Test answers - November 4, 2002
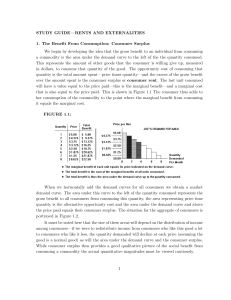
... P = 80, Q = 200. The elasticity of demand at this point will be given by dQ/dP P/Q = 1/0.1 80/200 = 4. The correct answer is (O). 5. Since demand is elastic at point AA@, the percentage change in quantity demanded will be larger than the percentage change in price (for small changes in price ...
... P = 80, Q = 200. The elasticity of demand at this point will be given by dQ/dP P/Q = 1/0.1 80/200 = 4. The correct answer is (O). 5. Since demand is elastic at point AA@, the percentage change in quantity demanded will be larger than the percentage change in price (for small changes in price ...
Exercise 5.2
... b. will suffer an economic loss, but should continue to operate at the minimum of its average variable costs c. will just break even, with neither a profit nor a loss, and should operate d. will suffer an economic loss and should shut down e. should operate at a higher output level where it can suff ...
... b. will suffer an economic loss, but should continue to operate at the minimum of its average variable costs c. will just break even, with neither a profit nor a loss, and should operate d. will suffer an economic loss and should shut down e. should operate at a higher output level where it can suff ...
Monopoly
... sell one more unit, the revenue received from previously sold units also decreases. ...
... sell one more unit, the revenue received from previously sold units also decreases. ...
Perfect Competition
... result is called collusion. OPEC is a cartel that is made up of countries that export petroleum. They member countries force the firms that actually produce the oil to obey the price floor (or so they promise the other countries in the cartel.) The price floor doesn’t apply to domestic sales of oil ...
... result is called collusion. OPEC is a cartel that is made up of countries that export petroleum. They member countries force the firms that actually produce the oil to obey the price floor (or so they promise the other countries in the cartel.) The price floor doesn’t apply to domestic sales of oil ...
Unit 2 LAYOUT - EricksonClassroom
... a. Create a demand schedule and graph for one of your products b. CHANGE 1: The government has just decreased taxes which means everybody has more money to spend – demonstrate how this will affect your demand graph c. CHANGE 2: The government has just increased the tax rate for your business so your ...
... a. Create a demand schedule and graph for one of your products b. CHANGE 1: The government has just decreased taxes which means everybody has more money to spend – demonstrate how this will affect your demand graph c. CHANGE 2: The government has just increased the tax rate for your business so your ...
SL 151 - Rose
... the ATC, AVC and MC curves all shift up, but the AFC curve is unaffected. the ATC and the AFC curves shift up, but the AVC and the MC curves are unaffected. the ATC, AFC and MC curves shift upward, but the AVC curve is unaffected. the ATC and AFC curves shift downwards, but the AVC and the MC curves ...
... the ATC, AVC and MC curves all shift up, but the AFC curve is unaffected. the ATC and the AFC curves shift up, but the AVC and the MC curves are unaffected. the ATC, AFC and MC curves shift upward, but the AVC curve is unaffected. the ATC and AFC curves shift downwards, but the AVC and the MC curves ...
Microeconomics - WordPress.com
... SR and LR Equilibrium of a Firm in Perfect Competition The firm’s existing plant has short-run cost curves SRATC0 and MC0 while market price is p0. The firm produces q0, where MC0 equals price and total costs are just being covered. Although the firm is in short-run equilibrium, it can earn p ...
... SR and LR Equilibrium of a Firm in Perfect Competition The firm’s existing plant has short-run cost curves SRATC0 and MC0 while market price is p0. The firm produces q0, where MC0 equals price and total costs are just being covered. Although the firm is in short-run equilibrium, it can earn p ...
Q - people.vcu.edu
... resolved by the market. Complications: One solution by sellers is to force multiple purchases (e.g., Impose a price ceiling on rents, but then make people agree to unusual lease terms, or to purchase other high cost items along with the lease). In fact, it is possible that given rent controls, the n ...
... resolved by the market. Complications: One solution by sellers is to force multiple purchases (e.g., Impose a price ceiling on rents, but then make people agree to unusual lease terms, or to purchase other high cost items along with the lease). In fact, it is possible that given rent controls, the n ...