Study Guide - Nervous System
... 28. Blood-Brain-Barrier is formed of capillary cells with tight junctions and other features and does not allow all things in blood to enter brain. Choroid plexus is a network of fine capillaries present in the roof of all 4 ventricles and secrete Cerebrospinal fluid = CSF. CSF supports brain, provi ...
... 28. Blood-Brain-Barrier is formed of capillary cells with tight junctions and other features and does not allow all things in blood to enter brain. Choroid plexus is a network of fine capillaries present in the roof of all 4 ventricles and secrete Cerebrospinal fluid = CSF. CSF supports brain, provi ...
Ch 3 Biological Bases of Behavior
... – Neurotransmitters: the chemical signal that transmits across the synapse – Dendrites: receive messages from other neurons – Glial Cells: Supports neuron structure; cleans up unused neurotransmitters ...
... – Neurotransmitters: the chemical signal that transmits across the synapse – Dendrites: receive messages from other neurons – Glial Cells: Supports neuron structure; cleans up unused neurotransmitters ...
Communication Breakdown KEY
... Patient #6- Susan, a 35 year-old teacher, has been referred to you from a psychologist who works in your building. She was being treated for depression and mild mood swings, but now that she has started having physical symptoms, the psychologist thinks she needs a neurology consult. Obviously nervo ...
... Patient #6- Susan, a 35 year-old teacher, has been referred to you from a psychologist who works in your building. She was being treated for depression and mild mood swings, but now that she has started having physical symptoms, the psychologist thinks she needs a neurology consult. Obviously nervo ...
Slide ()
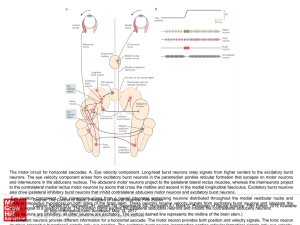
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
Cognitive Psychology
... • Neurons communicate by sending chemical messages called neurotransmitters to other neurons. • These neurotransmitters travel from axon to either the dendrite or the cell body across the ...
... • Neurons communicate by sending chemical messages called neurotransmitters to other neurons. • These neurotransmitters travel from axon to either the dendrite or the cell body across the ...
The Nerve Cells Reading
... Around the cell body are nerve fibers called axons and dendrites. Dendrites are long, thin spidery-looking parts. One nerve cell may have more than 10,000 dendrites. The word dendrite comes from a Greek word meaning "tree." Around the cell body is also a longer, slightly thicker part called an axon. ...
... Around the cell body are nerve fibers called axons and dendrites. Dendrites are long, thin spidery-looking parts. One nerve cell may have more than 10,000 dendrites. The word dendrite comes from a Greek word meaning "tree." Around the cell body is also a longer, slightly thicker part called an axon. ...
Presentation - Ch 2 Sections Demo-6-7
... Adrenal glands consist of the adrenal medulla and the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. ...
... Adrenal glands consist of the adrenal medulla and the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. ...
Unit IV-D Outline
... f. Schwann cells – produce layers of a white, fatty substance called myelin which covers the axon, gaps between neighboring cells are called nodes of Ranvier g. nerve cells of mature animals cannot divide, so cannot be replaced; but if cell body is unhurt, damage axons and dendrites outside the brai ...
... f. Schwann cells – produce layers of a white, fatty substance called myelin which covers the axon, gaps between neighboring cells are called nodes of Ranvier g. nerve cells of mature animals cannot divide, so cannot be replaced; but if cell body is unhurt, damage axons and dendrites outside the brai ...
Chapter 14 - Angelo State University
... • Can get tapeworms from beef as well. Adult tapeworms not too bad. Symptoms absent or mild. • Much more serious to eat embryonated eggs of pork or beef tapeworm. Bladder worms develop in various organs, including the brain. Symptoms similar to tumor, and can get serious reactions t ...
... • Can get tapeworms from beef as well. Adult tapeworms not too bad. Symptoms absent or mild. • Much more serious to eat embryonated eggs of pork or beef tapeworm. Bladder worms develop in various organs, including the brain. Symptoms similar to tumor, and can get serious reactions t ...
Nervous Tissue
... blocking the release of substance P – acupuncture may produce loss of pain sensation because of release of opioids-like substances such as endorphins or dynorphins ...
... blocking the release of substance P – acupuncture may produce loss of pain sensation because of release of opioids-like substances such as endorphins or dynorphins ...
KKDP 3: The role of the neuron (dendrites, axon, myelin and
... KKDP 3: The role of the neuron (dendrites, axon, myelin and axon terminals) as the primary cell involved in the reception and transmission of information across the synapse (excluding details related to signal transduction) ROLE OF THE NEURON ...
... KKDP 3: The role of the neuron (dendrites, axon, myelin and axon terminals) as the primary cell involved in the reception and transmission of information across the synapse (excluding details related to signal transduction) ROLE OF THE NEURON ...
Brain
... • Have ion pumps that allow them to alter ion concentrations of the CSF • Help cleanse CSF by removing wastes ...
... • Have ion pumps that allow them to alter ion concentrations of the CSF • Help cleanse CSF by removing wastes ...
PowerPoint Presentation - An overview of - e
... The forebrain (cerebrum) can be divided into lobes that rest in the corresponding cranial fossa. The frontal lobe lies under the frontal bone in the anterior cranial fossa, the temporal lobe lies under the temporal bone in the middle cranial fossa and the occipital lobe lies under the occipital bon ...
... The forebrain (cerebrum) can be divided into lobes that rest in the corresponding cranial fossa. The frontal lobe lies under the frontal bone in the anterior cranial fossa, the temporal lobe lies under the temporal bone in the middle cranial fossa and the occipital lobe lies under the occipital bon ...
Biology 3201
... Responsible for transferring impulses from receptors to CNS and back to effectors. ...
... Responsible for transferring impulses from receptors to CNS and back to effectors. ...
Nervous System Review ANSWERS File
... 39. In the diagram above, number 5 represents A. Depolarization D. Threshold E. Resting potential B. Repolarization C. Action potential 40. Which statement is NOT true about the development of an action potential? A. There is a rapid change in polarity from about -65mV to about + 40 mV B. It can be ...
... 39. In the diagram above, number 5 represents A. Depolarization D. Threshold E. Resting potential B. Repolarization C. Action potential 40. Which statement is NOT true about the development of an action potential? A. There is a rapid change in polarity from about -65mV to about + 40 mV B. It can be ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... Numbered according to the level of the vertebral column at which they emerge from the spinal cavity Lumbar, Sacral, and Coccygeal nerves descend from their point of origin at the lower end of the spinal cord Lower end of the cord is called the cauda equina, which means “horses tail” in Latin ...
... Numbered according to the level of the vertebral column at which they emerge from the spinal cavity Lumbar, Sacral, and Coccygeal nerves descend from their point of origin at the lower end of the spinal cord Lower end of the cord is called the cauda equina, which means “horses tail” in Latin ...
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
Anat 1: Ch 17 (SS99)
... Sympathetic Division Thoracolumbar division Preganglionic neurons (cell bodies) located between T1 & L2 of spinal cord Ganglionic neurons (cell bodies) in ganglia near ...
... Sympathetic Division Thoracolumbar division Preganglionic neurons (cell bodies) located between T1 & L2 of spinal cord Ganglionic neurons (cell bodies) in ganglia near ...
Anikeeva
... General route for synthesis of monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles that is biocompatible and can attach directly onto the plasma membrane ...
... General route for synthesis of monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles that is biocompatible and can attach directly onto the plasma membrane ...
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide
... Functions-Reflex Centers • Inferior Colliculimovement of head and trunk in response to sound stimuli • Superior Colliculimovement of eyes, head and neck in response to visual stimuli ...
... Functions-Reflex Centers • Inferior Colliculimovement of head and trunk in response to sound stimuli • Superior Colliculimovement of eyes, head and neck in response to visual stimuli ...
Alzheimer Disease - Bellarmine University
... • There are at least 13 other proteins that form these that are associated with diseases that do not in any way resemble AD • They have different core proteins but the structures appears microscopically the same. ...
... • There are at least 13 other proteins that form these that are associated with diseases that do not in any way resemble AD • They have different core proteins but the structures appears microscopically the same. ...
Brain Functions
... Billions of neurons are chained together in a network of nerves. Nerves are a large amounts of neurons linked together in a small place. Your nerves send tiny electronic signals through your body to the brain stem and to the main brain. The neurons inside your brain have three basic parts. Every tin ...
... Billions of neurons are chained together in a network of nerves. Nerves are a large amounts of neurons linked together in a small place. Your nerves send tiny electronic signals through your body to the brain stem and to the main brain. The neurons inside your brain have three basic parts. Every tin ...
Natwest Bank - Brain Mind Forum
... five hundred million form a ‘secondary brain’ in the intestines, and the remaining five hundred million connect up every organ and muscle. Neurons There are many different types of neurons, but they all broadly follow the same pattern. They have a nucleus and a number of tentacles, very roughly like ...
... five hundred million form a ‘secondary brain’ in the intestines, and the remaining five hundred million connect up every organ and muscle. Neurons There are many different types of neurons, but they all broadly follow the same pattern. They have a nucleus and a number of tentacles, very roughly like ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.