What is the Universe made of?
... matter is made up of combinations of 6 quarks, 6 leptons and their antiparticles. Particles such as the electron and neutrino are known as leptons. Particles such as the proton and neutron are made of three quarks, and are called baryons. Scientists often refer to ordinary matter as baryonic matter. ...
... matter is made up of combinations of 6 quarks, 6 leptons and their antiparticles. Particles such as the electron and neutrino are known as leptons. Particles such as the proton and neutron are made of three quarks, and are called baryons. Scientists often refer to ordinary matter as baryonic matter. ...
Gravity - PhysicsAPB
... Find the gravitational attraction between an electron and a proton in a hydrogen atom ( r = 10-6 m ). ...
... Find the gravitational attraction between an electron and a proton in a hydrogen atom ( r = 10-6 m ). ...
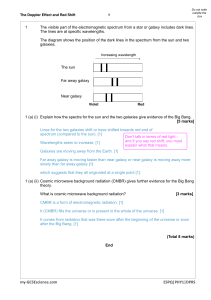
Red Shift Worksheet
... these objects moves through space toward an observer, the waves of electromagnetic radiation between the object and the observer move closer together. That is, the distance between the crests of the waves decreases, causing the wavelength to shorten. If that same object moved away from an observer, ...
... these objects moves through space toward an observer, the waves of electromagnetic radiation between the object and the observer move closer together. That is, the distance between the crests of the waves decreases, causing the wavelength to shorten. If that same object moved away from an observer, ...
Professor Emeritus, University of Canterbury Yevgeny Lifshitz
... • Einstein’ theory predicted that light passing close to a massive body would curve towards it. This amounts to 1.75” close to the sun. The only time that photographs can be taken successfully near the sun is during a solar eclipse so the observations had to wait for a suitable moment. This did not ...
... • Einstein’ theory predicted that light passing close to a massive body would curve towards it. This amounts to 1.75” close to the sun. The only time that photographs can be taken successfully near the sun is during a solar eclipse so the observations had to wait for a suitable moment. This did not ...
Astro twopages
... 1) All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus. 2) The line that joins a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas of their orbit in equal times. (Closer to the Sun you move more quickly -- angular momentum conservation; m r v ) 3) For objects of planet size or smaller orbiting t ...
... 1) All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus. 2) The line that joins a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas of their orbit in equal times. (Closer to the Sun you move more quickly -- angular momentum conservation; m r v ) 3) For objects of planet size or smaller orbiting t ...
Document
... sky objects such as remote galaxies, nebulae and star clusters. • Reasonably good for lunar and planetary work. • Low in optical aberrations. ...
... sky objects such as remote galaxies, nebulae and star clusters. • Reasonably good for lunar and planetary work. • Low in optical aberrations. ...
Lecture06d
... Newton’s Laws. In particular, Kepler’s 3rd Law follows directly from the Universal Law Gravitation: Equating the gravitational force with the centripetal force shows that, for any two planets (assuming circular orbits, and that the only gravitational influence is the Sun): ...
... Newton’s Laws. In particular, Kepler’s 3rd Law follows directly from the Universal Law Gravitation: Equating the gravitational force with the centripetal force shows that, for any two planets (assuming circular orbits, and that the only gravitational influence is the Sun): ...
Powerpoint file
... Fig. 1.—Top: Data and best-fit model for OGLE-2005-BLG-169. Bottom: Difference between this model and a single-lens model with the same (t0, u0, tE, ρ). It displays the classical form of a caustic entrance/exit that is often seen in binary microlensing events, where the amplitudes and timescales are ...
... Fig. 1.—Top: Data and best-fit model for OGLE-2005-BLG-169. Bottom: Difference between this model and a single-lens model with the same (t0, u0, tE, ρ). It displays the classical form of a caustic entrance/exit that is often seen in binary microlensing events, where the amplitudes and timescales are ...
dm - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... gravitating object. This one of the central results of Einstein's theory of gravitation. A distant bright star may be hidden behind a massive object, but it may become visible because its light can bend ...
... gravitating object. This one of the central results of Einstein's theory of gravitation. A distant bright star may be hidden behind a massive object, but it may become visible because its light can bend ...
Black Holes
... – Earth = 1 cm or a grape – Jupiter = 3 cm or 3 grapes (I’m not creative) – Sun = 3 km ...
... – Earth = 1 cm or a grape – Jupiter = 3 cm or 3 grapes (I’m not creative) – Sun = 3 km ...
Gravitational Waves – detectors, sources & science
... • “Action at a distance”. • Newton’s Law describes effect of gravity but does not explain it. ...
... • “Action at a distance”. • Newton’s Law describes effect of gravity but does not explain it. ...
Black Holes - Physics and Astronomy
... 1) Imagine you are far from any source of gravity, in free space, weightless. If you shine a light or throw a ball, it will move in a straight line. ...
... 1) Imagine you are far from any source of gravity, in free space, weightless. If you shine a light or throw a ball, it will move in a straight line. ...
Black Holes: The Ultimate Abyss from discovery channel
... 7. To zoom from one galaxy to another faster than the speed of light, some astrophysicists have proposed that we need to _____. A) squeeze the time dimension of space-time B) make worm holes that connect black holes C) build a spaceship that can travel faster than light D) find the entry and exit po ...
... 7. To zoom from one galaxy to another faster than the speed of light, some astrophysicists have proposed that we need to _____. A) squeeze the time dimension of space-time B) make worm holes that connect black holes C) build a spaceship that can travel faster than light D) find the entry and exit po ...
A physics student places an object 6.0 cm from a
... The indices of refraction for these three substances are n1, n2, and n3, respectively. Ray segments in 1 and in 3 are parallel. From the directions of the ray, one can conclude that ...
... The indices of refraction for these three substances are n1, n2, and n3, respectively. Ray segments in 1 and in 3 are parallel. From the directions of the ray, one can conclude that ...