The Nervous System
... A single neuron may branch many times a tits end plate (axon terminals) and join (make connections with) many different neurons Small vesicles containing chemicals called neurotransmitters are located in the end plates of axons. When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon it causes the ...
... A single neuron may branch many times a tits end plate (axon terminals) and join (make connections with) many different neurons Small vesicles containing chemicals called neurotransmitters are located in the end plates of axons. When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon it causes the ...
The Special Senses
... Special Senses • Olfaction, gustation, equilibrium, hearing, & vision • Found within complex sense organs • Pass information along the cranial nerves to specific areas of the cerebral cortex. ...
... Special Senses • Olfaction, gustation, equilibrium, hearing, & vision • Found within complex sense organs • Pass information along the cranial nerves to specific areas of the cerebral cortex. ...
The Nervous System
... – typically have a long dendrite and short axon – carry messages from sensory receptors to the CNS. – The cell bodies of the sensory neurons leading to the spinal cord are located in clusters, called ganglia, next to the spinal cord. – The axons usually terminate at interneurons. ...
... – typically have a long dendrite and short axon – carry messages from sensory receptors to the CNS. – The cell bodies of the sensory neurons leading to the spinal cord are located in clusters, called ganglia, next to the spinal cord. – The axons usually terminate at interneurons. ...
IV. PSYCHOBIOLOGY
... carries messages between them. – If severed, demonstrates how both sides work together. ...
... carries messages between them. – If severed, demonstrates how both sides work together. ...
CH 3 Practice Test
... directs the creations of new neurons in response to new learning experiences ...
... directs the creations of new neurons in response to new learning experiences ...
Chapter 3
... Clearly, skeletal muscle needs to track very closely commands to action. For example, try raising your arm in the air suddenly and then immediately lowering it again. The muscles and arm should follow your commands closely. Contraction of the muscle follows the command, which is effected through mot ...
... Clearly, skeletal muscle needs to track very closely commands to action. For example, try raising your arm in the air suddenly and then immediately lowering it again. The muscles and arm should follow your commands closely. Contraction of the muscle follows the command, which is effected through mot ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... 3 Types of neurons • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle ...
... 3 Types of neurons • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle ...
1 MCB3210F NAME EXAM 1A SECTION CELLS, TISSUES
... 25. The potassium equilibrium potential of a cell is -94 mV. What does this mean? A) at the resting membrane potential of neurons, potassium is at equilibrium B) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is zero C) at -94 mV, the electrical force for potassium movement is zero D) at -94 m ...
... 25. The potassium equilibrium potential of a cell is -94 mV. What does this mean? A) at the resting membrane potential of neurons, potassium is at equilibrium B) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is zero C) at -94 mV, the electrical force for potassium movement is zero D) at -94 m ...
Unit XIV: Regulation
... - nerves are bundles of neurons 1 – Sensory Neurons – located in sense organs – receptors carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain 2 – Interneurons – located in the central nervous system interpret impulses 3 – Motor Neurons – located at effectors carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
... - nerves are bundles of neurons 1 – Sensory Neurons – located in sense organs – receptors carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain 2 – Interneurons – located in the central nervous system interpret impulses 3 – Motor Neurons – located at effectors carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
Exam
... 25. The potassium equilibrium potential of a cell is -94 mV. What does this mean? A) at the resting membrane potential of neurons, potassium is at equilibrium B) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is zero C) at -94 mV, the electrical force for potassium movement is zero D) at -94 m ...
... 25. The potassium equilibrium potential of a cell is -94 mV. What does this mean? A) at the resting membrane potential of neurons, potassium is at equilibrium B) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is zero C) at -94 mV, the electrical force for potassium movement is zero D) at -94 m ...
The NERVOUS SYSTEM
... The NS does not work alone in maintaining homeostasis. It enlists the Endocrine system for regulating and maintain body functions. • The Neurons (nervous cells) must perform 4 specialized functions 1. Receive information from the internal or external environment 2. Integrate the information received ...
... The NS does not work alone in maintaining homeostasis. It enlists the Endocrine system for regulating and maintain body functions. • The Neurons (nervous cells) must perform 4 specialized functions 1. Receive information from the internal or external environment 2. Integrate the information received ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... Calcium ions (Ca2+) then diffuse into the terminal, and the rise in Ca2+ concentration in the terminal causes some of the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the terminal membrane, releasing the neurotransmitter by exocytosis. ...
... Calcium ions (Ca2+) then diffuse into the terminal, and the rise in Ca2+ concentration in the terminal causes some of the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the terminal membrane, releasing the neurotransmitter by exocytosis. ...
neuron
... • Neurons usually do not touch each other or other cells • A small gap, called a synaptic cleft, is present between the axon terminal and the receiving cell • Electrical activity in the neuron usually causes the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft ...
... • Neurons usually do not touch each other or other cells • A small gap, called a synaptic cleft, is present between the axon terminal and the receiving cell • Electrical activity in the neuron usually causes the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Nervous system
... 1. the damage of primary motor area of cerebral cortex 2. damage of ventral horn of spinal cord 3. damage of peripheral nerves 4. interruption of corticospinal pathway 5. damage of the muscle 6. disturbances of neuromuscular junction 10. The primary link of the Eaton-Lambert syndrome pathogenesis is ...
... 1. the damage of primary motor area of cerebral cortex 2. damage of ventral horn of spinal cord 3. damage of peripheral nerves 4. interruption of corticospinal pathway 5. damage of the muscle 6. disturbances of neuromuscular junction 10. The primary link of the Eaton-Lambert syndrome pathogenesis is ...
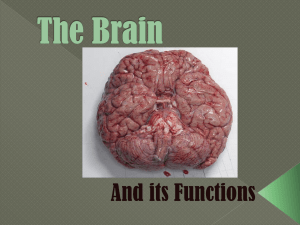
The Brain
... neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active rol ...
... neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active rol ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... Left Hemisphere’s Parietal Lobes: Specializes in locating the source of speech sounds, such as when someone says your name Also works with the temporal lobe to extract meaning from speech and writing ...
... Left Hemisphere’s Parietal Lobes: Specializes in locating the source of speech sounds, such as when someone says your name Also works with the temporal lobe to extract meaning from speech and writing ...
Lectures on mathematical neuroscience
... can encode information - place cells in hippocampus - coincidence detection for sound localization - orientation selectivity in visual cortex ...
... can encode information - place cells in hippocampus - coincidence detection for sound localization - orientation selectivity in visual cortex ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, Signaling - Biology E
... 23. Explain how an action potential is transmitted from one cell to another across a synapse in four steps. ! First, an action potential arrives, depolarizing the presynaptic membrane. Next, the depolarization opens voltage-gated channels, triggering an influx of Ca2+. Third, the elevated Ca2+ conce ...
... 23. Explain how an action potential is transmitted from one cell to another across a synapse in four steps. ! First, an action potential arrives, depolarizing the presynaptic membrane. Next, the depolarization opens voltage-gated channels, triggering an influx of Ca2+. Third, the elevated Ca2+ conce ...
The Nervous System
... ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the falling phase. – K+ channels are slow to open and slow to clo ...
... ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the falling phase. – K+ channels are slow to open and slow to clo ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... 35. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. 36. Indicate the voltage changes associated with EPSPs and IPSPs, and how these potentials are related to various ion channels. 37. Distinguish betwee ...
... 35. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. 36. Indicate the voltage changes associated with EPSPs and IPSPs, and how these potentials are related to various ion channels. 37. Distinguish betwee ...
Chapter 12 - Mesa Community College
... 35. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. 36. Indicate the voltage changes associated with EPSPs and IPSPs, and how these potentials are related to various ion channels. 37. Distinguish betwee ...
... 35. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. 36. Indicate the voltage changes associated with EPSPs and IPSPs, and how these potentials are related to various ion channels. 37. Distinguish betwee ...
Senses
... • These fibers synapse with neurons located in the enlargements of the olfactory bulbs • Within the olfactory bulbs the sensory impulses are analyzed and additional impulses travel along the olfactory tracts to portions of the limbic system ...
... • These fibers synapse with neurons located in the enlargements of the olfactory bulbs • Within the olfactory bulbs the sensory impulses are analyzed and additional impulses travel along the olfactory tracts to portions of the limbic system ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.