Nerve Cell Communication - URMC
... outside of the neuron is positively charged. When the neuron is stimulated, an electrical change causes the outside of the neuron to become negatively charged. This electrical change is an impulse that travels very rapidly along the length of the neuron. Impulses = Action Potential = Electrical ...
... outside of the neuron is positively charged. When the neuron is stimulated, an electrical change causes the outside of the neuron to become negatively charged. This electrical change is an impulse that travels very rapidly along the length of the neuron. Impulses = Action Potential = Electrical ...
Full text - Ip Lab - Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
... Properties of ephrin/Eph underlying their role in synaptogenesis Introduction Neurons communicate with each other via chemical neurotransmission at synapses, morphologically and functionally specialized structures where synaptic vesicles are concentrated at the active zone of the pre-synaptic axon t ...
... Properties of ephrin/Eph underlying their role in synaptogenesis Introduction Neurons communicate with each other via chemical neurotransmission at synapses, morphologically and functionally specialized structures where synaptic vesicles are concentrated at the active zone of the pre-synaptic axon t ...
hydroxytryptamine-containing neurons in the snail Effect of
... Road, Cambridge CB2 2QD, U.K.) There is evidence for trans-synaptic regulation of enzyme synthesis in the adrenergic neurons of the superior cervical ganglion. In the superior cervical ganglia of the adult rat the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase responds to stress and various drug treatments by an incre ...
... Road, Cambridge CB2 2QD, U.K.) There is evidence for trans-synaptic regulation of enzyme synthesis in the adrenergic neurons of the superior cervical ganglion. In the superior cervical ganglia of the adult rat the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase responds to stress and various drug treatments by an incre ...
Neurotransmitter and Neuromodulator Activity in
... Ogawa et aL, 1984; Renehan et aL, 1996). The relative magnitudes of excitatory response to different taste modalities vary in different rNST locations (Halpern, 1965; McPheeters et aL, 1990). When compared to responses of peripheral taste fibers, second order rNST neurons respond with a higher frequ ...
... Ogawa et aL, 1984; Renehan et aL, 1996). The relative magnitudes of excitatory response to different taste modalities vary in different rNST locations (Halpern, 1965; McPheeters et aL, 1990). When compared to responses of peripheral taste fibers, second order rNST neurons respond with a higher frequ ...
Skeletal System
... bound sacs filled with molecular neurotransmitters These molecules transmit signals across the synapse ...
... bound sacs filled with molecular neurotransmitters These molecules transmit signals across the synapse ...
FlyEM`s formal project plan
... Ken Hayworth, overcomes this barrier by cutting 20-100 micron thick sections. Each of these slabs is appropriate for FIB-SEM, and has near perfect surfaces that can be seamlessly stitched together in reconstruction. Numerous tissues, both mouse and fly, have been explored under different fixations, ...
... Ken Hayworth, overcomes this barrier by cutting 20-100 micron thick sections. Each of these slabs is appropriate for FIB-SEM, and has near perfect surfaces that can be seamlessly stitched together in reconstruction. Numerous tissues, both mouse and fly, have been explored under different fixations, ...
K + - CARNES AP BIO
... – (3.41) The student is able to create a representation that describes how organisms exchange information in response to internal changes and external cues, and which can result in changes in behavior. – (3.42) The student is able to describe how organisms exchange information in response to interna ...
... – (3.41) The student is able to create a representation that describes how organisms exchange information in response to internal changes and external cues, and which can result in changes in behavior. – (3.42) The student is able to describe how organisms exchange information in response to interna ...
NSF 3 - DBBS
... label mechanically sensitive neurons and affiliated cells (Meyers et al., 2001). I hypothesize that mammalian sensory neurons containing mechanosensitive ion channels take up FM1-43 into their cell bodies in response to physiological stretch. To test this, I will culture dissociated somatosensory ne ...
... label mechanically sensitive neurons and affiliated cells (Meyers et al., 2001). I hypothesize that mammalian sensory neurons containing mechanosensitive ion channels take up FM1-43 into their cell bodies in response to physiological stretch. To test this, I will culture dissociated somatosensory ne ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 5.1 Intracellular recording of the
... FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 5.1 Intracellular recording of the membrane potential and action potential generation in the squid giant axon. (A) A glass micropipette, about 100 μm in diameter, was filled with seawater and lowered into the giant axon of the squid after it had been dissected free. The axon is ...
... FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 5.1 Intracellular recording of the membrane potential and action potential generation in the squid giant axon. (A) A glass micropipette, about 100 μm in diameter, was filled with seawater and lowered into the giant axon of the squid after it had been dissected free. The axon is ...
No Slide Title
... When the action potential reaches the terminal buttons, they release chemical neurotransmitters across the synapse with the the next target neuron ...
... When the action potential reaches the terminal buttons, they release chemical neurotransmitters across the synapse with the the next target neuron ...
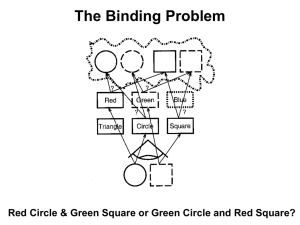
Optional extra slides on the Binding Problem
... may perceive incorrect feature conjunctions when attention is divided over different objects and features. (Triesman, 1999; Wolfe and Cave, 1999). ...
... may perceive incorrect feature conjunctions when attention is divided over different objects and features. (Triesman, 1999; Wolfe and Cave, 1999). ...
Pre- or postsynaptic distribution of distinct endocannabinoid
... Molecular and anatomical architecture of the endocannabinoid system The endocannabinoid molecules are endogenous bioactive lipid-derivatives acting on type 1 and 2 cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), the molecular targets of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC; Gaoni & Mechoulam, 1964), the main active co ...
... Molecular and anatomical architecture of the endocannabinoid system The endocannabinoid molecules are endogenous bioactive lipid-derivatives acting on type 1 and 2 cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), the molecular targets of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC; Gaoni & Mechoulam, 1964), the main active co ...
PDF file - Izhikevich
... Step 3 is the same as step 2 except that we consider common postsynaptic targets of B, C, D, F and G. Neurons I, J and L will be added to the group, while H and K will be discarded because of their nonmatching delays. By repeating these steps until either there are no more common postsynaptic target ...
... Step 3 is the same as step 2 except that we consider common postsynaptic targets of B, C, D, F and G. Neurons I, J and L will be added to the group, while H and K will be discarded because of their nonmatching delays. By repeating these steps until either there are no more common postsynaptic target ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... • With muscarinic stimulation M current is turned off leading to a small depolarization • If stimulation is repated, repetitive spikes appear • Muscarinic receptors modulates the repetitive firing properties and enhance the ability of ANS to control visceral activity ...
... • With muscarinic stimulation M current is turned off leading to a small depolarization • If stimulation is repated, repetitive spikes appear • Muscarinic receptors modulates the repetitive firing properties and enhance the ability of ANS to control visceral activity ...
... a pivotal role in aging, diabetes, and obesity. Second, while a great deal has been learned about mechanisms regulating secretion of classical neurotransmitters, far less is known about those regulating secretion of neuropeptides and hormones. Classical neurotransmitters are packaged in synaptic ves ...
Central Nervous System
... 7) When opened, the ligand-gated cation channels do not allow diffusion of Clbecause :a- the size of Cl- is bigger than the bore of the channels b- intracellular negativity causes complete inhibition of Cl- influx c- the channels are specific for diffusion of Na + only d- the inner surface of the ch ...
... 7) When opened, the ligand-gated cation channels do not allow diffusion of Clbecause :a- the size of Cl- is bigger than the bore of the channels b- intracellular negativity causes complete inhibition of Cl- influx c- the channels are specific for diffusion of Na + only d- the inner surface of the ch ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... A. Cholinergic Neurons and Cholinergic Receptors 1. Cholinergic neurons release the neurotransmitter acetlycholine and include all sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons, all parasympathetic postganglionic neurons, and sympathetic postganglionic neurons that innervate most sweat gland ...
... A. Cholinergic Neurons and Cholinergic Receptors 1. Cholinergic neurons release the neurotransmitter acetlycholine and include all sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons, all parasympathetic postganglionic neurons, and sympathetic postganglionic neurons that innervate most sweat gland ...
PDF
... basis functions,’’ Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 9 (1997): 222–237. E. Salinas and L.F. Abbott. ‘‘Transfer of coded information from sensory to motor networks,’’ Journal of Neuroscience 15 (1995): 6461–6474. E. Salinas and L.F. Abbott. ‘‘Invariant visual responses from attentional gain fields,’’ ...
... basis functions,’’ Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 9 (1997): 222–237. E. Salinas and L.F. Abbott. ‘‘Transfer of coded information from sensory to motor networks,’’ Journal of Neuroscience 15 (1995): 6461–6474. E. Salinas and L.F. Abbott. ‘‘Invariant visual responses from attentional gain fields,’’ ...
Anatomie und Zellbiologie: Simon - Medizinische Fakultät Heidelberg
... regulate the expression of other genes as activators or repressors. They play a major role in the formation and maintenance of cellular properties during development and in the adult. En-1 and En-2 are two homeodomain containing transcription factors which were originally cloned by sequence homology ...
... regulate the expression of other genes as activators or repressors. They play a major role in the formation and maintenance of cellular properties during development and in the adult. En-1 and En-2 are two homeodomain containing transcription factors which were originally cloned by sequence homology ...
Psychobiology Neurons= transmit information, human brain has 86
... Neurons= transmit information, human brain has 86 billion ...
... Neurons= transmit information, human brain has 86 billion ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.