International Trade
... An absolute disadvantage in a product does not preclude having a comparative advantage in that product ...
... An absolute disadvantage in a product does not preclude having a comparative advantage in that product ...
Microeconomics
... I welcome you to contact me on my cell phone any day of the week (except Shabbat), no later than 10pm. The only thing that I ask is that you don’t say: “I apologize for contacting you at home / on the weekend” – there is no apology necessary! I am connected via e-mail 24 hours a day, six days a week ...
... I welcome you to contact me on my cell phone any day of the week (except Shabbat), no later than 10pm. The only thing that I ask is that you don’t say: “I apologize for contacting you at home / on the weekend” – there is no apology necessary! I am connected via e-mail 24 hours a day, six days a week ...
PRESENTATION NAME - Greene Central School District
... rules governing international trade • WTO was created to police the agreements by GATT (General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade) • Supporters believe globalization and expansion of trade increased ...
... rules governing international trade • WTO was created to police the agreements by GATT (General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade) • Supporters believe globalization and expansion of trade increased ...
and foreign price
... Three steps to obtain the opportunity cost of cheese in terms of wine: Step 1: 1 labor can produce ____ wine Step 2: producing 1 unit of cheese needs _____ labor Step 3: that amount of labor in step 2 can produce____ wine Therefore, the opportunity cost of cheese in terms of wine is ___. The meanin ...
... Three steps to obtain the opportunity cost of cheese in terms of wine: Step 1: 1 labor can produce ____ wine Step 2: producing 1 unit of cheese needs _____ labor Step 3: that amount of labor in step 2 can produce____ wine Therefore, the opportunity cost of cheese in terms of wine is ___. The meanin ...
powerpoint file
... The Economic Argument for Free-Trade • The theoretical justification for free-trade resides in the concept of comparative advantage. – Comparative advantage dictates that each nation should specialize in those products that it can produce the least inefficiently compared with production in other na ...
... The Economic Argument for Free-Trade • The theoretical justification for free-trade resides in the concept of comparative advantage. – Comparative advantage dictates that each nation should specialize in those products that it can produce the least inefficiently compared with production in other na ...
The Production Possibility Model, Trade, and Globalization
... • If a method of production will change income distribution we cannot determine if that method is efficient or not • Efficiency has meaning when analyzing a particular goal • In our society, most people prefer more to less, and many policies have relatively small distribution effects ...
... • If a method of production will change income distribution we cannot determine if that method is efficient or not • Efficiency has meaning when analyzing a particular goal • In our society, most people prefer more to less, and many policies have relatively small distribution effects ...
Mid-term
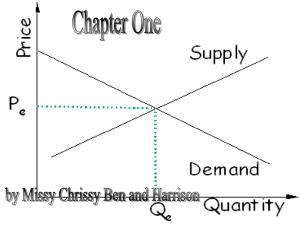
... b. (4) Based on the demand curve above, if the price of twinkies decreases, what will happen to total consumer expenditures on twinkies? c. (4)Based on the demand curve above (and considerable empirical evidence), what would happen to farmers’ incomes in a perfectly competitive market setting when t ...
... b. (4) Based on the demand curve above, if the price of twinkies decreases, what will happen to total consumer expenditures on twinkies? c. (4)Based on the demand curve above (and considerable empirical evidence), what would happen to farmers’ incomes in a perfectly competitive market setting when t ...
Homework #1
... Bill and Bob work for UW. They are in charge of cleaning classrooms and of advising students about registration. In a day, Bill can clean 20 classrooms and advise 0 students or he can advise 50 students and clean 0 classrooms. Bill can also do any other combination of these two activities that sits ...
... Bill and Bob work for UW. They are in charge of cleaning classrooms and of advising students about registration. In a day, Bill can clean 20 classrooms and advise 0 students or he can advise 50 students and clean 0 classrooms. Bill can also do any other combination of these two activities that sits ...
The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice
... dictate what will be produced (or not produced) by choosing what to purchase (and what not to purchase). • Free enterprise: under a free market system, individual producers must figure out how to plan, organize, and coordinate the production of products and services. • The distribution of output is ...
... dictate what will be produced (or not produced) by choosing what to purchase (and what not to purchase). • Free enterprise: under a free market system, individual producers must figure out how to plan, organize, and coordinate the production of products and services. • The distribution of output is ...
Key - KSU Web Home
... costs and marginal costs of consuming coffee are zero for all levels of consumption). In order to maximize her total economic surplus she should consume _____ cups of coffee per day. B. ...
... costs and marginal costs of consuming coffee are zero for all levels of consumption). In order to maximize her total economic surplus she should consume _____ cups of coffee per day. B. ...
1.4 Comparative Advantage and Opportunity Costs
... 1.5 Comparative Advantage with More Than Two Commodities and Countries 1.6 Theory of Reciprocal Demand 1.7 Offer Curves and the Terms of Trade ...
... 1.5 Comparative Advantage with More Than Two Commodities and Countries 1.6 Theory of Reciprocal Demand 1.7 Offer Curves and the Terms of Trade ...
Decisions & Effects
... Production and Trading • Remember, Trading is a Utility-Increasing Activity! • Barter is exchanging one good for another: for example, trading apples for bread. • Comparative Advantage: The situation where someone can produce a good at lower opportunity cost than someone else can. • Economists have ...
... Production and Trading • Remember, Trading is a Utility-Increasing Activity! • Barter is exchanging one good for another: for example, trading apples for bread. • Comparative Advantage: The situation where someone can produce a good at lower opportunity cost than someone else can. • Economists have ...
PROTECTIONISM
... comparative advantage theory. Free trade allows the maximization of world production, thus making it possible for each consumer in the world to consume more goods then he or she could without free trade. As there more goods and service can be produced country’s GDP rises. This leads to rise in per c ...
... comparative advantage theory. Free trade allows the maximization of world production, thus making it possible for each consumer in the world to consume more goods then he or she could without free trade. As there more goods and service can be produced country’s GDP rises. This leads to rise in per c ...
Economics 101 - Iowa State University Department of Economics
... 13. Which of the following could cause the market demand curve for hot dogs to shift to the left? a. an increase in the price of hot dogs. b. a decrease in the price of hamburgers. c. an increase in the size of the population. d. an increase in the price of hot dog buns or rolls 14. Which of the fol ...
... 13. Which of the following could cause the market demand curve for hot dogs to shift to the left? a. an increase in the price of hot dogs. b. a decrease in the price of hamburgers. c. an increase in the size of the population. d. an increase in the price of hot dog buns or rolls 14. Which of the fol ...
Review Questions 2 – 23.11.2016 Question 1 Suppose a perfectly
... (incl. all opportunity costs): Quantity of gizmos ...
... (incl. all opportunity costs): Quantity of gizmos ...
Study Guide 2015
... Determine the “Terms of Trade” between Brazil & Mexico (range of mutually beneficial trade) i. Hint: Terms of trade can be found by using the opportunity cost table. The terms of trade are greater than and less than each country’s opportunity cost of the product. ii. If they trade at their exact opp ...
... Determine the “Terms of Trade” between Brazil & Mexico (range of mutually beneficial trade) i. Hint: Terms of trade can be found by using the opportunity cost table. The terms of trade are greater than and less than each country’s opportunity cost of the product. ii. If they trade at their exact opp ...
Is Free Trade - Omnifoo.info
... Your piece of your state's cake is your benefit in the economy. Even if the size of your cake stays the same, Globalization will change the percentage of the total cake, depending on whether you are a “winner” or “loser” from free trade. ...
... Your piece of your state's cake is your benefit in the economy. Even if the size of your cake stays the same, Globalization will change the percentage of the total cake, depending on whether you are a “winner” or “loser” from free trade. ...
Chapter 9 International Trade
... Effects of an Import Quota • Limit on the quantity of a good that can be produced abroad and sold domestically • Shifts supply curve to right by size of quota • Leads to exact same result as a tariff except instead of having gov’t revenue, license holders get the surplus ...
... Effects of an Import Quota • Limit on the quantity of a good that can be produced abroad and sold domestically • Shifts supply curve to right by size of quota • Leads to exact same result as a tariff except instead of having gov’t revenue, license holders get the surplus ...
Chapter 18 The markets for the factors of production Factors of
... demand for workers are derived from its primary goal of maximizing profits ...
... demand for workers are derived from its primary goal of maximizing profits ...
ECON 102 SPRING 2007 –FIRST MIDTERM
... Types of unemployment – there are 4 types of unemployment 1) Frictional unemployment- due to the normal workings of the labor market. It involves people being temporarily between jobs or searching for a new job 2) Structural unemployment- due to changes in the structure of the economy 3) Seasonal un ...
... Types of unemployment – there are 4 types of unemployment 1) Frictional unemployment- due to the normal workings of the labor market. It involves people being temporarily between jobs or searching for a new job 2) Structural unemployment- due to changes in the structure of the economy 3) Seasonal un ...
to download_chapter5 - Sok Chanrithy`s WEB
... and probably always will be, two sides to the argument. Some argue that trade with other countries makes it harder for Some people to make a good living. Others argue that just letting everybody trade freely is best for both the country and the world. ...
... and probably always will be, two sides to the argument. Some argue that trade with other countries makes it harder for Some people to make a good living. Others argue that just letting everybody trade freely is best for both the country and the world. ...
What are Wants and Needs?
... Opportunity Cost is the value of the item that is lost when one makes a trade off. ...
... Opportunity Cost is the value of the item that is lost when one makes a trade off. ...
How Things - eXtension
... Comparative advantage A. Countries that can produce a product or good more efficiently and cost-effectively have an advantage for that good compared to other countries. Example: In Brazil, patent rights are often not enforced, so farmers there do not pay a royalty for Roundup herbicide. The cost fo ...
... Comparative advantage A. Countries that can produce a product or good more efficiently and cost-effectively have an advantage for that good compared to other countries. Example: In Brazil, patent rights are often not enforced, so farmers there do not pay a royalty for Roundup herbicide. The cost fo ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.