Common bile duct: On its way to 2nd part of duodenum. Therefore
... Despite its complexity, the human body is composed of only four basic types tissue. These tissues do not exist as isolated units, but rather in association one with Systematic Anatomy Gross another Regional and in variable proportions and combinations, Anatomy forming different organs and structure ...
... Despite its complexity, the human body is composed of only four basic types tissue. These tissues do not exist as isolated units, but rather in association one with Systematic Anatomy Gross another Regional and in variable proportions and combinations, Anatomy forming different organs and structure ...
An ontology-based search engine for digital
... same concepts across distinct hierarchies within a single dimension. For instance, the hippocampus can be conceptually partitioned into sub-regions (e.g., CA3, CA1) or in layers (e.g., stratum oriens, stratum radiatum) in two parallel hierarchies within the brain region dimension. Defining the equiv ...
... same concepts across distinct hierarchies within a single dimension. For instance, the hippocampus can be conceptually partitioned into sub-regions (e.g., CA3, CA1) or in layers (e.g., stratum oriens, stratum radiatum) in two parallel hierarchies within the brain region dimension. Defining the equiv ...
1 Brain Development, SIDS and Shaken Baby By Rhonda Crabbs
... body size. The skull must be big enough to hold the brain, which is 25% of its adult weight at birth. The neonate’s body, by comparison is typically only 5% of its adult size. When an infant reaches the age of two, the brain is almost 75% of its adult weight and the body is only about 20% of its adu ...
... body size. The skull must be big enough to hold the brain, which is 25% of its adult weight at birth. The neonate’s body, by comparison is typically only 5% of its adult size. When an infant reaches the age of two, the brain is almost 75% of its adult weight and the body is only about 20% of its adu ...
GI Physiology - joshcorwin.com
... The GI tract has its own division of the nervous system. Specialized nervous system located in the wall of the GI tract from the esophagus all the way to the anus. It is composed of two layers of neurons. 1. Myenteric Plexus: the outer layer, lies between the longitudinal and circular layers of musc ...
... The GI tract has its own division of the nervous system. Specialized nervous system located in the wall of the GI tract from the esophagus all the way to the anus. It is composed of two layers of neurons. 1. Myenteric Plexus: the outer layer, lies between the longitudinal and circular layers of musc ...
The triune organism – an abstract
... Part 1: Hypotheses and methods In science and education the world is divided in (more or less) separate fields of research. An organism may e.g. be studied in light of its anatomy, physiology, genetics, molecular biology, ethology, etc. This catalogue of specialized subjects has become very long, an ...
... Part 1: Hypotheses and methods In science and education the world is divided in (more or less) separate fields of research. An organism may e.g. be studied in light of its anatomy, physiology, genetics, molecular biology, ethology, etc. This catalogue of specialized subjects has become very long, an ...
Trigeminal pathways handout
... synapse in spinal nucleus of V. The tract is continuous with the dorsolateral fasciculus (Lissauer’s tract) in the spinal cord, again emphasizing the similarities with the ALS system. 2. The Spinal (descending) nucleus extends caudally as far as C2-C3 and is continuous with the dorsal horn. This mea ...
... synapse in spinal nucleus of V. The tract is continuous with the dorsolateral fasciculus (Lissauer’s tract) in the spinal cord, again emphasizing the similarities with the ALS system. 2. The Spinal (descending) nucleus extends caudally as far as C2-C3 and is continuous with the dorsal horn. This mea ...
Copy of the full paper
... Many of the principles first established from work on small circuits in invertebrates hold for the larger circuits in the vertebrate nervous system, in particular in those regions of the mammalian nervous system where the structure is relatively simple and the repertoire of intrinsic excitability we ...
... Many of the principles first established from work on small circuits in invertebrates hold for the larger circuits in the vertebrate nervous system, in particular in those regions of the mammalian nervous system where the structure is relatively simple and the repertoire of intrinsic excitability we ...
Paper
... chemo-architectonic gradient, or genetically governed trajectory. The comprehensive ensemble over all brain neurons of axonal origin, type, termination, and trajectory relative to other structures, at least from an anatomical perspective, defines what is called ‘‘the connectome.’’ Functional network ...
... chemo-architectonic gradient, or genetically governed trajectory. The comprehensive ensemble over all brain neurons of axonal origin, type, termination, and trajectory relative to other structures, at least from an anatomical perspective, defines what is called ‘‘the connectome.’’ Functional network ...
2605_lect5
... • Cerebral dialysis – measures extracellular concentration of specific chemicals in live animals ...
... • Cerebral dialysis – measures extracellular concentration of specific chemicals in live animals ...
Dynamics of Spontaneous Activity in Neocortical Slices
... neocortical brain slices can sustain spontaneous activity. In the past, slices have been used to study the responses of neurons to electrical or pharmacological stimulations. At the same time, EPSPs and IPSPs are routinely recorded intracellularly from neurons in slices even under conditions in whic ...
... neocortical brain slices can sustain spontaneous activity. In the past, slices have been used to study the responses of neurons to electrical or pharmacological stimulations. At the same time, EPSPs and IPSPs are routinely recorded intracellularly from neurons in slices even under conditions in whic ...
CNS Slide Show
... – plays key role in motor control by relaying signals from cerebellum to cerebrum and providing feedback loops between the cerebral cortex and the basal nuclei – involved in the memory and emotional functions of the limbic system – a complex of structures that include some cerebral cortex of the tem ...
... – plays key role in motor control by relaying signals from cerebellum to cerebrum and providing feedback loops between the cerebral cortex and the basal nuclei – involved in the memory and emotional functions of the limbic system – a complex of structures that include some cerebral cortex of the tem ...
Visual Motion-Detection Circuits in Flies: Small
... and Borkent (1989), Woodly (1989), McAlpine (1989), Sinclair et al. (1993), and Cumming et al. (1995). Camera lucida drawings of insects illustrate the morphological variety of investigated taxa. Common names: tipulids, crane flies; culicids, mosquitoes; simuliids, black flies; tabanids, horseflies; ...
... and Borkent (1989), Woodly (1989), McAlpine (1989), Sinclair et al. (1993), and Cumming et al. (1995). Camera lucida drawings of insects illustrate the morphological variety of investigated taxa. Common names: tipulids, crane flies; culicids, mosquitoes; simuliids, black flies; tabanids, horseflies; ...
Rapid Alterations in Diffusion-weighted Images with Anatomic
... Image analysis was performed for each rat on a single slice immediately anterior to the slice where the hippocampus can be seen curling inferiorly. This position corresponded approximately to bregma 23.60 mm and maximized the cross-sectional area of each ROI (Fig 1) (21). Cheshire image processing s ...
... Image analysis was performed for each rat on a single slice immediately anterior to the slice where the hippocampus can be seen curling inferiorly. This position corresponded approximately to bregma 23.60 mm and maximized the cross-sectional area of each ROI (Fig 1) (21). Cheshire image processing s ...
Hypothesized neural dynamics of working memory
... Informational combinatorics? Subtle volume conductive influences might act in summative or synergistic interactions with other neural information coding processes, perhaps at temporarily sensitized particular locations, which thereby act as receivers of an electrical rhythm “broadcast” across a volu ...
... Informational combinatorics? Subtle volume conductive influences might act in summative or synergistic interactions with other neural information coding processes, perhaps at temporarily sensitized particular locations, which thereby act as receivers of an electrical rhythm “broadcast” across a volu ...
Contemporary Principles of Pathologic Neurotoxicity Assessment in
... Iba1 IHC reveals the most activity beginning ~4-5 days after an insult or exposure, peaking at 5-7 days and persisting for two weeks or more. CD68 also reveals a subset of ...
... Iba1 IHC reveals the most activity beginning ~4-5 days after an insult or exposure, peaking at 5-7 days and persisting for two weeks or more. CD68 also reveals a subset of ...
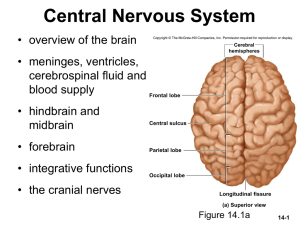
Chapter 14
... head injury or certain degenerative brain diseases; pure form is rare Retrograde amnesia – inability to remember events that occurred prior to brain damage Korsakoff’s syndrome – permanent anterograde amnesia caused by brain damage resulting from chronic alcoholism or malnutrition (due to thiamine d ...
... head injury or certain degenerative brain diseases; pure form is rare Retrograde amnesia – inability to remember events that occurred prior to brain damage Korsakoff’s syndrome – permanent anterograde amnesia caused by brain damage resulting from chronic alcoholism or malnutrition (due to thiamine d ...
NeuroD2 Is Necessary for Development and Survival of Central
... University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2N 4N1 ...
... University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2N 4N1 ...
Anterograde amnesia
... head injury or certain degenerative brain diseases; pure form is rare • Retrograde amnesia – inability to remember events that occurred prior to brain damage • Korsakoff’s syndrome – permanent anterograde amnesia caused by brain damage resulting from chronic alcoholism or malnutrition (due to thiami ...
... head injury or certain degenerative brain diseases; pure form is rare • Retrograde amnesia – inability to remember events that occurred prior to brain damage • Korsakoff’s syndrome – permanent anterograde amnesia caused by brain damage resulting from chronic alcoholism or malnutrition (due to thiami ...
trans - RUF International
... The TRANS theory assumes that there is a primary generator loop which uses the reentry paths between Thalamus and Cortex. This loop cannot easily be detected, but it is shown how it can be detected indirectly from a spectrum of neural activity in secondary neurons connected to the primary generator ...
... The TRANS theory assumes that there is a primary generator loop which uses the reentry paths between Thalamus and Cortex. This loop cannot easily be detected, but it is shown how it can be detected indirectly from a spectrum of neural activity in secondary neurons connected to the primary generator ...
Linear Combinations of Optic Flow Vectors for Estimating Self
... robot scenario. All model neurons have in common that image regions near the rotation or translation axis receive less weight. In these regions, the self-motion components to be estimated generate only small flow vectors which are easily corrupted by noise. Equation (11) predicts that the estimator ...
... robot scenario. All model neurons have in common that image regions near the rotation or translation axis receive less weight. In these regions, the self-motion components to be estimated generate only small flow vectors which are easily corrupted by noise. Equation (11) predicts that the estimator ...
trans - RUF International
... The TRANS theory assumes that there is a primary generator loop which uses the reentry paths between Thalamus and Cortex. This loop cannot easily be detected, but it is shown how it can be detected indirectly from a spectrum of neural activity in secondary neurons connected to the primary generator ...
... The TRANS theory assumes that there is a primary generator loop which uses the reentry paths between Thalamus and Cortex. This loop cannot easily be detected, but it is shown how it can be detected indirectly from a spectrum of neural activity in secondary neurons connected to the primary generator ...
Powerpoint Slides
... • Determine the performance deficits of patients who have lesions (brain damage) to a specific part of the brain • Example: Broca’s aphasia – damage to left frontal cortex speech deficits ...
... • Determine the performance deficits of patients who have lesions (brain damage) to a specific part of the brain • Example: Broca’s aphasia – damage to left frontal cortex speech deficits ...
The caudal part of the frontal cortex is strongly involved - LIRA-Lab
... process described above should mainly occur during development, we postulated that also in adult animals some vestigial residuals of this visuomotor coupling could have resisted in F5 motor neurons (generally considered as devoid of any visual property). To investigate this hypothesis, we programmed ...
... process described above should mainly occur during development, we postulated that also in adult animals some vestigial residuals of this visuomotor coupling could have resisted in F5 motor neurons (generally considered as devoid of any visual property). To investigate this hypothesis, we programmed ...
adult rat spinal cord culture on an organosilane surface in
... 1 mM, MgCl2 2 mM, Na2ATP 5 mM, HEPES 10 mM; pH 5 7.2). Voltage clamp and current clamp experiments were performed with a Multiclamp 700A (Axon, Union City, CA) amplifier. Signals were filtered at 3 kHz and digitized at 20 kHz with an Axon Digidata 1322A interface. Data recording and analysis was per ...
... 1 mM, MgCl2 2 mM, Na2ATP 5 mM, HEPES 10 mM; pH 5 7.2). Voltage clamp and current clamp experiments were performed with a Multiclamp 700A (Axon, Union City, CA) amplifier. Signals were filtered at 3 kHz and digitized at 20 kHz with an Axon Digidata 1322A interface. Data recording and analysis was per ...
Porges and Carter (2010). Neurobiology and
... adversity. However, systems that support sociality, because they are intertwined with restorative physiological states, also may be protective against the costly or destructive effects of chronic fear or stress. Below we expand on the mechanics of these three distinct neural circuits, which are desc ...
... adversity. However, systems that support sociality, because they are intertwined with restorative physiological states, also may be protective against the costly or destructive effects of chronic fear or stress. Below we expand on the mechanics of these three distinct neural circuits, which are desc ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.