S2017 Makeup Prelim 1
... the right of PPF is not feasible. We don’t know where along the PPF is best because we don’t know the preference of the economy. 3 C Danny has an absolute advantage in both basketball and baseballs. The opportunity cost of make one basketball is 1 baseball for Danny, and ½ baseball for Robert. So Ro ...
... the right of PPF is not feasible. We don’t know where along the PPF is best because we don’t know the preference of the economy. 3 C Danny has an absolute advantage in both basketball and baseballs. The opportunity cost of make one basketball is 1 baseball for Danny, and ½ baseball for Robert. So Ro ...
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH WORKSHEET (FIRST
... 2. Explain the central problem of what to produce? 3. What is the root cause of all economic problem? 4. Define demand. 5. Explain consumer’s equilibrium in case of single commodity using utility approach. 6. Distinguish between change in demand and change in quantity demanded. 7. What are factors a ...
... 2. Explain the central problem of what to produce? 3. What is the root cause of all economic problem? 4. Define demand. 5. Explain consumer’s equilibrium in case of single commodity using utility approach. 6. Distinguish between change in demand and change in quantity demanded. 7. What are factors a ...
Section 9 - Economics
... • Quantity demanded • Describes the amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing & able to buy at each particular price during a given time period • “willing and able” • ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
... • Quantity demanded • Describes the amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing & able to buy at each particular price during a given time period • “willing and able” • ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
ECON241 (Fall 2010)
... You are the manager of a monopolistically competitive firm, and your demand and cost functions are given by Q = 20 – 2P and C(Q) = 104 – 14Q + Q2 (a) Find the inverse demand function for your firm’s product The inverse linear demand function is P = 10 – 0.5Q. (b) Determine the profit-maximizing pric ...
... You are the manager of a monopolistically competitive firm, and your demand and cost functions are given by Q = 20 – 2P and C(Q) = 104 – 14Q + Q2 (a) Find the inverse demand function for your firm’s product The inverse linear demand function is P = 10 – 0.5Q. (b) Determine the profit-maximizing pric ...
Chap011
... not, the decision to produce depends only on whether the next unit will bring more revenue to the firm than its out-of-pocket costs of producing that unit. In other words, if the price (marginal revenue) does not cover the variable inputs, it would be better to close down and lose only the fixed cos ...
... not, the decision to produce depends only on whether the next unit will bring more revenue to the firm than its out-of-pocket costs of producing that unit. In other words, if the price (marginal revenue) does not cover the variable inputs, it would be better to close down and lose only the fixed cos ...
b20_file371_25458_0
... 2. Understand the role of property rights, marginal analysis, and incentives play in motivating people to pursue their economic interests. (MC=MB) 3. Understand the concept of opportunity costs and be able to explain how the production possibilities curve is a theoretical tool used to illustrate thi ...
... 2. Understand the role of property rights, marginal analysis, and incentives play in motivating people to pursue their economic interests. (MC=MB) 3. Understand the concept of opportunity costs and be able to explain how the production possibilities curve is a theoretical tool used to illustrate thi ...
Name: JJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJ Date: JJJJJJJJJJJJJJ
... pint of brew sells for $3. The market wage of a brew master is $150 per day. Barry's Brewpub will hire another brew master only if Barry believes the new brew master will: A) produce the same number of pints per day as the last brew master hired. B) produce 50 or more pints per day. C) raise total p ...
... pint of brew sells for $3. The market wage of a brew master is $150 per day. Barry's Brewpub will hire another brew master only if Barry believes the new brew master will: A) produce the same number of pints per day as the last brew master hired. B) produce 50 or more pints per day. C) raise total p ...
投影片 1
... Unemployment rates were similar in the U.S. and Europe in 1970s and 1980s, but are higher in Europe since then (Fig. 3.9) 3 reasons for higher unemployment rates in Europe: generous unemployment insurance systems, high tax rates, government policies that interfere with labor markets ...
... Unemployment rates were similar in the U.S. and Europe in 1970s and 1980s, but are higher in Europe since then (Fig. 3.9) 3 reasons for higher unemployment rates in Europe: generous unemployment insurance systems, high tax rates, government policies that interfere with labor markets ...
1) Economics is the study of how people choose
... C) machinery that meets or exceeds federal safety standards for use by humans. D) the accumulated skill and knowledge of workers. 10) The production possibility frontier A) refers to the technology used in such goods as computers and military aircraft. B) once applied to U.S. technology but now refe ...
... C) machinery that meets or exceeds federal safety standards for use by humans. D) the accumulated skill and knowledge of workers. 10) The production possibility frontier A) refers to the technology used in such goods as computers and military aircraft. B) once applied to U.S. technology but now refe ...
Topic 6 – Production
... When MP < AP, AP is falling When MP = AP, AP is at its maximum Example: GPAs and test scores Law of Diminishing (Marginal) Returns – Beyond some point, output grows at a diminishing rate with increases in the variable input. It has been said that, “if it weren’t for the law of diminishing returns, t ...
... When MP < AP, AP is falling When MP = AP, AP is at its maximum Example: GPAs and test scores Law of Diminishing (Marginal) Returns – Beyond some point, output grows at a diminishing rate with increases in the variable input. It has been said that, “if it weren’t for the law of diminishing returns, t ...
Chapter_12_Micro_online_14e
... Q12.3 An increase in the price of a resource would cause 1) producers to substitute other inputs for the resource. 2) consumers to increase consumption of the goods that increase in price as the result of the higher resource price. 3) an increase in the demand for products that use the resource int ...
... Q12.3 An increase in the price of a resource would cause 1) producers to substitute other inputs for the resource. 2) consumers to increase consumption of the goods that increase in price as the result of the higher resource price. 3) an increase in the demand for products that use the resource int ...
Homework #5 - Iowa State University Department of Economics
... C) small changes in marginal cost will not result in changes in the price or quantity. D) each firm believes that its competitors' demand curves are kinked, but its demand curve is not kinked. 15) In the long run, a firm in A) monopolistic competition will produce where P = ATC. B) an oligopoly will ...
... C) small changes in marginal cost will not result in changes in the price or quantity. D) each firm believes that its competitors' demand curves are kinked, but its demand curve is not kinked. 15) In the long run, a firm in A) monopolistic competition will produce where P = ATC. B) an oligopoly will ...
Chapter 8 - uc-davis economics
... The threat of tariffs being imposed on these products led President Bush to reconsider the U.S. tariffs on steel, and on December 5, 2003, he announced that they would be suspended, after being in place for only 19 months, rather than the three years as initially planned. ...
... The threat of tariffs being imposed on these products led President Bush to reconsider the U.S. tariffs on steel, and on December 5, 2003, he announced that they would be suspended, after being in place for only 19 months, rather than the three years as initially planned. ...
Q = 100K 0.5 L 0.5
... Suppose that a firm’s production function is given by Q = K² L. Further suppose that w = $10 and r = $20 a) Suppose the firm wants to produce 27,000 units of output. What is the most efficient combination of labor and capital? Solution: MPL = K², MPK = 2KL MRTS = MPL / MPK = K / 2L K / 2L = 10 / 20. ...
... Suppose that a firm’s production function is given by Q = K² L. Further suppose that w = $10 and r = $20 a) Suppose the firm wants to produce 27,000 units of output. What is the most efficient combination of labor and capital? Solution: MPL = K², MPK = 2KL MRTS = MPL / MPK = K / 2L K / 2L = 10 / 20. ...
Lecture Notes #2 on Chapters 3 and 4
... Production Possibilities Frontier and Economic Efficiency One way of representing the idea of scarcity is with a production possibilities frontier, or a diagram showing the set of goods that an economy can produce. For simplification, this is usually done for an economy that produces only two good. ...
... Production Possibilities Frontier and Economic Efficiency One way of representing the idea of scarcity is with a production possibilities frontier, or a diagram showing the set of goods that an economy can produce. For simplification, this is usually done for an economy that produces only two good. ...
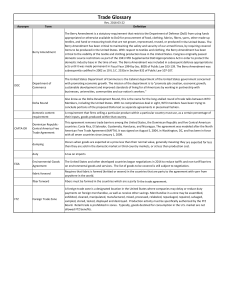
Trade Glossary - Industrial Fabrics Association International
... Trade Agreements can create opportunities for Americans and help to grow the U.S. economy. USTR has principal responsibility for administering U.S. trade agreements. This involves monitoring our trading partners' implementation of trade agreements with the United States, enforcing America's right ...
... Trade Agreements can create opportunities for Americans and help to grow the U.S. economy. USTR has principal responsibility for administering U.S. trade agreements. This involves monitoring our trading partners' implementation of trade agreements with the United States, enforcing America's right ...
Lessons 1 -2
... • The key points are as follows: • The AVC and ATC will always be U - shaped. This represents the law of diminishing returns mentioned earlier • Towards the left output is low – small workers using fixed capital. • Employ more = increased output, however, as more workers productivity falls and cost ...
... • The key points are as follows: • The AVC and ATC will always be U - shaped. This represents the law of diminishing returns mentioned earlier • Towards the left output is low – small workers using fixed capital. • Employ more = increased output, however, as more workers productivity falls and cost ...
Practice Exam 2 Key
... a. The additional utility from consuming one more unit of a product b. The additional product produced from one more unit of an input c. The amount of one good that must be given up to acquire more of another good while holding total utility constant d. The percentage change in the quantity demanded ...
... a. The additional utility from consuming one more unit of a product b. The additional product produced from one more unit of an input c. The amount of one good that must be given up to acquire more of another good while holding total utility constant d. The percentage change in the quantity demanded ...
PROBLEM SET - 4 Multiple Choice Questions
... 4. Suppose that the market for lima beans is in equilibrium. Then, both the supply and demand curves for lima beans shift to the left. As a result, the equilibrium price ___________ and the equilibrium quantity will ___________. a. will fall; fall b. will fall; rise c. cannot be determined; fall d. ...
... 4. Suppose that the market for lima beans is in equilibrium. Then, both the supply and demand curves for lima beans shift to the left. As a result, the equilibrium price ___________ and the equilibrium quantity will ___________. a. will fall; fall b. will fall; rise c. cannot be determined; fall d. ...
Assignment 1
... #2. The Special Products Company produces expensive and unusual gift to be sold in specialized stores. The latest new-product proposal suggests a limited edition grandfather clock. The management needs to decide whether to introduce this product and, if so, how many of these grandfather clocks to pr ...
... #2. The Special Products Company produces expensive and unusual gift to be sold in specialized stores. The latest new-product proposal suggests a limited edition grandfather clock. The management needs to decide whether to introduce this product and, if so, how many of these grandfather clocks to pr ...
Market Failure - uwcmaastricht-econ
... marginal benefit falls as quantity consumed increases, the consumer will be willing to buy each extra unit only if the price falls. ...
... marginal benefit falls as quantity consumed increases, the consumer will be willing to buy each extra unit only if the price falls. ...
Economics (Reading Packet)
... shipping, but it will take at least a week to get to your home. Or you can buy it today for only $35.95 at a store in a nearby town, but it will take an hour of your time and about $4.00 of gas to drive there and back. One way to sort through these alternatives is to lay them out on a decision mat ...
... shipping, but it will take at least a week to get to your home. Or you can buy it today for only $35.95 at a store in a nearby town, but it will take an hour of your time and about $4.00 of gas to drive there and back. One way to sort through these alternatives is to lay them out on a decision mat ...
Overview of the CFTA - CSOs Consultations in Accra - twn
... • Lack of a Productive capacity is one of the barriers to Intra African Trade. There is the question of what to trade between African countries. • The absence of critical connecting infrastructure as well as Non Tariff Barriers is another challenge to overcoming fragmentation of African markets. • F ...
... • Lack of a Productive capacity is one of the barriers to Intra African Trade. There is the question of what to trade between African countries. • The absence of critical connecting infrastructure as well as Non Tariff Barriers is another challenge to overcoming fragmentation of African markets. • F ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.