Autobiography for 2016 Kavli Prize in Neuroscience Carla J. Shatz
... an easy time for me or for my students. But nowadays, with the advent of powerful in vivo microscopy, mouse genetics, optogenetics and the ability to observe and to make direct manipulations of neural activity, it is heartwarming to see how these early observations made so long ago have not only gai ...
... an easy time for me or for my students. But nowadays, with the advent of powerful in vivo microscopy, mouse genetics, optogenetics and the ability to observe and to make direct manipulations of neural activity, it is heartwarming to see how these early observations made so long ago have not only gai ...
Synaptic transmission
... • Though there are two types( chemical and electrical), but, since almost all the synapses un CNS are chemical synapses, so these are discussed in detail. • In these, the first neuron secretes at its nerve ending synapse a chemical substance called a neurotransmitter (or often called simply transmit ...
... • Though there are two types( chemical and electrical), but, since almost all the synapses un CNS are chemical synapses, so these are discussed in detail. • In these, the first neuron secretes at its nerve ending synapse a chemical substance called a neurotransmitter (or often called simply transmit ...
the Unit 2 study guide in RTF format (which you may re
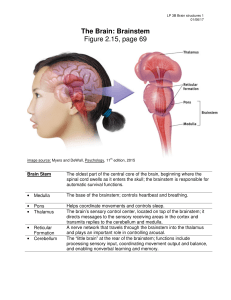
... What are basal ganglia and where are they located? What structures make up the limbic system, and what does the limbic system regulate? What is the function of the thalamus? What functions does the hypothalamus regulate? What does the amygdala do? What does the hippocampus do? What does the cerebell ...
... What are basal ganglia and where are they located? What structures make up the limbic system, and what does the limbic system regulate? What is the function of the thalamus? What functions does the hypothalamus regulate? What does the amygdala do? What does the hippocampus do? What does the cerebell ...
excitatory neurotransmitter
... axon to the axon terminals. At the axon terminals, the message is converted to its chemical form to cross the synapse. The chemical form of a neural message is known as a neurotransmitter. When the neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminals, they cross the synapse to the next neuron in t ...
... axon to the axon terminals. At the axon terminals, the message is converted to its chemical form to cross the synapse. The chemical form of a neural message is known as a neurotransmitter. When the neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminals, they cross the synapse to the next neuron in t ...
Worksheet - Nervous System I Lecture Notes Page
... singular, long __________________(afferent/efferent) processes that originate at the axon hillock of the cell body. Axons may have branches called _________________________, but all axons have numerous branches at their ends called ______________ _____________________________. Changes in organelles ...
... singular, long __________________(afferent/efferent) processes that originate at the axon hillock of the cell body. Axons may have branches called _________________________, but all axons have numerous branches at their ends called ______________ _____________________________. Changes in organelles ...
Welcome to Anatomy and Physiology!
... Binds structures, provides support and protection, fills spaces, stores fat, produces blood cells, and ...
... Binds structures, provides support and protection, fills spaces, stores fat, produces blood cells, and ...
Specialized Cells
... strength, support, and framework to the body by enclosing organs in the skeletal system (bones). Osteoclasts ...
... strength, support, and framework to the body by enclosing organs in the skeletal system (bones). Osteoclasts ...
Another Efferent (outgoing) System Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... • preganglionic neurons are LONG and go all the way out to body organs to reach ganglia. • postganglionic neurons are short, going from those ganglia to nearby organ/gland cells. • All release ACh. • Parasympathetic nerves tend to operate individually, as needed. ...
... • preganglionic neurons are LONG and go all the way out to body organs to reach ganglia. • postganglionic neurons are short, going from those ganglia to nearby organ/gland cells. • All release ACh. • Parasympathetic nerves tend to operate individually, as needed. ...
power point for chap 11
... • Electrically insulating fibers from one another • Increasing speed of nerve impulse transmission ...
... • Electrically insulating fibers from one another • Increasing speed of nerve impulse transmission ...
Neuron File
... between the axon of one neuron and a dendrite or soma of another. Synaptic signals may be excitatory or inhibitory. If the net excitation received by a neuron over a short period of time is large enough, the neuron generates a brief pulse called an action potential, which originates at the soma and ...
... between the axon of one neuron and a dendrite or soma of another. Synaptic signals may be excitatory or inhibitory. If the net excitation received by a neuron over a short period of time is large enough, the neuron generates a brief pulse called an action potential, which originates at the soma and ...
The Nervous System
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
The Nervous System
... function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. The data is then processed by way of integration of data, which occurs only in the brain. After the brain has processed the information, impulses are then conducted from the brain and spinal cord to muscles ...
... function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. The data is then processed by way of integration of data, which occurs only in the brain. After the brain has processed the information, impulses are then conducted from the brain and spinal cord to muscles ...
January 23, set B
... (image source: Schacter, Gilbert and Wegner, (2011), Psychology 2 edition) ...
... (image source: Schacter, Gilbert and Wegner, (2011), Psychology 2 edition) ...
Philosophy and the Brain
... • “I beseech you tell me how the soul of man (since it is but a thinking substance) can determine the spirits of the body to produce voluntary actions” ...
... • “I beseech you tell me how the soul of man (since it is but a thinking substance) can determine the spirits of the body to produce voluntary actions” ...
Nervous and Immune Systems
... 2. Sodium ions (Na+) rush into the axon causing depolarization in the neuron and initiating an action potential 3. Depolarization moves down the axon causing more voltage-gated sodium channels to open 4. Another action potential occurs further down the axon resulting in the transmission of the signa ...
... 2. Sodium ions (Na+) rush into the axon causing depolarization in the neuron and initiating an action potential 3. Depolarization moves down the axon causing more voltage-gated sodium channels to open 4. Another action potential occurs further down the axon resulting in the transmission of the signa ...
Nervous System and Mental Health
... – Receives/interprets nerve impulses from sensory receptors in tongue, skin, and ...
... – Receives/interprets nerve impulses from sensory receptors in tongue, skin, and ...
Neural Control - Del Mar College
... In radially symmetrical animals, excitable neurons interconnect as a nerve net Most animals are bilaterally symmetrical with a nervous system that has a concentration of neurons at the anterior end and one or more nerve cords running the length of the body ...
... In radially symmetrical animals, excitable neurons interconnect as a nerve net Most animals are bilaterally symmetrical with a nervous system that has a concentration of neurons at the anterior end and one or more nerve cords running the length of the body ...
8165 Brain Nervous Sys CE 8x11
... and subsystems, indicate its relation to other systems, and identify what its input and its output are expected to be. ■ Understand that the nervous system works by electrochemical signals in the nerves and from one nerve to the next. The hormonal system exerts its influences by chemicals that circu ...
... and subsystems, indicate its relation to other systems, and identify what its input and its output are expected to be. ■ Understand that the nervous system works by electrochemical signals in the nerves and from one nerve to the next. The hormonal system exerts its influences by chemicals that circu ...
Full Text PDF - Jaypee Journals
... with the closure of the neural tube, primordial endo thelial blood-containing channels are established, from which all other vessels in the brain are derived. In the fifth week, capital venous plexuses, the capital vein and three aortic arches are present. The internal carotid arteries develop earl ...
... with the closure of the neural tube, primordial endo thelial blood-containing channels are established, from which all other vessels in the brain are derived. In the fifth week, capital venous plexuses, the capital vein and three aortic arches are present. The internal carotid arteries develop earl ...
AAAS Summary
... immobile or unconscious, triggers a significant increase in neuroapoptosis in several regions of the developing brain. Extrapolating from Rodents to Humans Evidence documenting that drugs commonly used in obstetric or pediatric medicine can cause extensive apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developi ...
... immobile or unconscious, triggers a significant increase in neuroapoptosis in several regions of the developing brain. Extrapolating from Rodents to Humans Evidence documenting that drugs commonly used in obstetric or pediatric medicine can cause extensive apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developi ...
Animal Physiology, Chapter 10
... – Make adjustments to ensure optimal support for body activities – Operate via subconscious control – Have viscera as most of their effectors ...
... – Make adjustments to ensure optimal support for body activities – Operate via subconscious control – Have viscera as most of their effectors ...
PNS/Reflexes
... A. Structure- Bundles- endo, peri, and epineuria, fascicles B. Regeneration C. Cranial Nerves – Know for Lab Practical 4 (see handout) D. Spinal Nerves- nerves originating from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are mixed (carry both sensory and motor neurons). Remember that as a spinal nerve "approache ...
... A. Structure- Bundles- endo, peri, and epineuria, fascicles B. Regeneration C. Cranial Nerves – Know for Lab Practical 4 (see handout) D. Spinal Nerves- nerves originating from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are mixed (carry both sensory and motor neurons). Remember that as a spinal nerve "approache ...
Dedication - Impress Communications
... muscular, nervous, circulatory, and organ systems. The introductory chapter is followed by chapters on regional anatomy. These include the introduction, upper limb, lower limb, thorax, abdomen, perineum and pelvis, back, and head and neck. Anatomy forms a foundation of clinical medicine and surgery ...
... muscular, nervous, circulatory, and organ systems. The introductory chapter is followed by chapters on regional anatomy. These include the introduction, upper limb, lower limb, thorax, abdomen, perineum and pelvis, back, and head and neck. Anatomy forms a foundation of clinical medicine and surgery ...
Brain Paradox
... Biopsychology • The scientific study of the biology of behavior. • It is a research intensive field. • New findings continually update our current state of knowledge. ...
... Biopsychology • The scientific study of the biology of behavior. • It is a research intensive field. • New findings continually update our current state of knowledge. ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.