The Nervous System
... Endoneurium surrounds each fiber Groups of fibers are bound into fascicles by perineurium Fascicles are bound together by epineurium Mixed nerves – both sensory and motor fibers Afferent (sensory) nerves – carry impulses toward the CNS Efferent (motor) nerves – carry impulses away from t ...
... Endoneurium surrounds each fiber Groups of fibers are bound into fascicles by perineurium Fascicles are bound together by epineurium Mixed nerves – both sensory and motor fibers Afferent (sensory) nerves – carry impulses toward the CNS Efferent (motor) nerves – carry impulses away from t ...
B) Central Nervous System NTG spring 2010
... • Extends from the foramen magnum (skull) to the first or second vertebra • About 42 cm (17 inches) long and 1.8 cm (3/4 inch) thick • Provides a two way conduction pathway to and from the brain (white matter) • It is a major reflex center (gray matter) • Protected by bone, cerebrospinal fluid and m ...
... • Extends from the foramen magnum (skull) to the first or second vertebra • About 42 cm (17 inches) long and 1.8 cm (3/4 inch) thick • Provides a two way conduction pathway to and from the brain (white matter) • It is a major reflex center (gray matter) • Protected by bone, cerebrospinal fluid and m ...
III. NEURAL COMMUNICATION A. Resting Potential In this section
... Predominately positive (+) ions rush into the cell and negative (-) ions rush out. This results in a voltage spike in the cell to +30 millivolts, called the action potential. The cell then pumps out + ions, causing - to return and the cell returns to its resting potential ...
... Predominately positive (+) ions rush into the cell and negative (-) ions rush out. This results in a voltage spike in the cell to +30 millivolts, called the action potential. The cell then pumps out + ions, causing - to return and the cell returns to its resting potential ...
Brain Imaging Jigsaw Articles
... researchers to define the distributions of a number of them. The images produced by PET scans cannot compete with those produced by fMRI scans in terms of resolution, but often provide spectacular color contrasts (the warmer colors represent the more active areas of the brain). With PET scans, the ...
... researchers to define the distributions of a number of them. The images produced by PET scans cannot compete with those produced by fMRI scans in terms of resolution, but often provide spectacular color contrasts (the warmer colors represent the more active areas of the brain). With PET scans, the ...
The Nervous System - Blackwell Publishing
... neurons. Their interactive nature is precisely what is so special about them. Each neuron’s activity is controlled not just by its own internal condition, but by the myriad inputs it receives from other neurons, from sensory detection apparatuses (for example, those detectors located in the skin), o ...
... neurons. Their interactive nature is precisely what is so special about them. Each neuron’s activity is controlled not just by its own internal condition, but by the myriad inputs it receives from other neurons, from sensory detection apparatuses (for example, those detectors located in the skin), o ...
D. What Causes Multiple Sclerosis?
... confirmed. Women however do not have more severe MS than men. No one has been able to prove conclusively that there significantly more women than men with MS. Although most researchers conclude there are more women than men suffering from autoimmune diseases. The researchers found that symptoms of M ...
... confirmed. Women however do not have more severe MS than men. No one has been able to prove conclusively that there significantly more women than men with MS. Although most researchers conclude there are more women than men suffering from autoimmune diseases. The researchers found that symptoms of M ...
Nervous Systems
... diffuse nerve net (Figure 49.2a), which controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike the nervous systems of other animals, the nerve net of cnidarians lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve ce ...
... diffuse nerve net (Figure 49.2a), which controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike the nervous systems of other animals, the nerve net of cnidarians lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve ce ...
Rhymes, Songs, Stories and Fingerplays in Early Childhood
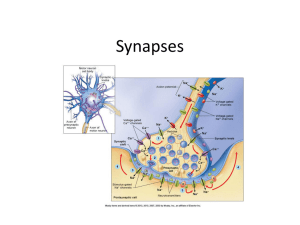
... ending that contains receptor sites for neurotransmitters and, 3. a synaptic cleft or space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic endings. ...
... ending that contains receptor sites for neurotransmitters and, 3. a synaptic cleft or space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic endings. ...
THE ELECTRICAL BRAIN
... were especially prominent in certain interneurons (which communicate only with other neurons) in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. These cells, in turn, inhibit, or help to regulate, higher-level nerve networks that process sensory perception and control muscle movements. Apparently, the interneu ...
... were especially prominent in certain interneurons (which communicate only with other neurons) in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. These cells, in turn, inhibit, or help to regulate, higher-level nerve networks that process sensory perception and control muscle movements. Apparently, the interneu ...
The mind`s mirror
... Automatically, you recoil in sympathy. Or you're watching a race, and you feel your own heart racing with excitement as the runners vie to cross the finish line first. Or you see a woman sniff some unfamiliar food and wrinkle her nose in disgust. Suddenly, your own stomach turns at the thought of th ...
... Automatically, you recoil in sympathy. Or you're watching a race, and you feel your own heart racing with excitement as the runners vie to cross the finish line first. Or you see a woman sniff some unfamiliar food and wrinkle her nose in disgust. Suddenly, your own stomach turns at the thought of th ...
MARIJUANA - ctclearinghouse.org
... actively investigating anandamide’s function in the brain. This research will not only help in gaining a greater understanding of how marijuana acts in the brain and why it is abused, but it will also provide new clues about how the healthy brain works. ...
... actively investigating anandamide’s function in the brain. This research will not only help in gaining a greater understanding of how marijuana acts in the brain and why it is abused, but it will also provide new clues about how the healthy brain works. ...
Na+ - cloudfront.net
... In what order are signals relayed from one neuron to the next? What feature of the NS allows your body to rapidly respond to the environment? What 3 neurons are involved in the process from #7 above? What is an action potential? What is the name of the chemical that is released from synaptic termina ...
... In what order are signals relayed from one neuron to the next? What feature of the NS allows your body to rapidly respond to the environment? What 3 neurons are involved in the process from #7 above? What is an action potential? What is the name of the chemical that is released from synaptic termina ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 2.1 Locomotor behavior in hydra
... FIGURE 2.6 Invertebrate ganglia (G) usually display two neuron classes: motor neurons (m) and interneurons (i), both typically unipolar, with dendrites arising from a single axon. Here neuronal cell bodies are arranged peripherally and synapses occur in a central region called the neuropil. Sensory ...
... FIGURE 2.6 Invertebrate ganglia (G) usually display two neuron classes: motor neurons (m) and interneurons (i), both typically unipolar, with dendrites arising from a single axon. Here neuronal cell bodies are arranged peripherally and synapses occur in a central region called the neuropil. Sensory ...
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
... • Mechanisms in chronically epileptic tissue – Increased synaptic connectivity • mossy fiber sprouting ...
... • Mechanisms in chronically epileptic tissue – Increased synaptic connectivity • mossy fiber sprouting ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... 1 Department of Neurosurgery, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and ; 2 Center for Brain Injury and Repair, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA ; ...
... 1 Department of Neurosurgery, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and ; 2 Center for Brain Injury and Repair, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA ; ...
Alzheimer`s disease: when the mind goes astray
... and ND. Which comes first? And what influence does the one have on the other? Do they progress together? Is there a common denominator? From what molecular process do these two lesions originate? So many questions for one problem alone: the causes of this disease are still well hidden. ...
... and ND. Which comes first? And what influence does the one have on the other? Do they progress together? Is there a common denominator? From what molecular process do these two lesions originate? So many questions for one problem alone: the causes of this disease are still well hidden. ...
autonomic nervous system i
... • involuntary emptying of the bladder, when it occurs, does so in seconds • marked changes in blood pressure (rise or fall) can take place in about 5 secs. A precipitous fall in blood pressure causes fainting. ...
... • involuntary emptying of the bladder, when it occurs, does so in seconds • marked changes in blood pressure (rise or fall) can take place in about 5 secs. A precipitous fall in blood pressure causes fainting. ...
Neuroglia - wsscience
... “Medications for Parkinson's fall into three groups. The first group includes drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain. The second group affects other neurotransmitters in the body in order to ease some of the symptoms of the disease. The third group includes medications that help cont ...
... “Medications for Parkinson's fall into three groups. The first group includes drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain. The second group affects other neurotransmitters in the body in order to ease some of the symptoms of the disease. The third group includes medications that help cont ...
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... • Theory: info is stored in form of increased flow of info at synapses in particular pathways • Certain neurotransmitters and structural changes in synapses may affect short vs. intermediate vs. long term memories • Ex: more synapses and receptors are built when we create long term memories ...
... • Theory: info is stored in form of increased flow of info at synapses in particular pathways • Certain neurotransmitters and structural changes in synapses may affect short vs. intermediate vs. long term memories • Ex: more synapses and receptors are built when we create long term memories ...
Bio70 Psychobiology Fall 2006 First Midterm October 12 Version A
... 23. Which of the following is true of local neurons? a. They exchange information with distant neurons. b. They abide by the all-or-none principle. c. The change in membrane potential increases as it travels. d. They have short dendrites and axons. ...
... 23. Which of the following is true of local neurons? a. They exchange information with distant neurons. b. They abide by the all-or-none principle. c. The change in membrane potential increases as it travels. d. They have short dendrites and axons. ...
File
... Somatic Education (HSE) is and how it works. Since the methods of HSE are all scientifically based and work directly with the brain and nervous system, I will provide an overview of the structures and functions involved. Created by Thomas Hanna, HSE is the use of sensory-motor learning to reawaken ...
... Somatic Education (HSE) is and how it works. Since the methods of HSE are all scientifically based and work directly with the brain and nervous system, I will provide an overview of the structures and functions involved. Created by Thomas Hanna, HSE is the use of sensory-motor learning to reawaken ...
Antonio Damasio SELF COMES TO MIND Constructing the Conscious Brain (2010)
... of visual, auditory and somatic information before this information is forwarded to the EARLY SENSORY CORTICES for vision, hearing and somatic sensation which produce images in the mind ...
... of visual, auditory and somatic information before this information is forwarded to the EARLY SENSORY CORTICES for vision, hearing and somatic sensation which produce images in the mind ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY OF HANNA SOMATIC EDUCATION By
... Somatic Education (HSE) is and how it works. Since the methods of HSE are all scientifically based and work directly with the brain and nervous system, I will provide an overview of the structure ...
... Somatic Education (HSE) is and how it works. Since the methods of HSE are all scientifically based and work directly with the brain and nervous system, I will provide an overview of the structure ...
Chapter-01
... Nerve cells or receptors that are capable of receiving stimuli from within the body and external environment are located in sense organs and in other different organs. Receptors are modified neurons. They are of different types. Rods and cones in the eye, sound receptors in the ear, taste receptors ...
... Nerve cells or receptors that are capable of receiving stimuli from within the body and external environment are located in sense organs and in other different organs. Receptors are modified neurons. They are of different types. Rods and cones in the eye, sound receptors in the ear, taste receptors ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.