Change in demand - Our Lady's College
... A free good is any good whose quantity is sufficient to satisfy all our wants, i.e. it is not scarce. As people do not prefer to have more of it, they will not pay for it. They need not to give up something to get it. The opportunity cost in production is zero. Air and seawater are the examples of f ...
... A free good is any good whose quantity is sufficient to satisfy all our wants, i.e. it is not scarce. As people do not prefer to have more of it, they will not pay for it. They need not to give up something to get it. The opportunity cost in production is zero. Air and seawater are the examples of f ...
I. Introduction and Overview.
... the Wage and the Quantity Demanded of Labor 2. Substitution Effect When the price of an input changes, while the price of a substitute input remains the same, profit-maximizing employers will tend to use more of the one that is now relatively cheaper and less of the one that is now relatively more e ...
... the Wage and the Quantity Demanded of Labor 2. Substitution Effect When the price of an input changes, while the price of a substitute input remains the same, profit-maximizing employers will tend to use more of the one that is now relatively cheaper and less of the one that is now relatively more e ...
4.2 Tariffs
... Dumping is recognized as a form of international price discrimination. It occurs when foreign buyers are charged lower prices than domestic buyers for an identical product, after allowing for transportation costs and tariff duties. Selling in foreign markets at a price below the cost of production ...
... Dumping is recognized as a form of international price discrimination. It occurs when foreign buyers are charged lower prices than domestic buyers for an identical product, after allowing for transportation costs and tariff duties. Selling in foreign markets at a price below the cost of production ...
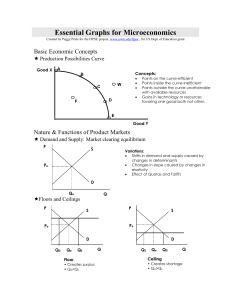
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rat ...
... variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rat ...
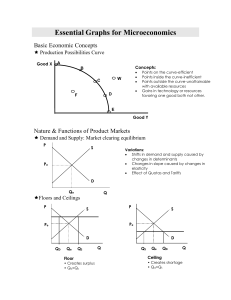
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics - pm
... variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rat ...
... variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rat ...
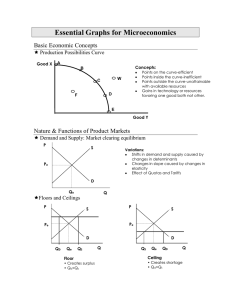
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rat ...
... variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rat ...
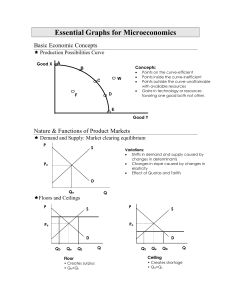
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rat ...
... variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rat ...
Which of the following is an implicit cost
... a. and she will therefore consume more of both goods. b. but the substitution effect will insure that she consumes more X and less Y. c. so she will consume more of good X, but she might consume more, less, or the same of good Y. d. but the substitution effect will negate the positive effect of the ...
... a. and she will therefore consume more of both goods. b. but the substitution effect will insure that she consumes more X and less Y. c. so she will consume more of good X, but she might consume more, less, or the same of good Y. d. but the substitution effect will negate the positive effect of the ...
Mid-exam review class
... Lemma: Ordinal utility holds that the size of the utility difference between any two consumption bundles doesn’t matter. So what we care is only the ordinal represented by the amount of utility function. Positive Monotonic transformation of the utility function represents the same preference a ...
... Lemma: Ordinal utility holds that the size of the utility difference between any two consumption bundles doesn’t matter. So what we care is only the ordinal represented by the amount of utility function. Positive Monotonic transformation of the utility function represents the same preference a ...
Chapter4
... demanded, the incentive to replace labor with other inputs is ___________ If the supply of the other input is ________ (relatively _____ supply curve), the increase in demand will result in only a moderate price increase, so firms will be more likely to make substantial changes in the relative share ...
... demanded, the incentive to replace labor with other inputs is ___________ If the supply of the other input is ________ (relatively _____ supply curve), the increase in demand will result in only a moderate price increase, so firms will be more likely to make substantial changes in the relative share ...
A Shopkeeper Economy - Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas
... for food increases the derived demand for ingredients, which causes an exactly offsetting increase in the price of food ingredients (assuming the factor inputs are inelastically supplied). However, if the intermediate inputs themselves are produced under strictly fixed costs, then the derived demand ...
... for food increases the derived demand for ingredients, which causes an exactly offsetting increase in the price of food ingredients (assuming the factor inputs are inelastically supplied). However, if the intermediate inputs themselves are produced under strictly fixed costs, then the derived demand ...
Lecture 1: Introduction
... the risk of either failing to cover its debt or being unable to raise more capital Accounting Tricks……. ...
... the risk of either failing to cover its debt or being unable to raise more capital Accounting Tricks……. ...
Concordia University
... If Fidel packs 75 brats in a given hour, then he would have missed the chance of packing 75 pizzas in that same hour. Then, for each brat he packed, he missed the chance of packing one pizza. The opportunity cost of packing one brat for Fidel is then packing one pizza. Similarly, the opportunity cos ...
... If Fidel packs 75 brats in a given hour, then he would have missed the chance of packing 75 pizzas in that same hour. Then, for each brat he packed, he missed the chance of packing one pizza. The opportunity cost of packing one brat for Fidel is then packing one pizza. Similarly, the opportunity cos ...
Perfectly Competitive Markets
... freely available – all firms have access to technology One can become the seller or buyer with relative ease (free entry and exit) In a perfectly competitive market, firms compete with each other on production/procurement costs. In a perfectly competitive market, a firm’s marketing strategy focuse ...
... freely available – all firms have access to technology One can become the seller or buyer with relative ease (free entry and exit) In a perfectly competitive market, firms compete with each other on production/procurement costs. In a perfectly competitive market, a firm’s marketing strategy focuse ...
office of independent study
... state, a citizen of your country, and finally as a part of nation within the world economy. For example, if you wish to purchase a new house, your decision is affected by the policies of your state and federal governments. Your state may make low-interest loans available to first-time home buyers or ...
... state, a citizen of your country, and finally as a part of nation within the world economy. For example, if you wish to purchase a new house, your decision is affected by the policies of your state and federal governments. Your state may make low-interest loans available to first-time home buyers or ...
chap 1 - SFU.ca
... i. What is Min’s utility maximizing combination of A and B? ii. Show that this combination satisfies the utility maximizing rule. b. Now assume that the price of A falls to $4, and the price of B remains at $2. i. What is the new utility maximizing combination of A and B? ii. What is the own-price e ...
... i. What is Min’s utility maximizing combination of A and B? ii. Show that this combination satisfies the utility maximizing rule. b. Now assume that the price of A falls to $4, and the price of B remains at $2. i. What is the new utility maximizing combination of A and B? ii. What is the own-price e ...
Microeconomics - Testbank 1 (Hubbard/O`Brien)
... 8) run increases at first and then falls is because: A as more labor is hired, they are not as skilled as the ) first ones hired. B there are fewer opportunities for division of labor ) and specialization. C the management is inefficient. ...
... 8) run increases at first and then falls is because: A as more labor is hired, they are not as skilled as the ) first ones hired. B there are fewer opportunities for division of labor ) and specialization. C the management is inefficient. ...
Decision Making and Demand and Supply
... – identical or homogeneous goods→price is the only decision factor – perfect information →there is only one price – free entry and exit →profits (economic) will be zero in the long-run ...
... – identical or homogeneous goods→price is the only decision factor – perfect information →there is only one price – free entry and exit →profits (economic) will be zero in the long-run ...
econ2302
... 22. If the marginal cost curve is rising, then which of the following must be true? A. The average total cost curve must be rising B. The average total cost curve must be below the marginal cost curve C. The average total cost curve must be above the marginal cost curve D. Total costs must be risin ...
... 22. If the marginal cost curve is rising, then which of the following must be true? A. The average total cost curve must be rising B. The average total cost curve must be below the marginal cost curve C. The average total cost curve must be above the marginal cost curve D. Total costs must be risin ...
Doha Development Round - Schmidt
... PPP exchange rate (the "real exchange rate") fluctuations are mostly due to market exchange rate movements. Aside from this volatility, consistent deviations of the market and PPP exchange rates are observed, for example (market exchange rate) prices of non-traded goods and services are usually lowe ...
... PPP exchange rate (the "real exchange rate") fluctuations are mostly due to market exchange rate movements. Aside from this volatility, consistent deviations of the market and PPP exchange rates are observed, for example (market exchange rate) prices of non-traded goods and services are usually lowe ...
Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 101
... 3. The law of demand states that a. Goods that are more scarce tend to be more expensive. b. When a good or service is less available, people don't consume as much of it; therefore, the price will fall. c. There is an inverse relationship between the price and the quantity demanded of a good or serv ...
... 3. The law of demand states that a. Goods that are more scarce tend to be more expensive. b. When a good or service is less available, people don't consume as much of it; therefore, the price will fall. c. There is an inverse relationship between the price and the quantity demanded of a good or serv ...
Fall 2012 - Montana State University
... The above diagram depicts the equilibrium in the market for sweaters. Assume there is a price floor set at $5/sweater. Which of the following would result from the floor? a. There will be a shortage of sweaters. b. There will be a surplus of sweaters. c. Demand for sweaters will shift inward. d. The ...
... The above diagram depicts the equilibrium in the market for sweaters. Assume there is a price floor set at $5/sweater. Which of the following would result from the floor? a. There will be a shortage of sweaters. b. There will be a surplus of sweaters. c. Demand for sweaters will shift inward. d. The ...
Honors Economics Unit 2 Study Guide
... A shift in the demand curve comes from a change in the non-price determinants (income, related goods, etc.) 4. What economic system is the United States economy based on? (79) Market 5. What are the determinants of demand? How do each affect demand?(86-88) (Know all five) a. Income – Less income, le ...
... A shift in the demand curve comes from a change in the non-price determinants (income, related goods, etc.) 4. What economic system is the United States economy based on? (79) Market 5. What are the determinants of demand? How do each affect demand?(86-88) (Know all five) a. Income – Less income, le ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.