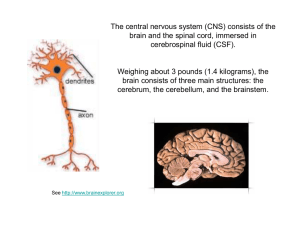
Composition of the Nervous System
... •Neurons are structural and functional unit responsible for transfer of information via electrical (ionic movement) and chemical communication. •Neurons are excitable cells that are capable of transmitting signals along cell membrane by action potentials to other excitable cells (other neurons or mu ...
... •Neurons are structural and functional unit responsible for transfer of information via electrical (ionic movement) and chemical communication. •Neurons are excitable cells that are capable of transmitting signals along cell membrane by action potentials to other excitable cells (other neurons or mu ...
consciousness
... by proposing that the division of labour is determined by the use to which visual information is to be put, once it has reached the striate cortex. They suggest that a ventral stream, terminating in the inferotemporal cortex, is involved in maintaining an enduring, viewpoint-independent, representat ...
... by proposing that the division of labour is determined by the use to which visual information is to be put, once it has reached the striate cortex. They suggest that a ventral stream, terminating in the inferotemporal cortex, is involved in maintaining an enduring, viewpoint-independent, representat ...
The Brain
... system that wraps around the back of the thalamus • Helps processing new memories for permanent storage • Looks something like a seahorse (hippo is Greek for “horse”) ...
... system that wraps around the back of the thalamus • Helps processing new memories for permanent storage • Looks something like a seahorse (hippo is Greek for “horse”) ...
I. Nervous System
... The nervous system can be characterized according to the functional and anatomical principles. According to the functional principle the nervous system (NS) consists of: 1. the somatic nervous system which is responsible for coordinating voluntary body movements (i.e. activities that are under consc ...
... The nervous system can be characterized according to the functional and anatomical principles. According to the functional principle the nervous system (NS) consists of: 1. the somatic nervous system which is responsible for coordinating voluntary body movements (i.e. activities that are under consc ...
Brain Plasticity and Behavior
... studied? Given that neuroscientists have a pretty good idea of what regions of the brain are involved in particular behaviors, they can narrow their search to the likely areas, but are still left with an extraordinarily complex system to examine. There is, however, a procedure that makes the job eas ...
... studied? Given that neuroscientists have a pretty good idea of what regions of the brain are involved in particular behaviors, they can narrow their search to the likely areas, but are still left with an extraordinarily complex system to examine. There is, however, a procedure that makes the job eas ...
Module 3 - Victor Valley College
... • Reflex sequence – sensors • sensors trigger neurons that start the withdrawal effect – afferent neurons • carry information from the senses to the spinal cord ...
... • Reflex sequence – sensors • sensors trigger neurons that start the withdrawal effect – afferent neurons • carry information from the senses to the spinal cord ...
Alterations in Neurons of the Brainstem Due to Administration of
... the treated tissue, with which the mean of each group was generated and these were then compared in ratio of cells against the control tissue. The result presented only reflect the ratio of the control against the 4weeks treated as it showed the most obvious increase though the 8 and 12 weeks groups ...
... the treated tissue, with which the mean of each group was generated and these were then compared in ratio of cells against the control tissue. The result presented only reflect the ratio of the control against the 4weeks treated as it showed the most obvious increase though the 8 and 12 weeks groups ...
multiple choice
... 1) REM sleep is inhibited by A) increased activity of neurons within the locus coeruleus. B) increased activity of peribrachial neurons. C) increased activity of neurons within the raphe nucleus. D) decreased activity of neurons within the thalamus. E) A and C are correct. 2) Although the amygdala i ...
... 1) REM sleep is inhibited by A) increased activity of neurons within the locus coeruleus. B) increased activity of peribrachial neurons. C) increased activity of neurons within the raphe nucleus. D) decreased activity of neurons within the thalamus. E) A and C are correct. 2) Although the amygdala i ...
THE BRAIN & FIVE SENSES
... Just above the Medulla, the brainstem enlarges to form the PONS. PONS mean BRIDGE, and this area of the brain stem contains mostly white matter that provides a link between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum. Above the PONS and continuous with it is the MIDBRAIN, the smallest division of the lo ...
... Just above the Medulla, the brainstem enlarges to form the PONS. PONS mean BRIDGE, and this area of the brain stem contains mostly white matter that provides a link between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum. Above the PONS and continuous with it is the MIDBRAIN, the smallest division of the lo ...
Chapter 2: The Biological Basis of Behavior
... a. both positive and negative ions are concentrated outside the neural membrane b. positive ions are concentrated outside the neural membrane while negative ions are concentrated inside the membrane c. negative ions are concentrated outside the neural membrane while positive ions are concentrated in ...
... a. both positive and negative ions are concentrated outside the neural membrane b. positive ions are concentrated outside the neural membrane while negative ions are concentrated inside the membrane c. negative ions are concentrated outside the neural membrane while positive ions are concentrated in ...
Midterm 1 - studyfruit
... membrane is selectively permeable to that ion alone ■ Goldman equation is a mathematical formula that takes into consideration the relative permeability of the membrane to different ions Most potassium channels have four subunits that are arranged like the staves of a barrel to form a pore ■ Pore lo ...
... membrane is selectively permeable to that ion alone ■ Goldman equation is a mathematical formula that takes into consideration the relative permeability of the membrane to different ions Most potassium channels have four subunits that are arranged like the staves of a barrel to form a pore ■ Pore lo ...
Internal Regulation I
... somatic motor: motivating appropriate behaviors by the somatic motor system ...
... somatic motor: motivating appropriate behaviors by the somatic motor system ...
Psychology
... The visual sensory information (watching the orchestra) would be detected in the retina by photoreceptors and sent to the occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) for processing also. Information would also be processed in the association areas and linked to other parts of the brain to allow Karina to ...
... The visual sensory information (watching the orchestra) would be detected in the retina by photoreceptors and sent to the occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) for processing also. Information would also be processed in the association areas and linked to other parts of the brain to allow Karina to ...
Central Nervous System
... trigger zone – Spatial summation occurs when two or more presynaptic terminals simultaneously stimulate a postsynaptic neuron – Temporal summation occurs when two or more action potentials arrive in succession at a single presynaptic terminal ...
... trigger zone – Spatial summation occurs when two or more presynaptic terminals simultaneously stimulate a postsynaptic neuron – Temporal summation occurs when two or more action potentials arrive in succession at a single presynaptic terminal ...
2015-2016_1Semester_Exam1_050116
... The upper control of somatomotor nuclei located the brainstem is provided by the 2nd order neural / 3rd order neural projection originating from the ventral posterior necleus / somatosensory cortex. Similar regulatory influence reaches neurons in the dorsal horn/fasciculus (n. or tr. Gracilis + cune ...
... The upper control of somatomotor nuclei located the brainstem is provided by the 2nd order neural / 3rd order neural projection originating from the ventral posterior necleus / somatosensory cortex. Similar regulatory influence reaches neurons in the dorsal horn/fasciculus (n. or tr. Gracilis + cune ...
Regulation Notes Activity Page 38: Endocrine/Nerve Cell Coloring
... –Constricts and dilates blood vessels to increase or decrease blood flow ...
... –Constricts and dilates blood vessels to increase or decrease blood flow ...
Review of Neurobiology
... that underlie addiction Roll back the loss of cognitive and motor functions that occur Develop interventions to stop brain damage, repair damage, and retrain the brain Restore brain function after it has been changed by drug use ...
... that underlie addiction Roll back the loss of cognitive and motor functions that occur Develop interventions to stop brain damage, repair damage, and retrain the brain Restore brain function after it has been changed by drug use ...
Chapter 3 The Nervous System and the Brain
... fibers. These fibers supply the cardiac muscles, smooth muscles, and the glands. The glands, smooth muscles and the cardiac muscles make up the Autonomic Nervous System. The Autonomic Nervous System is then made up of two divisions. The first is the Parasympathetic Division, which is important for t ...
... fibers. These fibers supply the cardiac muscles, smooth muscles, and the glands. The glands, smooth muscles and the cardiac muscles make up the Autonomic Nervous System. The Autonomic Nervous System is then made up of two divisions. The first is the Parasympathetic Division, which is important for t ...
O`Kane - LaGuardia Community College
... 16. While walking down the street, you get startled by a passing car that honks its horn right next to you. Your response is to jump away from the noise. What part of the brain was the primary center involved in this reflex motion? A. Medulla oblongata B. Limbic lobe C. Inferior colliculi D. Superi ...
... 16. While walking down the street, you get startled by a passing car that honks its horn right next to you. Your response is to jump away from the noise. What part of the brain was the primary center involved in this reflex motion? A. Medulla oblongata B. Limbic lobe C. Inferior colliculi D. Superi ...
IMAGING TECHNIQUES AT-A
... differentiates the brain’s gray matter (primarily nerve cell bodies) from white matter (primarily axons and their myelin sheaths) which are the nerve cell communication cables that connect brain regions. Many disease processes result in water content changes; these are reflected in the image produc ...
... differentiates the brain’s gray matter (primarily nerve cell bodies) from white matter (primarily axons and their myelin sheaths) which are the nerve cell communication cables that connect brain regions. Many disease processes result in water content changes; these are reflected in the image produc ...
Unit 3B: The Brain Messing with the Brain Scientists can electrically
... Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce images of brain’s soft tissue Reveals blood flow and thereby brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans; shows brain function as well as structure ...
... Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce images of brain’s soft tissue Reveals blood flow and thereby brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans; shows brain function as well as structure ...
Types of Neurons of ANS
... Most sympathetic postganglionic axons Exceptions: sympathetic postganglionic fibers secrete ACh at sweat glands and some blood vessels in skeletal ...
... Most sympathetic postganglionic axons Exceptions: sympathetic postganglionic fibers secrete ACh at sweat glands and some blood vessels in skeletal ...
Document
... • develops from a bipolar neuron in the embryo - axon and dendrite fuse and then branch into 2 branches near the soma - both have the structure of axons (propagate APs) - the axon that projects toward the periphery = dendrites ...
... • develops from a bipolar neuron in the embryo - axon and dendrite fuse and then branch into 2 branches near the soma - both have the structure of axons (propagate APs) - the axon that projects toward the periphery = dendrites ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.