2nd 9 weeks
... The integumentary, skeletal, and muscular systems work together to support, protect, and move body structures as well as maintain homeostasis. The nervous and endocrine systems work in an integrative manner to maintain homeostasis and communicate with all other body systems. Standards ...
... The integumentary, skeletal, and muscular systems work together to support, protect, and move body structures as well as maintain homeostasis. The nervous and endocrine systems work in an integrative manner to maintain homeostasis and communicate with all other body systems. Standards ...
Nervous System
... system sends electrical signals around the body, allowing the body to react to its surroundings quickly. Without the nervous system, we would not be able to function normally. The ability of the nervous system to monitor and respond to the surrounding depends on the transmission of signals from one ...
... system sends electrical signals around the body, allowing the body to react to its surroundings quickly. Without the nervous system, we would not be able to function normally. The ability of the nervous system to monitor and respond to the surrounding depends on the transmission of signals from one ...
Frequently asked questions Psychology 1010.06M A Biologically-Oriented
... • increase speed of neurons ...
... • increase speed of neurons ...
Chapter 5: The First Two Years
... billion neurons, but not enough dendrites and synapses • During the first months and years, major spurts of growth and refinement in axons, dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s br ...
... billion neurons, but not enough dendrites and synapses • During the first months and years, major spurts of growth and refinement in axons, dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s br ...
Nerve
... c) microglia: phagocytotic cells responsible for waste disposal in the CNS B. Spinal Cord (see Ross, plate 44, p300) 1. The spinal cord can be divided into 2 parts: a) white matter (myelinated axons and glial cells; mostly oligodendrocytes) b) gray matter (neuronal cell bodies and dendrites; looks ...
... c) microglia: phagocytotic cells responsible for waste disposal in the CNS B. Spinal Cord (see Ross, plate 44, p300) 1. The spinal cord can be divided into 2 parts: a) white matter (myelinated axons and glial cells; mostly oligodendrocytes) b) gray matter (neuronal cell bodies and dendrites; looks ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... Neurons = nerve cells, the building blocks of our neural information system. Soma or cyton or cell body = cell body of the neuron, the nucleus or brain of the cell Dendrites = bushy fibers that receive neural information Axon = the elongated-tail ending in branchlike axon terminals that transmit inf ...
... Neurons = nerve cells, the building blocks of our neural information system. Soma or cyton or cell body = cell body of the neuron, the nucleus or brain of the cell Dendrites = bushy fibers that receive neural information Axon = the elongated-tail ending in branchlike axon terminals that transmit inf ...
Lecture 7 (Jan 31): BRAIN DEVELOPMENT and EVOLUTION
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
PSYCH-UNIT-2-0 -NOTES-BIO-INTRO
... accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say h ...
... accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say h ...
Slide ()
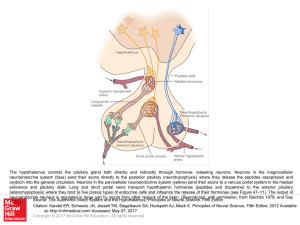
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
Slide ()
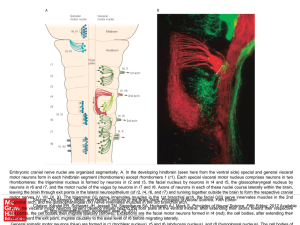
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... 4. What role do artificial neural nets (ANNs) play in understanding how the brain works? (Give some examples). See Section 4.0. A neural net can be considered as a line graph with nodes (connection points) and links. © Elsevier Ltd 2007 ...
... 4. What role do artificial neural nets (ANNs) play in understanding how the brain works? (Give some examples). See Section 4.0. A neural net can be considered as a line graph with nodes (connection points) and links. © Elsevier Ltd 2007 ...
disorders of the nervous system
... defined, because neurological disorders often manifest both organic and mental symptoms. For a discussion of functional mental illness, see Mental Disorders. Diseases of the nervous system include genetic malformations, poisonings, metabolic defects, vascular disorders, inflammations, degeneration, ...
... defined, because neurological disorders often manifest both organic and mental symptoms. For a discussion of functional mental illness, see Mental Disorders. Diseases of the nervous system include genetic malformations, poisonings, metabolic defects, vascular disorders, inflammations, degeneration, ...
Nervous System
... rami communicantes) arise from lateral column of spinal cord, emerge through ventral rami and connected to the ganglia of sympathetic chain. • 3- From the ganglia postganglionic fibres (nonmedullated-grey rami communicantes) run for some distancebefore reaching the organ of supply. ...
... rami communicantes) arise from lateral column of spinal cord, emerge through ventral rami and connected to the ganglia of sympathetic chain. • 3- From the ganglia postganglionic fibres (nonmedullated-grey rami communicantes) run for some distancebefore reaching the organ of supply. ...
The Nervous System - Gordon State College
... The upper segments of the spinal cord control the upper parts of the body, while the lower segments control the lower body. The spinal cord also controls some automatic, involuntary responses to sensory stimuli called reflexes. ...
... The upper segments of the spinal cord control the upper parts of the body, while the lower segments control the lower body. The spinal cord also controls some automatic, involuntary responses to sensory stimuli called reflexes. ...
Nervous System powerpoint new
... - a series of X-ray beams passed through the head. -images are then developed on sensitive film. -creates cross-sectional images of the brain ...
... - a series of X-ray beams passed through the head. -images are then developed on sensitive film. -creates cross-sectional images of the brain ...
Document
... thought, movement, emotion 2. cerebellum allows for balance so body can move smoothly 3. brain stem controls basic life functions Brain stem (breathing, heart beat) ...
... thought, movement, emotion 2. cerebellum allows for balance so body can move smoothly 3. brain stem controls basic life functions Brain stem (breathing, heart beat) ...
chapter 44 lecture slides
... The Central Nervous System • Sponges are only major phylum without nerves • Cnidarians have the simplest nervous system – Neurons linked to each other in a nerve net – No associative activity • Free-living flatworms (phylum Platyhelminthes) are simplest animals with associative activity – Two nerve ...
... The Central Nervous System • Sponges are only major phylum without nerves • Cnidarians have the simplest nervous system – Neurons linked to each other in a nerve net – No associative activity • Free-living flatworms (phylum Platyhelminthes) are simplest animals with associative activity – Two nerve ...
Neuro2
... receive many simultaneous stimuli because of their many dendrites. As one, long continuous fiber pseudounipolar neurons can conduct impulses through the body very rapidly. 5) Vesicles full of fun stuff like adrenaline and acetylcholine (or maybe just peptides) are formed at trans Golgi network. Thes ...
... receive many simultaneous stimuli because of their many dendrites. As one, long continuous fiber pseudounipolar neurons can conduct impulses through the body very rapidly. 5) Vesicles full of fun stuff like adrenaline and acetylcholine (or maybe just peptides) are formed at trans Golgi network. Thes ...
The Anatomy of the Sheep Brain
... Anatomically, the human brain shares many basic structures and brain areas with the brains of other animals. For example, in the sheep brain (see Image below), one observes a cerebrum, a brain stem, cerebellum, medulla oblongata and glands, such as the pineal gland and the pituitary gland. Like the ...
... Anatomically, the human brain shares many basic structures and brain areas with the brains of other animals. For example, in the sheep brain (see Image below), one observes a cerebrum, a brain stem, cerebellum, medulla oblongata and glands, such as the pineal gland and the pituitary gland. Like the ...
Biology of Humans 2/e
... The four main functions of glial cells are to surround neurons and hold them in place, to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons, to insulate one neuron from another, and to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. ...
... The four main functions of glial cells are to surround neurons and hold them in place, to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons, to insulate one neuron from another, and to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. ...
chapter 44 lecture slides
... The Central Nervous System • Sponges are only major phylum without nerves • Cnidarians have the simplest nervous system – Neurons linked to each other in a nerve net – No associative activity • Free-living flatworms (phylum Platyhelminthes) are simplest animals with associative activity – Two nerve ...
... The Central Nervous System • Sponges are only major phylum without nerves • Cnidarians have the simplest nervous system – Neurons linked to each other in a nerve net – No associative activity • Free-living flatworms (phylum Platyhelminthes) are simplest animals with associative activity – Two nerve ...
Tayler
... The brain uses neurotransmitters to tell your heart to beat, your lung to breathe, and your stomach to digest Once the neurotransmitter is picked up by receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, the molecule is internalized in the neuron and the impulse continues. This process of nerve cell communi ...
... The brain uses neurotransmitters to tell your heart to beat, your lung to breathe, and your stomach to digest Once the neurotransmitter is picked up by receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, the molecule is internalized in the neuron and the impulse continues. This process of nerve cell communi ...
Biology and Behavior note frame
... a. The state of a neuron when it is at _______________ and capable of _______________ an action potential b. The neuron is set and _______________ _______________ _______________ 4. All-or-None Principle a. The principle stating that ___________________________________________ ______________________ ...
... a. The state of a neuron when it is at _______________ and capable of _______________ an action potential b. The neuron is set and _______________ _______________ _______________ 4. All-or-None Principle a. The principle stating that ___________________________________________ ______________________ ...
Normal Edema
... Organization of the CNS and disease • Not all cells in the CNS are ‘equal’: while some disease processes affect some groups of cells more than others (‘selective vulnerability’), other disease processes could affect other areas more. • Not all areas in the brain are equal: most areas in the brain h ...
... Organization of the CNS and disease • Not all cells in the CNS are ‘equal’: while some disease processes affect some groups of cells more than others (‘selective vulnerability’), other disease processes could affect other areas more. • Not all areas in the brain are equal: most areas in the brain h ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.