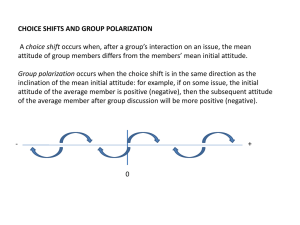
CHOICE SHIFTS AND GROUP POLARIZATION A choice shift
... Social decision scheme theory postulates that group decisions can be understood in terms of the initial distribution of attitudes and a decision scheme, or decision rule, that members use to obtain a decision . Given a demand for a group decision, disagreement triggers the employment of a particular ...
... Social decision scheme theory postulates that group decisions can be understood in terms of the initial distribution of attitudes and a decision scheme, or decision rule, that members use to obtain a decision . Given a demand for a group decision, disagreement triggers the employment of a particular ...
Behaviorist Theory
... Founder John B. Watson. He believed psychology should only concern itself with the study of behavior and one's documented behaviors. Watson's work was based on the experiments of Ivan Pavlov's model of classical conditioning based off one's personality and characteristics. (Schunk, ...
... Founder John B. Watson. He believed psychology should only concern itself with the study of behavior and one's documented behaviors. Watson's work was based on the experiments of Ivan Pavlov's model of classical conditioning based off one's personality and characteristics. (Schunk, ...
File - Delia Andrade
... conscious or the unconscious mind. In contrast with the other psychological methods behaviorism focuses only on observable behavior. It's based on the belief that behaviors can be measured, trained, and changed. Behaviorists believe a person’s environment determines their behavior, in other words th ...
... conscious or the unconscious mind. In contrast with the other psychological methods behaviorism focuses only on observable behavior. It's based on the belief that behaviors can be measured, trained, and changed. Behaviorists believe a person’s environment determines their behavior, in other words th ...
Social Entrepreneurship
... engage widespread support in order to maximize the number of local people that will stand up, seize their idea, and implement it. Every leading social entrepreneur is a mass recruiter of local changemakers—a role model proving that citizens who channel their passion into action can do almost anyth ...
... engage widespread support in order to maximize the number of local people that will stand up, seize their idea, and implement it. Every leading social entrepreneur is a mass recruiter of local changemakers—a role model proving that citizens who channel their passion into action can do almost anyth ...
Empowerment dynamics in collective action
... H2 If identity is defined broadly, empowerment generalizes to other issues/actions CP6: I’ve progressed in that now I would, given time permitting and everything else, I would actually go and help in another campaign somewhere else even if it’s only for a day if there’s a rally or something, which i ...
... H2 If identity is defined broadly, empowerment generalizes to other issues/actions CP6: I’ve progressed in that now I would, given time permitting and everything else, I would actually go and help in another campaign somewhere else even if it’s only for a day if there’s a rally or something, which i ...
Chapter 51 Behavioral Ecology
... Why study animal behavior? Understand • Human nervous system. • Child development. • Human communication. • Natural selection. ...
... Why study animal behavior? Understand • Human nervous system. • Child development. • Human communication. • Natural selection. ...
Marketable methods - University of Alberta
... individual style which Baldwin too conceived of in typological terms. What the development of mental testing did was to redefine the problem of individual differences (not in terms of typology or types but in terms of comparison of individual performances. Thus, the quality of a performance was no l ...
... individual style which Baldwin too conceived of in typological terms. What the development of mental testing did was to redefine the problem of individual differences (not in terms of typology or types but in terms of comparison of individual performances. Thus, the quality of a performance was no l ...
PEOPLE, PLACE, SPACE_2ndproof
... and avoiding negative objects. A person is contained within a region until the tensions of the particular force field encompassing the person at the moment are resolved or changed through either a rearrangement of psychological dynamics or changes in the environment. Psychological experience then is ...
... and avoiding negative objects. A person is contained within a region until the tensions of the particular force field encompassing the person at the moment are resolved or changed through either a rearrangement of psychological dynamics or changes in the environment. Psychological experience then is ...
PPT
... • Auguste Comte (coined the term sociology after he discovered that his preferred term, social physics, had already been used by a Belgian statistician. ...
... • Auguste Comte (coined the term sociology after he discovered that his preferred term, social physics, had already been used by a Belgian statistician. ...
The First Cognitive Psychologists
... -no radioactive material involved -hemoglobin carries oxygen -contains iron molecules -have magnetic properties ...
... -no radioactive material involved -hemoglobin carries oxygen -contains iron molecules -have magnetic properties ...
Organizational Behaviour
... They argued that social relationships play a major role in the development of personality. Many argued that people attempt to establish significant and rewarding relationships with others and so adopt personalities that are acceptable to those around them. ...
... They argued that social relationships play a major role in the development of personality. Many argued that people attempt to establish significant and rewarding relationships with others and so adopt personalities that are acceptable to those around them. ...
Famous Experiments
... 1. self-fulfilling prophecy: the expectations we have about others can influence the way those others behave 2. dispositional attributions—people’s failings, bad behaviors were attributed to their eye color rather than situation 3. prejudices and discrimination are learned behaviors, attitudes 4. ha ...
... 1. self-fulfilling prophecy: the expectations we have about others can influence the way those others behave 2. dispositional attributions—people’s failings, bad behaviors were attributed to their eye color rather than situation 3. prejudices and discrimination are learned behaviors, attitudes 4. ha ...
Psychology grades 9-12
... How heredity interacts with environment to influence behavior: nature vs. nurture, maturation, heredity and DNA, genome, Human Genome Project, genes, chromosomes, genotype, phenotype, Diathesis-Stress Theory; use of twin and adoption studies to assess the influence of heredity and environment on beh ...
... How heredity interacts with environment to influence behavior: nature vs. nurture, maturation, heredity and DNA, genome, Human Genome Project, genes, chromosomes, genotype, phenotype, Diathesis-Stress Theory; use of twin and adoption studies to assess the influence of heredity and environment on beh ...
Chapter 9-Canvas
... Need for an objective psychology that would focus on behavior instead of consciousness Zeitgeist: overall movement of American psychology was in a behavioristic direction Missing link: the agent of a revolution whose inevitability and success were assured (Watson) ...
... Need for an objective psychology that would focus on behavior instead of consciousness Zeitgeist: overall movement of American psychology was in a behavioristic direction Missing link: the agent of a revolution whose inevitability and success were assured (Watson) ...
Chapter 2 - People Server at UNCW
... Psychology “describes behavioral, emotional, or cognitive dysfunctions that are unexpected in their cultural context and associated with personal distress or substantial impairment in functioning” (DSM-IV) ...
... Psychology “describes behavioral, emotional, or cognitive dysfunctions that are unexpected in their cultural context and associated with personal distress or substantial impairment in functioning” (DSM-IV) ...
Macmillan, Malcolm - Psychology Board of Australia
... (usually) the first two years of a doctoral degree or over the whole of a master’s. Consider how well equipped a health psychologist working on health promotion would be to enter organisational psychology. The research skills, and therefore the ability to evaluate research-based practice, are very d ...
... (usually) the first two years of a doctoral degree or over the whole of a master’s. Consider how well equipped a health psychologist working on health promotion would be to enter organisational psychology. The research skills, and therefore the ability to evaluate research-based practice, are very d ...
Social Marketing, TCR, Public Policy...What*s the Future Hold?
... lives and the society of which they are a part (Adapted from Andreasan, 1994) ...
... lives and the society of which they are a part (Adapted from Andreasan, 1994) ...
Social Development - University of Alberta
... on the social environment and the environment, in turn, acts on us attractive, socially adept child is well received and valued by peers, which in turn increases self-esteem and self-efficacy, which makes him more well liked reverse also true ...
... on the social environment and the environment, in turn, acts on us attractive, socially adept child is well received and valued by peers, which in turn increases self-esteem and self-efficacy, which makes him more well liked reverse also true ...
science
... b) decide on the essential points, then write down key words and expressions that remind you of them c) expand your key words into a sentence or two Example: Some scientists and students as well as some other people from the non-academic environment do not like the idea that the word ‘science’ is ap ...
... b) decide on the essential points, then write down key words and expressions that remind you of them c) expand your key words into a sentence or two Example: Some scientists and students as well as some other people from the non-academic environment do not like the idea that the word ‘science’ is ap ...
Social Responsibility and Ethics
... 4. Identify and evaluate different strategies for responding to social issues. 5. Discuss the 10 commandments of social responsibility. 6. Explain what values are, how they form the basis of an individual’s ethical behavior, and how they may vary in a global business environment. 7. Describe how adv ...
... 4. Identify and evaluate different strategies for responding to social issues. 5. Discuss the 10 commandments of social responsibility. 6. Explain what values are, how they form the basis of an individual’s ethical behavior, and how they may vary in a global business environment. 7. Describe how adv ...
social problems 1 - analyzingsocialproblems
... between biography and history reminds us that the process works in both directions: ...
... between biography and history reminds us that the process works in both directions: ...
Chapter 3 The Process of Science: Studying Animal Behavior
... barn swallows tend to prefer mates with the longest tails. One hypothesis to explain this result is that a male must be healthy for long tail feathers to develop. Natural selection would favor female birds choosing these longer-tailed males. ...
... barn swallows tend to prefer mates with the longest tails. One hypothesis to explain this result is that a male must be healthy for long tail feathers to develop. Natural selection would favor female birds choosing these longer-tailed males. ...
Unit 1: Motivation, Emotion and Stress - Ms. Anderson
... ■ A need creates a state of arousal called a drive. ■ Drive keeps us motivated and working to fulfill the need. ■ If we are driven by our need for achievement (money, fame, property), we keep working to fulfill this need. ...
... ■ A need creates a state of arousal called a drive. ■ Drive keeps us motivated and working to fulfill the need. ■ If we are driven by our need for achievement (money, fame, property), we keep working to fulfill this need. ...
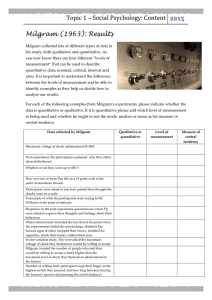
milgram-levels-of-measurement
... Milgram collected lots of different types of data in his study, both qualitative and quantitative. As you now know there are four different “levels of measurement” that can be sued to describe quantitative data; nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. It is important to understand the difference betwe ...
... Milgram collected lots of different types of data in his study, both qualitative and quantitative. As you now know there are four different “levels of measurement” that can be sued to describe quantitative data; nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. It is important to understand the difference betwe ...