Economics: Today and Tomorrow
... quantity demanded rises and the quantity supplied falls (and vice versa). • The point at which the quantity demanded and quantity supplied meet is called the equilibrium price. ...
... quantity demanded rises and the quantity supplied falls (and vice versa). • The point at which the quantity demanded and quantity supplied meet is called the equilibrium price. ...
Managerial Economics MGCR 293 Practice
... b) What is the output level where average variable cost is a minimum? It is a minimum when dAVC/dQ = -7 +2Q = 0 Æ Q = 7/2 c) What is the value of average variable cost and marginal cost at the output specified in the answer part B? If Q = 7/2, average variable cost equals 65- 7(7/2) + (7/2)2 = 52.7 ...
... b) What is the output level where average variable cost is a minimum? It is a minimum when dAVC/dQ = -7 +2Q = 0 Æ Q = 7/2 c) What is the value of average variable cost and marginal cost at the output specified in the answer part B? If Q = 7/2, average variable cost equals 65- 7(7/2) + (7/2)2 = 52.7 ...
session_07_ch_8_perfect VIDEO LECTURE
... additional unit sold. MR = chg TR / chg q Because the perfectly competitive firm sells each additional unit at the same price, the Marginal Revenue Curve is the Demand Curve. Average Revenue is the ratio of total revenue to total quantity sold. It represents the average price received for each uni ...
... additional unit sold. MR = chg TR / chg q Because the perfectly competitive firm sells each additional unit at the same price, the Marginal Revenue Curve is the Demand Curve. Average Revenue is the ratio of total revenue to total quantity sold. It represents the average price received for each uni ...
Document
... In general, efficiency is the optimal use of societies scarce resources •Perfect Competition forces producers to use limited resources to their fullest. •Inefficient firms have higher costs and are the first to leave the industry. •Perfectly competitive industries are extremely efficient There are t ...
... In general, efficiency is the optimal use of societies scarce resources •Perfect Competition forces producers to use limited resources to their fullest. •Inefficient firms have higher costs and are the first to leave the industry. •Perfectly competitive industries are extremely efficient There are t ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES MEASURING THE WELFARE GAIN FROM PERSONAL COMPUTERS:
... Chatterjee (1994) and Rebelo (1992) employ such utility functions to model savings behavior. When < 0, so that there is a subsistence level of consumption, savings will be small at low levels of income. Kongsamut, Rebelo and Xie (2000) study long-run sectoral reallocations using such a utility funct ...
... Chatterjee (1994) and Rebelo (1992) employ such utility functions to model savings behavior. When < 0, so that there is a subsistence level of consumption, savings will be small at low levels of income. Kongsamut, Rebelo and Xie (2000) study long-run sectoral reallocations using such a utility funct ...
Document
... Air Sunshine has two types of customers, business travelers willing to pay $550 per ticket and students willing to pay $150 per ticket. There are 2,000 of each kind of customer. Air Sunshine has constant marginal cost of $125 per seat. If Air Sunshine could charge these two types of customers differ ...
... Air Sunshine has two types of customers, business travelers willing to pay $550 per ticket and students willing to pay $150 per ticket. There are 2,000 of each kind of customer. Air Sunshine has constant marginal cost of $125 per seat. If Air Sunshine could charge these two types of customers differ ...
PROFIT-MAXIMIZATION - Technical Supplement
... if Q = 3, then ΔTC/ΔQ = 18 if Q = 4, then ΔTC/ΔQ = 24 if Q = 5, then ΔTC/ΔQ = 30 if Q = 6, then ΔTC/ΔQ = 36 and so on. ΔTC/ΔQ is, of course, the marginal cost (MC). So the rising values (6, 12, 18, etc.) shows that the slope is steepening the more we produce (as we see intuitively in the diagram), ...
... if Q = 3, then ΔTC/ΔQ = 18 if Q = 4, then ΔTC/ΔQ = 24 if Q = 5, then ΔTC/ΔQ = 30 if Q = 6, then ΔTC/ΔQ = 36 and so on. ΔTC/ΔQ is, of course, the marginal cost (MC). So the rising values (6, 12, 18, etc.) shows that the slope is steepening the more we produce (as we see intuitively in the diagram), ...
chapter outline
... 6. Because the firm's marginal cost curve determines how much the firm is willing to supply at any price, it is the competitive firm's supply curve. C. The Firm's Short-Run Decision to Shut Down 1. In certain circumstances, a firm will decide to shut down and produce zero output. 2. There is a diffe ...
... 6. Because the firm's marginal cost curve determines how much the firm is willing to supply at any price, it is the competitive firm's supply curve. C. The Firm's Short-Run Decision to Shut Down 1. In certain circumstances, a firm will decide to shut down and produce zero output. 2. There is a diffe ...
Price Discrimination
... • The firm finds the total amount to produce by equating the marginal revenue and marginal cost in the market as a whole. This is labeled as QT. • If the firm were forced to charge a uniform price, it would find the price by examining the aggregate demand DT at the output level QT. This is represent ...
... • The firm finds the total amount to produce by equating the marginal revenue and marginal cost in the market as a whole. This is labeled as QT. • If the firm were forced to charge a uniform price, it would find the price by examining the aggregate demand DT at the output level QT. This is represent ...
Supply - Henry County Schools
... in Panel B of Figure 5.1. To draw it, we transfer each of the price-quantity observations in the schedule over to the graph, and then connect the points to form the curve. The result is a supply curve, a graph showing the various quantities supplied at each and every price that might prevail in the ...
... in Panel B of Figure 5.1. To draw it, we transfer each of the price-quantity observations in the schedule over to the graph, and then connect the points to form the curve. The result is a supply curve, a graph showing the various quantities supplied at each and every price that might prevail in the ...
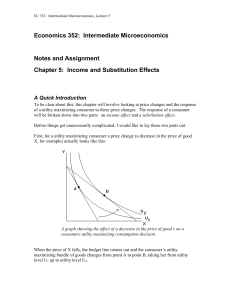
Chapter 5: Income and Substitution Effects
... substitution effect. This is called a Giffen good, which the textbook describes under the heading Giffen’s paradox. If the income effect is negative and outweighs or dominates the substitution effect, then it could be possible that a decrease in the price of X will lead to less, rather than more, X ...
... substitution effect. This is called a Giffen good, which the textbook describes under the heading Giffen’s paradox. If the income effect is negative and outweighs or dominates the substitution effect, then it could be possible that a decrease in the price of X will lead to less, rather than more, X ...
Lecture 8
... Policy makers may care about the consumption of particular goods, such as health care or housing. If we know income elasticities, we can predict the extent to which people buy more of these goods when they receive a cash grant incomes in general rise. ...
... Policy makers may care about the consumption of particular goods, such as health care or housing. If we know income elasticities, we can predict the extent to which people buy more of these goods when they receive a cash grant incomes in general rise. ...