Quiz 9
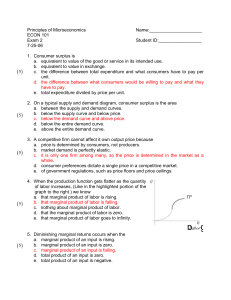
... If a firm’s marginal revenue is above its marginal cost, an increase in production will usually a. increase profits. b. leave profits unchanged. c. decrease profits. d. increase marginal revenue. ...
... If a firm’s marginal revenue is above its marginal cost, an increase in production will usually a. increase profits. b. leave profits unchanged. c. decrease profits. d. increase marginal revenue. ...
Quiz 11
... If a firm’s marginal revenue is above its marginal cost, an increase in production will usually a. increase profits. b. leave profits unchanged. c. decrease profits. d. increase marginal revenue. ...
... If a firm’s marginal revenue is above its marginal cost, an increase in production will usually a. increase profits. b. leave profits unchanged. c. decrease profits. d. increase marginal revenue. ...
In Utils
... peanuts and bananas is positive. A widespread disease has destroyed the banana crop. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of peanuts in the short run? Explain. ...
... peanuts and bananas is positive. A widespread disease has destroyed the banana crop. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of peanuts in the short run? Explain. ...
AP Economics Syllabus 2016-2017
... "Nobody spends somebody else's money as carefully as he spends his own. Nobody uses somebody else's resources as carefully as he uses his own. So if you want efficiency and effectiveness, if you want knowledge to be properly utilized, you have to do it through the means of private property." - Milto ...
... "Nobody spends somebody else's money as carefully as he spends his own. Nobody uses somebody else's resources as carefully as he uses his own. So if you want efficiency and effectiveness, if you want knowledge to be properly utilized, you have to do it through the means of private property." - Milto ...
Chapter 16 Key Question Solutions
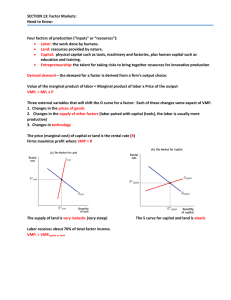
... summation of these curves. The market demand curve for the private good will determine—in combination with market supply—an actual price-quantity outcome in the marketplace. Because potential buyers of public goods do not reveal their individual preferences in the market, the collective demand curve ...
... summation of these curves. The market demand curve for the private good will determine—in combination with market supply—an actual price-quantity outcome in the marketplace. Because potential buyers of public goods do not reveal their individual preferences in the market, the collective demand curve ...
FINAL study guide
... Law of supply/demand Elasticity Demand elasticity Inelastic demand Elastic demand Unit elastic Substitutes compliments Change in quantity demand/supply Change/shift in demand/supply Subsidy Demand/supply curve Market equilibrium Equilibrium price/quantity Surplus Shortage Marginal utility Increasing ...
... Law of supply/demand Elasticity Demand elasticity Inelastic demand Elastic demand Unit elastic Substitutes compliments Change in quantity demand/supply Change/shift in demand/supply Subsidy Demand/supply curve Market equilibrium Equilibrium price/quantity Surplus Shortage Marginal utility Increasing ...