Pol
... service (taken together) are willing and able to sell at any given price (Expressed as S) Quantity supplied- The amount of a good or service all producers of that good or service (taken together) are willing and able to sell at one particular price (Expressed as qS) Law of Supply- Says that when the ...
... service (taken together) are willing and able to sell at any given price (Expressed as S) Quantity supplied- The amount of a good or service all producers of that good or service (taken together) are willing and able to sell at one particular price (Expressed as qS) Law of Supply- Says that when the ...
Document
... Barriers to entry Duopoly - Two sellers Pure oligopoly - Homogeneous product Differentiated oligopoly - Differentiated product ...
... Barriers to entry Duopoly - Two sellers Pure oligopoly - Homogeneous product Differentiated oligopoly - Differentiated product ...
Study Guide for Final Practice Problem Answers
... 13. Suppose a barber shop has fixed cost equal to $1,000/month and total costs equal to $5000/month. This shop will continue to operate in the short run as long its total revenue is greater than $4,000 (their variable costs)? 14. Explain what Adam Smith was referring to when he used the analogy of a ...
... 13. Suppose a barber shop has fixed cost equal to $1,000/month and total costs equal to $5000/month. This shop will continue to operate in the short run as long its total revenue is greater than $4,000 (their variable costs)? 14. Explain what Adam Smith was referring to when he used the analogy of a ...
Basics
... putting upward pressure on wages. At WE the market is in equilibrium and firms are wage takers. ...
... putting upward pressure on wages. At WE the market is in equilibrium and firms are wage takers. ...
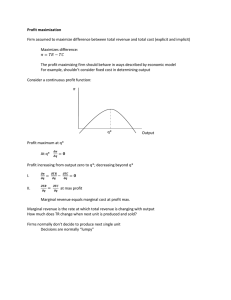
Marginal revenue curve
... can be calculated by multiplying profits per unit (P* - A) times the firm’s chosen output level q*. For this situation to truly be a maximum profit, the marginal cost curve must also be be increasing (it would be a profit minimum if the marginal cost curve was decreasing). ...
... can be calculated by multiplying profits per unit (P* - A) times the firm’s chosen output level q*. For this situation to truly be a maximum profit, the marginal cost curve must also be be increasing (it would be a profit minimum if the marginal cost curve was decreasing). ...
Cost
... Businesses have two types of cost: • Variable costs, also known as shortterm costs, are those that managers can quickly raise or lower by means of decisions they make today. • Fixed or long-term costs are harder to change - or more precisely, a decision by a business to change its fixed costs will t ...
... Businesses have two types of cost: • Variable costs, also known as shortterm costs, are those that managers can quickly raise or lower by means of decisions they make today. • Fixed or long-term costs are harder to change - or more precisely, a decision by a business to change its fixed costs will t ...
CHAPTER 5 WHAT IS SUPPLY?
... IE: As you add chili powder to chili the chili will change until it does not taste like chili anymore. The workers in a business are the chili powder and you need to find out what the perfect amount of chili powder is. ...
... IE: As you add chili powder to chili the chili will change until it does not taste like chili anymore. The workers in a business are the chili powder and you need to find out what the perfect amount of chili powder is. ...
2005.2nd Midterm.pp
... •Economies and Diseconomies of Scale –Economies of scale are features of a firm’s technology that lead to falling long-run average cost as output increases. –Diseconomies of scale are features of a firm’s technology that lead to rising long-run average cost as output increases. –Constant returns to ...
... •Economies and Diseconomies of Scale –Economies of scale are features of a firm’s technology that lead to falling long-run average cost as output increases. –Diseconomies of scale are features of a firm’s technology that lead to rising long-run average cost as output increases. –Constant returns to ...