate to any specific case – Statistical and experimental: Valid but impossible to extend to future ...
ppt - Computer Science Department
... Machine Learning is… Machine learning is a subfield of computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence. ...
... Machine Learning is… Machine learning is a subfield of computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence. ...