Chapter 02: Neurons and Glia
... synthesized) Soma-independent (isolated axon still can transport ...
... synthesized) Soma-independent (isolated axon still can transport ...
Chapter 9 Nervous System
... Other neurotransmitters may decrease membrane permeability to sodium ions, reducing the chance that it will reach threshold, and are thus________________________. The effect on the postsynaptic neuron depends on which presynaptic knobs are activated. When an action potential reaches the synaptic kno ...
... Other neurotransmitters may decrease membrane permeability to sodium ions, reducing the chance that it will reach threshold, and are thus________________________. The effect on the postsynaptic neuron depends on which presynaptic knobs are activated. When an action potential reaches the synaptic kno ...
Lesson 4 Section 9.2 Electrochemical Impulse
... This happens from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of another Neurons have a rich supply of positive (+) and negative (-) ions both inside and outside the cell Negative ions are too large to pass through the cell membrane The positive ions do have the ability to diffuse in and out of the cell ...
... This happens from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of another Neurons have a rich supply of positive (+) and negative (-) ions both inside and outside the cell Negative ions are too large to pass through the cell membrane The positive ions do have the ability to diffuse in and out of the cell ...
Nervous System - Dr. Eric Schwartz
... • Myelinated axons are metabolically more efficient than unmyelinated ones. • Myelin adds speed, reduces metabolic cost, and saves room in the nervous system because the axons can be thinner. ...
... • Myelinated axons are metabolically more efficient than unmyelinated ones. • Myelin adds speed, reduces metabolic cost, and saves room in the nervous system because the axons can be thinner. ...
Linear associator
... receive input from the auditory system, and neurons of layer g receive input from the olfactory system. We know if a tone is consistently presented at the same time as food, the dog will eventually become conditioned to respond by salivating to the tone alone. In the previous lab, we hypothesized th ...
... receive input from the auditory system, and neurons of layer g receive input from the olfactory system. We know if a tone is consistently presented at the same time as food, the dog will eventually become conditioned to respond by salivating to the tone alone. In the previous lab, we hypothesized th ...
Nervous System Part 1
... Schwann cells are glia cells that that for the myelin sheath. They insulate the axons of neurons and increase the rate of action potential propagation. ...
... Schwann cells are glia cells that that for the myelin sheath. They insulate the axons of neurons and increase the rate of action potential propagation. ...
Neurophysiology Resting membrane potential (Vr)
... To ensure that the two concentrations never reach equilibrium we utilize a sodium-potassium pump. This system removes 3 sodium ions from the cell and transports 2 potassium ions back in. Note that this requires ATP (energy). Membrane potentials are used to convey signals. Generally there are two typ ...
... To ensure that the two concentrations never reach equilibrium we utilize a sodium-potassium pump. This system removes 3 sodium ions from the cell and transports 2 potassium ions back in. Note that this requires ATP (energy). Membrane potentials are used to convey signals. Generally there are two typ ...
Ch12 notes Martini 9e
... 3. Closed, not capable of opening (inactivated) Three Classes of Gated Channels 1. Chemically gated channels 2. Voltage-gated channels 3. Mechanically gated channels Chemically Gated Channels • Open in presence of specific chemicals (e.g., ACh) at a binding site • Found on neuron cell body and dendr ...
... 3. Closed, not capable of opening (inactivated) Three Classes of Gated Channels 1. Chemically gated channels 2. Voltage-gated channels 3. Mechanically gated channels Chemically Gated Channels • Open in presence of specific chemicals (e.g., ACh) at a binding site • Found on neuron cell body and dendr ...
Ion Channels - Interactive Physiology
... • Depolarization of the cell by the indirect method is time consuming. • The resulting synaptic potential is slow in onset, and long in duration. • Besides excitation, indirectly-acting neurotransmitters can also produce slow inhibition. • The neurotransmitters acetylcholine, glutamate, GABA, and se ...
... • Depolarization of the cell by the indirect method is time consuming. • The resulting synaptic potential is slow in onset, and long in duration. • Besides excitation, indirectly-acting neurotransmitters can also produce slow inhibition. • The neurotransmitters acetylcholine, glutamate, GABA, and se ...
Autonomic nervous system
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
Slide 1
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
What structures comprise the sympathetic division?
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
Chemicals in and Around the Cell.
... Imagine a molecule of neurotransmitter floating through the extra cellular space in the synapse until it reaches one of these receptors. When the neurotransmitter gets close, it fits into the protein molecule like a key in a lock. This changes the shape of the protein molecule and sets off a change ...
... Imagine a molecule of neurotransmitter floating through the extra cellular space in the synapse until it reaches one of these receptors. When the neurotransmitter gets close, it fits into the protein molecule like a key in a lock. This changes the shape of the protein molecule and sets off a change ...
Sample
... Imagine a molecule of neurotransmitter floating through the extra cellular space in the synapse until it reaches one of these receptors. When the neurotransmitter gets close, it fits into the protein molecule like a key in a lock. This changes the shape of the protein molecule and sets off a change ...
... Imagine a molecule of neurotransmitter floating through the extra cellular space in the synapse until it reaches one of these receptors. When the neurotransmitter gets close, it fits into the protein molecule like a key in a lock. This changes the shape of the protein molecule and sets off a change ...
The Chemistry of the Brain
... As neurons carry electrical impulses they must be insulated so that the information is not lost as it travels to the CNS. The myelin sheath acts as an insulator for the impulse as it travels through the axon. The presence of this insulation will also speed up the transmission of the impulse. ...
... As neurons carry electrical impulses they must be insulated so that the information is not lost as it travels to the CNS. The myelin sheath acts as an insulator for the impulse as it travels through the axon. The presence of this insulation will also speed up the transmission of the impulse. ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 3.1 Typical morphology of projection
... among the myelin sheath, the Schwann cell cytoplasm, and perhaps the axon as well. FIGURE 3.10 Astrocytes appear stellate when their intermediate filaments are stained (red, GFAP), but membrane labeling (green, membrane-associated EGFP) highlights the profusion of fine cellular processes that interc ...
... among the myelin sheath, the Schwann cell cytoplasm, and perhaps the axon as well. FIGURE 3.10 Astrocytes appear stellate when their intermediate filaments are stained (red, GFAP), but membrane labeling (green, membrane-associated EGFP) highlights the profusion of fine cellular processes that interc ...
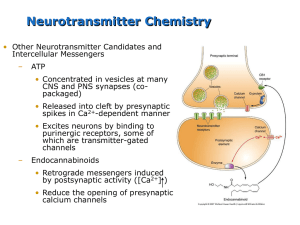
Chapter 06 - Neurotransmitter Systems
... Neurotransmitter Chemistry • Other Neurotransmitter Candidates and Intercellular Messengers ...
... Neurotransmitter Chemistry • Other Neurotransmitter Candidates and Intercellular Messengers ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 24.Sensory neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? autonomic &somatic 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.CNS 27.The neuron is the basic functional unit of the nervous syst ...
... 24.Sensory neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? autonomic &somatic 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.CNS 27.The neuron is the basic functional unit of the nervous syst ...
3/26
... while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
... while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION of the NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
Neural Transmission Project
... want to go to sleep, better hope the right ones are released. Synapse/synaptic gap: space between neurons. When neurotransmitters are floating between cells, you get the effect of the neuron. Dendrites: These grabby guys hold the receptors in their fingertips. Dendrites can be blocked or mimicked - ...
... want to go to sleep, better hope the right ones are released. Synapse/synaptic gap: space between neurons. When neurotransmitters are floating between cells, you get the effect of the neuron. Dendrites: These grabby guys hold the receptors in their fingertips. Dendrites can be blocked or mimicked - ...
Biology 12 - The Nervous System Study Guide
... 24. How do neuro-poisons such as strychnine and nerve gas work? What are the symptoms of exposure? 25. How do narcotics such as heroin and morphine work? 26. Explain the biochemical events that occur when an impulse is transmitted through a reflex arc. Begin with the opening of the sodium gates in a ...
... 24. How do neuro-poisons such as strychnine and nerve gas work? What are the symptoms of exposure? 25. How do narcotics such as heroin and morphine work? 26. Explain the biochemical events that occur when an impulse is transmitted through a reflex arc. Begin with the opening of the sodium gates in a ...
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... Lab-on-a-Chip groups. In this multidisciplinary project you will focus on (neuro)biology, microfabrication and electrochemistry (impedance spectroscopy). ...
... Lab-on-a-Chip groups. In this multidisciplinary project you will focus on (neuro)biology, microfabrication and electrochemistry (impedance spectroscopy). ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.