
EC 220 Microeconomics - College of Micronesia
... This course aims to introduce to students the concepts of scarcity and choice, and their influences in the decision-making process of individual consumers, groups of consumers, and firms. The course examines: price mechanism (demand, supply and price) and allocation of resources; comparative advanta ...
... This course aims to introduce to students the concepts of scarcity and choice, and their influences in the decision-making process of individual consumers, groups of consumers, and firms. The course examines: price mechanism (demand, supply and price) and allocation of resources; comparative advanta ...
Economics-Semester-I(Sem-I)
... Definition of Economics, Nature & Scope of Economics, Branches of Economics, Importance and uses of Economics in Law Module 2 Theory of Demand & Supply Demand and Supply Theory, Law of Demand & Supply, Determinants of demand & supply Utility Analysis: Cardinal Utility (Marshall), Ordinal Utility App ...
... Definition of Economics, Nature & Scope of Economics, Branches of Economics, Importance and uses of Economics in Law Module 2 Theory of Demand & Supply Demand and Supply Theory, Law of Demand & Supply, Determinants of demand & supply Utility Analysis: Cardinal Utility (Marshall), Ordinal Utility App ...
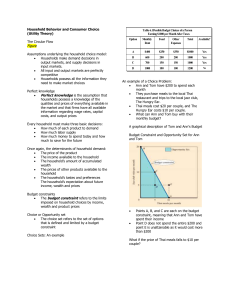
Household Behavior and Consumer Choice (Utility Theory) The
... Points A, B, and C are each on the budget constraint, meaning that Ann and Tom have spent their income Point D does not spend the entire $200 and point E is unattainable as it would cost more than $200 ...
... Points A, B, and C are each on the budget constraint, meaning that Ann and Tom have spent their income Point D does not spend the entire $200 and point E is unattainable as it would cost more than $200 ...
Ch08A-7e[1]
... enables us to derive the downward-sloping demand curve from the assumption of diminishing marginal rate of substitution. The model is also powerful because it implies that utility exists. By observing incomes and prices and the quantities bought at those prices, we can infer a person’s utility sched ...
... enables us to derive the downward-sloping demand curve from the assumption of diminishing marginal rate of substitution. The model is also powerful because it implies that utility exists. By observing incomes and prices and the quantities bought at those prices, we can infer a person’s utility sched ...
Continued …
... Given that the monopolist produces more than zero units, what output will it choose to produce if it seeks to maximise its profits and at what price will it sell this output. What is profit at this output? Would the monopolist be better off if he choose to produce zero units ...
... Given that the monopolist produces more than zero units, what output will it choose to produce if it seeks to maximise its profits and at what price will it sell this output. What is profit at this output? Would the monopolist be better off if he choose to produce zero units ...
The Forerunners of Marginalism
... This one-good-at-a-time approach is called partial equilibrium analysis. Assume that changes in that particular market will have no effect outside of that market. The monopoly pricing rule is the familiar condition that the price must be such that ...
... This one-good-at-a-time approach is called partial equilibrium analysis. Assume that changes in that particular market will have no effect outside of that market. The monopoly pricing rule is the familiar condition that the price must be such that ...
1 - Marshall University Personal Web Pages
... a. marginal utility from tacos decreases. b. marginal utility from tacos increases. c. total utility from tacos decreases then increase. d. both total and marginal utility from tacos decrease. 21. When a consumer spends all of his or her income and consumes a bundle of goods such that the marginal u ...
... a. marginal utility from tacos decreases. b. marginal utility from tacos increases. c. total utility from tacos decreases then increase. d. both total and marginal utility from tacos decrease. 21. When a consumer spends all of his or her income and consumes a bundle of goods such that the marginal u ...
Praxeology, Supply & Demand for Freedom University
... Market Demand—The total amount consumers are willing and able to purchase of a product at all possible prices, obtained by summing the quantities demanded at each price over all buyers. (Summed Horizontally) ...
... Market Demand—The total amount consumers are willing and able to purchase of a product at all possible prices, obtained by summing the quantities demanded at each price over all buyers. (Summed Horizontally) ...
No Slide Title
... If MU < P you will not buy that last hot dog ©1999 South-Western College Publishing ...
... If MU < P you will not buy that last hot dog ©1999 South-Western College Publishing ...
Name - Mr Wyka`s Weebly
... 2. ( ____/60) Use the chart regarding a perfectly competitive Yo-Yo factory to complete the following: a. Fully explain why the number of yo-yos produced increases at a decreasing rate as more workers are hired. Identify and explain the three stages of returns. ( ____/15) b. Explain how a firm decid ...
... 2. ( ____/60) Use the chart regarding a perfectly competitive Yo-Yo factory to complete the following: a. Fully explain why the number of yo-yos produced increases at a decreasing rate as more workers are hired. Identify and explain the three stages of returns. ( ____/15) b. Explain how a firm decid ...
Document
... Brandon also received a gift of $100 from his father who isn’t nearly as cautious about spending money as Brandon’s grandmother is. Brandon believes that it would somehow be wrong to spend his grandmother’s gift on frivolous things, but that it wouldn’t be wrong to spend his father’s gift on such th ...
... Brandon also received a gift of $100 from his father who isn’t nearly as cautious about spending money as Brandon’s grandmother is. Brandon believes that it would somehow be wrong to spend his grandmother’s gift on frivolous things, but that it wouldn’t be wrong to spend his father’s gift on such th ...
Consumer Choice
... willing to pay for it. – Utility: the pleasure or satisfaction obtained from using a good or service. – Total utility: the amount of satisfaction obtained from the consumption of a series of products. – Marginal utility: the change in total utility obtained by consuming one additional (marginal) uni ...
... willing to pay for it. – Utility: the pleasure or satisfaction obtained from using a good or service. – Total utility: the amount of satisfaction obtained from the consumption of a series of products. – Marginal utility: the change in total utility obtained by consuming one additional (marginal) uni ...
first exam review (without color)
... - Externality – definition – how does it affect what should happen to demand for a supply or private good to assure efficient allocation of resources - Be able to solve for effects of externality and imposing marginal social costs from it on market - What was the point of environmental costing in th ...
... - Externality – definition – how does it affect what should happen to demand for a supply or private good to assure efficient allocation of resources - Be able to solve for effects of externality and imposing marginal social costs from it on market - What was the point of environmental costing in th ...
ECONOMICS THE CONCEPT OF UTILITY LAW OF DIMINISHING
... From the above diagram, it is observed that when Q, yields MU5, the consumer is willing to pay as much as N5 (price) From the diagrams and table 2 above, it is observed that the first unit of the commodity (i.e quantity demanded) yields highest rate of utility (i.e MU5). The consumer is willing to ...
... From the above diagram, it is observed that when Q, yields MU5, the consumer is willing to pay as much as N5 (price) From the diagrams and table 2 above, it is observed that the first unit of the commodity (i.e quantity demanded) yields highest rate of utility (i.e MU5). The consumer is willing to ...
Utility, Wages, and Externalities (Micro Review
... • The individual firm in a perfectly competitive firm maximizes profit by hiring workers to the point where Wage rate = MRP ...
... • The individual firm in a perfectly competitive firm maximizes profit by hiring workers to the point where Wage rate = MRP ...

![Ch08A-7e[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008349098_2-8d04a5bee5f641b6234688b1f7420f1b-300x300.png)




















