File
... 4) The motor nerve transmits the signal to the muscles and makes it react. This reaction can be voluntary or involuntary ...
... 4) The motor nerve transmits the signal to the muscles and makes it react. This reaction can be voluntary or involuntary ...
DOC
... Neurotransmitters Neurons communicate using chemical messengers called NEUROTRANSMITTERS. A neuron sends an electrical signal that triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. Like a lock and key, the chemical attaches to a special receptor on another neuron. The message is sent. Some neurotransmitte ...
... Neurotransmitters Neurons communicate using chemical messengers called NEUROTRANSMITTERS. A neuron sends an electrical signal that triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. Like a lock and key, the chemical attaches to a special receptor on another neuron. The message is sent. Some neurotransmitte ...
word - My eCoach
... hormone that lowers blood sugar level and another that increases blood sugar level. Which statement best describes the feedback mechanism involving the human pancreas? a. The pancreas always produces less glucagon than insulin, regardless of blood glucose levels. b. The level of oxygen in the blood ...
... hormone that lowers blood sugar level and another that increases blood sugar level. Which statement best describes the feedback mechanism involving the human pancreas? a. The pancreas always produces less glucagon than insulin, regardless of blood glucose levels. b. The level of oxygen in the blood ...
File
... Background and Objectives: The consequences of injury in adult central nervous systems (CNS) are often devastating and irreversible. In the cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus), unilateral deafferentation of the auditory neurons of the prothoracic ganglia induces these cells to send dendrites across the mi ...
... Background and Objectives: The consequences of injury in adult central nervous systems (CNS) are often devastating and irreversible. In the cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus), unilateral deafferentation of the auditory neurons of the prothoracic ganglia induces these cells to send dendrites across the mi ...
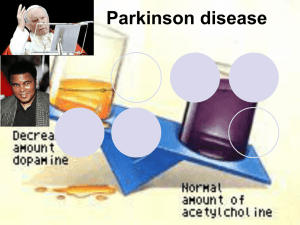
Parkinson disease
... trihexyphenedyl are used. They are less effective than dopaminergic drugs. they are more effective in reducing tremor than the other symptoms. They are useful in treatment of early and advanced parkinson disease, they can reduce parkinsonian symptoms caused by dopamine receptor antagonists eg ...
... trihexyphenedyl are used. They are less effective than dopaminergic drugs. they are more effective in reducing tremor than the other symptoms. They are useful in treatment of early and advanced parkinson disease, they can reduce parkinsonian symptoms caused by dopamine receptor antagonists eg ...
The BRAIN - davis.k12.ut.us
... Integrating Center - a region within the CNS (spinal cord or brain) that interprets the information from the sensory neuron and initiates an appropriate response Motor Neurons - the neurons arising from the integrating center that relay a nerve impulse to the part of the body that will respond to th ...
... Integrating Center - a region within the CNS (spinal cord or brain) that interprets the information from the sensory neuron and initiates an appropriate response Motor Neurons - the neurons arising from the integrating center that relay a nerve impulse to the part of the body that will respond to th ...
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic
... • Dendrites “sum-up” synaptic potentials, determining whether there will be an action potential in the axon • Shape and size of the dendritic arbor determines • Number of synapses • position of synapses with respect to the soma • May also affect the probability of being “found” by an axon durin ...
... • Dendrites “sum-up” synaptic potentials, determining whether there will be an action potential in the axon • Shape and size of the dendritic arbor determines • Number of synapses • position of synapses with respect to the soma • May also affect the probability of being “found” by an axon durin ...
Maximizing Instructional Time
... • The palm of your hand represents the cell body of your neuron. • Your arm represents the axon of your neuron. • Dendrites do not talk to other dendrites. • Dendrites talk to axons but they do not touch since the message has to cross an area called the synapse. • There is a substance that forms on ...
... • The palm of your hand represents the cell body of your neuron. • Your arm represents the axon of your neuron. • Dendrites do not talk to other dendrites. • Dendrites talk to axons but they do not touch since the message has to cross an area called the synapse. • There is a substance that forms on ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – PARASYMPATHETIC
... • Stimulates digestive glands • Increases motility of smooth muscle of digestive tract • Decreases heart rate ...
... • Stimulates digestive glands • Increases motility of smooth muscle of digestive tract • Decreases heart rate ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – PARASYMPATHETIC
... • Stimulates digestive glands • Increases motility of smooth muscle of digestive tract • Decreases heart rate • Causes bronchial constriction Sacral outflow (S2-4): form pelvic splanchnic nerves ...
... • Stimulates digestive glands • Increases motility of smooth muscle of digestive tract • Decreases heart rate • Causes bronchial constriction Sacral outflow (S2-4): form pelvic splanchnic nerves ...
taste smell touch
... bipolar neurons with olfactory branched cilia Olfactory receptors are surrounded by supporting cells Basal cells are on basal membrane ...
... bipolar neurons with olfactory branched cilia Olfactory receptors are surrounded by supporting cells Basal cells are on basal membrane ...
Receptive Fields
... differences are in the field parameters, which are overlapping by default, and the existence of inhibitory synapses between the three neurons. These synapses are part of a system known as lateral inhibition, in which neighboring receptive fields can often turn each other off in order to increase con ...
... differences are in the field parameters, which are overlapping by default, and the existence of inhibitory synapses between the three neurons. These synapses are part of a system known as lateral inhibition, in which neighboring receptive fields can often turn each other off in order to increase con ...
Print this Page Presentation Abstract Program#/Poster#: 532.07/GG10
... Presentation Title: How SOM+ and PV+ inhibitory neurons could differentially modulate surround suppression of cortical neurons Location: ...
... Presentation Title: How SOM+ and PV+ inhibitory neurons could differentially modulate surround suppression of cortical neurons Location: ...
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor B-2837-3_2
... binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis and survival. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces autophosphorylation of MET on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream sign ...
... binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis and survival. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces autophosphorylation of MET on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream sign ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological System
... A rapid exchange of sodium and potassium ions takes place when there is an impulse. The impulse moves across these ions in a millisecond along a nervous pathway. At the synapse, neurotransmitters act chemically to transfer an impulse from the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of another. As chemic ...
... A rapid exchange of sodium and potassium ions takes place when there is an impulse. The impulse moves across these ions in a millisecond along a nervous pathway. At the synapse, neurotransmitters act chemically to transfer an impulse from the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of another. As chemic ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Axodendritic synapses – representative type Synaptic vesicles on presynaptic side ...
... Axodendritic synapses – representative type Synaptic vesicles on presynaptic side ...
begin
... Motor or efferent: Action potentials away from CNS Interneurons or association neurons (CNS) Principle neurons / projection neurons (CNS) ...
... Motor or efferent: Action potentials away from CNS Interneurons or association neurons (CNS) Principle neurons / projection neurons (CNS) ...
Slide 1
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
November 1 CNS INTRO
... 2. Dorsal Root Ganglion neurons are derived from: A. The Caudal portion of the neural tube B. The Rostral portion of the neural tube C. Neural Crest Cells D. Somites 3. Neurulation refers specifically to: A. Neural Tube Defects B. The process of neural tube closure C. The differentiation of the neur ...
... 2. Dorsal Root Ganglion neurons are derived from: A. The Caudal portion of the neural tube B. The Rostral portion of the neural tube C. Neural Crest Cells D. Somites 3. Neurulation refers specifically to: A. Neural Tube Defects B. The process of neural tube closure C. The differentiation of the neur ...
PASSIVE TRANSPORT
... Depending on the type of energy used by carriers we can distinguish: Primary active transport use of chemical energy and cleavage of ATP to ADP Secondary active transport use of alternative energies, eg. electrochemical gradient for an ion Active transport is the main mode of exchange through th ...
... Depending on the type of energy used by carriers we can distinguish: Primary active transport use of chemical energy and cleavage of ATP to ADP Secondary active transport use of alternative energies, eg. electrochemical gradient for an ion Active transport is the main mode of exchange through th ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_8_lecture_part_1
... Requires actual structural change - Activation of genes, synthesis of mRNA, production of proteins, and formation of new synapses Long-term memory can be classified into: a) Nondeclarative (implicit): memory of simple skills, how to do things b) Declarative (explicit): memory of things that ...
... Requires actual structural change - Activation of genes, synthesis of mRNA, production of proteins, and formation of new synapses Long-term memory can be classified into: a) Nondeclarative (implicit): memory of simple skills, how to do things b) Declarative (explicit): memory of things that ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.