PowerPoint slides
... • Brain is physical system • Psychological systems (neuronal, cognitive, behavioural) adaptively selected for problems faced by our ancestors in Environment of Evolutionary Adaptiveness • Selective pressures have produced cognitive ...
... • Brain is physical system • Psychological systems (neuronal, cognitive, behavioural) adaptively selected for problems faced by our ancestors in Environment of Evolutionary Adaptiveness • Selective pressures have produced cognitive ...
Information Processing: Computer Simulation Theory
... From its beginning in the 1880’s, psychology in the United States was mostly functional and behavioral. Whereas German psychology was largely structural, with emphasis on the mental content of experiences (sensations, for example), functionalism was concerned less with the structure of the mind than ...
... From its beginning in the 1880’s, psychology in the United States was mostly functional and behavioral. Whereas German psychology was largely structural, with emphasis on the mental content of experiences (sensations, for example), functionalism was concerned less with the structure of the mind than ...
Syllabus: Advanced Topics in Biology: Population Genetics and
... Makeup days :TBA Students must have chosen the subjects for their presentations NOTE: 9/29– Mid-term Exam Genomes Basic concepts Population Genomics ...
... Makeup days :TBA Students must have chosen the subjects for their presentations NOTE: 9/29– Mid-term Exam Genomes Basic concepts Population Genomics ...
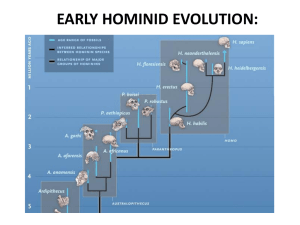
Discovery of Early Humans in Africa
... Species by Means of Natural Selection. The better adapted to survival an organism was, the greater chance it had of surviving and passing that trait on to offspring. Known as natural selection or survival of the fittest. ...
... Species by Means of Natural Selection. The better adapted to survival an organism was, the greater chance it had of surviving and passing that trait on to offspring. Known as natural selection or survival of the fittest. ...
Unit I- Psychological Approaches
... and what research methods are appropriate for undertaking this study. There may be several different theories within an approach, but they all share these common assumptions. ...
... and what research methods are appropriate for undertaking this study. There may be several different theories within an approach, but they all share these common assumptions. ...
Ancient DNA and Human Evolution
... outlines of this hypothesis remain remarkably unaltered, but many details of our African origin continue to be elusive. After decades of advances in human genetics, we are no longer data limited - either in terms of DNA samples or genomic loci, but there is little consensus on many key issues. These ...
... outlines of this hypothesis remain remarkably unaltered, but many details of our African origin continue to be elusive. After decades of advances in human genetics, we are no longer data limited - either in terms of DNA samples or genomic loci, but there is little consensus on many key issues. These ...
Natural Selection
... – No two individuals are exactly alike (with few exceptions) – The molecular instructions for life are the same ...
... – No two individuals are exactly alike (with few exceptions) – The molecular instructions for life are the same ...
Theorists - TeacherWeb
... Power can arise from religion, education, politics and family structure as easily as money; Believes society can be reformed & improved; He favours creation of bureaucracies to provide essential social services making revolution ...
... Power can arise from religion, education, politics and family structure as easily as money; Believes society can be reformed & improved; He favours creation of bureaucracies to provide essential social services making revolution ...
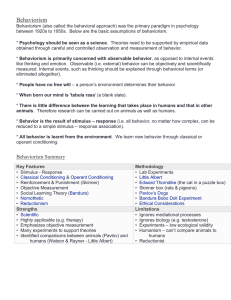
Overview of the Behaviorist Approach
... we actively choose how to behave. Reductionist means that the approach takes complex behaviors and tries to explain them in simplistic ways (e.g. S-R). • (-) Based on work with non-human animals. The approach has been criticized for making generalizations about human beings based on experiments on n ...
... we actively choose how to behave. Reductionist means that the approach takes complex behaviors and tries to explain them in simplistic ways (e.g. S-R). • (-) Based on work with non-human animals. The approach has been criticized for making generalizations about human beings based on experiments on n ...
EPSY 6325 THEORIES OF COUNSELING
... Systematic desensitization (define-example) Learning and behavior change S--->R = B; Operant conditioning Reinforcement (positive & negative), Extinction, Punishment Behavior therapy Goal and characteristics: overt behavior, short, specific goals, active therapist Techniques Systematic desensitizati ...
... Systematic desensitization (define-example) Learning and behavior change S--->R = B; Operant conditioning Reinforcement (positive & negative), Extinction, Punishment Behavior therapy Goal and characteristics: overt behavior, short, specific goals, active therapist Techniques Systematic desensitizati ...
Anthropology and Human Evolution
... Appeared as recently as 120,000 years ago. Neanderthals are the first modern humans. They lived throughout Europe and the Near East. ...
... Appeared as recently as 120,000 years ago. Neanderthals are the first modern humans. They lived throughout Europe and the Near East. ...
Behavioral modernity

Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current Homo sapiens from anatomically modern humans, hominins, and other primates. Although often debated, most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterized by abstract thinking, planning depth, symbolic behavior (e.g. art, ornamentation, music), exploitation of large game, blade technology, among others. Underlying these behaviors and technological innovations are cognitive and cultural foundations that have been documented experimentally and ethnographically. Some of these human universal patterns are cumulative cultural adaptation, social norms, language, cooperative breeding, and extensive help and cooperation beyond close kin. These traits have been viewed as largely responsible for the human replacement of Neanderthals in Western Europe, along with the climatic conditions of the Last Glacial Maximum, and the peopling of the rest of the world.Arising from differences in the archaeological record, a debate continues as to whether anatomically modern humans were behaviorally modern as well. There are many theories on the evolution of behavioral modernity. These generally fall into two camps: gradualist and cognitive approaches. The Later Upper Paleolithic Model refers to the idea that modern human behavior arose through cognitive, genetic changes abruptly around 40–50,000 years ago. Other models focus on how modern human behavior may have arisen through gradual steps; the archaeological signatures of such behavior only appearing through demographic or subsistence-based changes.