Ch 09 Nervous System
... In the normal communication process, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse, where it can bind to dopamine receptors on neighboring neurons. Normally, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a specialized protein called the dopamine transporter. If cocaine is prese ...
... In the normal communication process, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse, where it can bind to dopamine receptors on neighboring neurons. Normally, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a specialized protein called the dopamine transporter. If cocaine is prese ...
CNS
... • Portions of sensory and motor neurons reside in the gray matter as do interneurons. The posterior root of a spinal nerve enters here and the anterior root (containing motor fibers) exits the gray matter. • Spinal nerves are created by the joining of these two roots (part of PNS). • White matter is ...
... • Portions of sensory and motor neurons reside in the gray matter as do interneurons. The posterior root of a spinal nerve enters here and the anterior root (containing motor fibers) exits the gray matter. • Spinal nerves are created by the joining of these two roots (part of PNS). • White matter is ...
100 - Bloomfield Central School
... The bundle of fibers that connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain, which is sometimes severed to treat patients with seizures and epilepsy, is called… ...
... The bundle of fibers that connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain, which is sometimes severed to treat patients with seizures and epilepsy, is called… ...
Slide 1
... Stem cells are the foundation cells for every organ and tissue in the body. They are like a blank microchip that can ultimately be programmed to perform particular tasks. Under proper conditions, stem cells begin to develop or ‘differentiate’ into specialized cells that carry out a specific function ...
... Stem cells are the foundation cells for every organ and tissue in the body. They are like a blank microchip that can ultimately be programmed to perform particular tasks. Under proper conditions, stem cells begin to develop or ‘differentiate’ into specialized cells that carry out a specific function ...
Neuroscience insights on variations by age v2
... A child’s brain also goes through “critical” periods of construction. The largest part of the construction process of the new brain occurs in the early life of the fetus. During this early stage, the basic structure of the brain is created and the sensory organs form their basic connections along th ...
... A child’s brain also goes through “critical” periods of construction. The largest part of the construction process of the new brain occurs in the early life of the fetus. During this early stage, the basic structure of the brain is created and the sensory organs form their basic connections along th ...
Power Point Used in Lab
... A. High Na outside (3 ions pumped out) B. High K inside (2 ions pumped in) C. Produces a transmembrane potential (-70 mV) ...
... A. High Na outside (3 ions pumped out) B. High K inside (2 ions pumped in) C. Produces a transmembrane potential (-70 mV) ...
International Baccalaureate Biology Option
... Is enlarged principally by an increase in total area with extensive folding allowing it to fit within the cranium (skull). The cerebral hemispheres are responsible for higher order functions. The cerebral cortex is the The left cerebral hemisphere: outer layer of the cerebral ...
... Is enlarged principally by an increase in total area with extensive folding allowing it to fit within the cranium (skull). The cerebral hemispheres are responsible for higher order functions. The cerebral cortex is the The left cerebral hemisphere: outer layer of the cerebral ...
BIOL241NSintro12aJUL2012
... – bundles of axons with connective tissues and blood vessels – carry sensory information and motor commands in PNS: • cranial nerves—connect to brain • spinal nerves—attach to spinal cord ...
... – bundles of axons with connective tissues and blood vessels – carry sensory information and motor commands in PNS: • cranial nerves—connect to brain • spinal nerves—attach to spinal cord ...
The nervous system - Mr T Pities the Fool
... actions of the muscles Controls involuntary actions like blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, and swallowing The main communications link between the brain and the rest of the body ...
... actions of the muscles Controls involuntary actions like blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, and swallowing The main communications link between the brain and the rest of the body ...
Nervous System
... Microglia- protect the nervous system by destroying invasive microorganisms and other materials that could harm the system Astrocytes - maintenance of the nervous system; absorb harmful chemicals in the environment (Ex. Potassium) Ependymal cells- line the central cavities of the brain and spinal co ...
... Microglia- protect the nervous system by destroying invasive microorganisms and other materials that could harm the system Astrocytes - maintenance of the nervous system; absorb harmful chemicals in the environment (Ex. Potassium) Ependymal cells- line the central cavities of the brain and spinal co ...
Lecture 6C
... – Injecting radioactive substance into the bloodstream, which is taken up by active parts of the brain. – Advantages: ability to track changing activity in the brain, fast – Disadvantages: expensive, requires sophisticated staff, must be near a cyclotron, relatively slow ...
... – Injecting radioactive substance into the bloodstream, which is taken up by active parts of the brain. – Advantages: ability to track changing activity in the brain, fast – Disadvantages: expensive, requires sophisticated staff, must be near a cyclotron, relatively slow ...
The Zombie Diaries
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
Myers Module Four
... The autonomic nervous system controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, bloo ...
... The autonomic nervous system controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, bloo ...
17- The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
... stressful situation—running—the runner’s body reacts to stress. So, in effect, running really does change you. In this section, you will learn how your nervous system can produce a runner’s high. HOW THE NERVOUS SYSTEM WORKS The nervous system is never at rest. There is always a job for it to do. Ev ...
... stressful situation—running—the runner’s body reacts to stress. So, in effect, running really does change you. In this section, you will learn how your nervous system can produce a runner’s high. HOW THE NERVOUS SYSTEM WORKS The nervous system is never at rest. There is always a job for it to do. Ev ...
neurons and the nervous system
... neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping ...
... neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... 2. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. 3. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some ways such as: 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell bod ...
... 2. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. 3. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some ways such as: 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell bod ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Hippocampus – forms memories Amygdala – coordinates emotion, autonomic and endocrine systems via hypothalamus. ...
... Hippocampus – forms memories Amygdala – coordinates emotion, autonomic and endocrine systems via hypothalamus. ...
File
... Craniosacral division: the _____________ nervous system, in which nerves originate in the brain stem or sacral region of the spinal cord Dorsal ramus: the division of __________ spinal nerves that transmit motor impulses to the posterior _________ muscles and relay sensory impulses from skin of the ...
... Craniosacral division: the _____________ nervous system, in which nerves originate in the brain stem or sacral region of the spinal cord Dorsal ramus: the division of __________ spinal nerves that transmit motor impulses to the posterior _________ muscles and relay sensory impulses from skin of the ...
The Human Body Systems
... a) Large cell body contains the nucleus and multiple thread-like extensions. (1) Dendrites – thread-like “fingers” that carry electrical impulses toward the cell body (2) Axon - thread-like “fingers” that carry electrical impulses away from the cell body (3) Myelin Sheath – made of Schwann Cells, su ...
... a) Large cell body contains the nucleus and multiple thread-like extensions. (1) Dendrites – thread-like “fingers” that carry electrical impulses toward the cell body (2) Axon - thread-like “fingers” that carry electrical impulses away from the cell body (3) Myelin Sheath – made of Schwann Cells, su ...
Chapter 2
... – Depolarization= unfreezes or ungates the axon allowing the message to go through – Refractory period= resting period, when extra atoms are pushed out – Some signals excite and some inhibit ...
... – Depolarization= unfreezes or ungates the axon allowing the message to go through – Refractory period= resting period, when extra atoms are pushed out – Some signals excite and some inhibit ...
Neuron is the basic working unit of the nervous system, specialized
... ACTION POTENTIAL ‐ An electrical charge that travels along the axon to the neuron’s terminal, where it triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. This occurs when a neuron is activated and temporarily reverses the electrical state of its interior membrane from negative to positive. ACETYLCHOLIN ...
... ACTION POTENTIAL ‐ An electrical charge that travels along the axon to the neuron’s terminal, where it triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. This occurs when a neuron is activated and temporarily reverses the electrical state of its interior membrane from negative to positive. ACETYLCHOLIN ...
Nervous System
... • Disruption in the normal blood supply to the brain; stroke • Thrombotic – blood clot (thrombus) in the arteries leading to the brain • Embolic – an embolus (dislodged thrombus) travels to ...
... • Disruption in the normal blood supply to the brain; stroke • Thrombotic – blood clot (thrombus) in the arteries leading to the brain • Embolic – an embolus (dislodged thrombus) travels to ...
Summary of Chapter 7
... • The cerebrum is the control centre of voluntary movement, sensory interpretation and intelligence. It is also the centre of emotion (p. 208). ...
... • The cerebrum is the control centre of voluntary movement, sensory interpretation and intelligence. It is also the centre of emotion (p. 208). ...
B) Nervous System Introduction NtG Spring
... Surround neuron cell bodies located in the PNS ____________________________ and ________________________ neurons Similar to astrocytes Schwann cells Surround and form ______________________ _____________________ in the PNS Help with regeneration of damaged peripheral nerve fibers Nervous ...
... Surround neuron cell bodies located in the PNS ____________________________ and ________________________ neurons Similar to astrocytes Schwann cells Surround and form ______________________ _____________________ in the PNS Help with regeneration of damaged peripheral nerve fibers Nervous ...
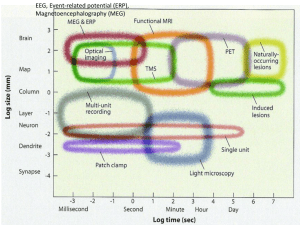
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.