Role of large scale Ocean-Atmosphere interactions in the
... The surface warming due to +4Wm-2 (anthropogenic forcing) is not limited to the mixed layer. Heat exchanges between the mixed layer and deeper layers control the timescale of the surface warming. ...
... The surface warming due to +4Wm-2 (anthropogenic forcing) is not limited to the mixed layer. Heat exchanges between the mixed layer and deeper layers control the timescale of the surface warming. ...
Unit 1
... This unit deals with the basic aspects of the geology of the sea floor and points out its relevance to marine biology. The basic structural features of the ocean basins and the earth are described. The theory of plate tectonics is discussed as the mechanism for the creation of the sea floor and the ...
... This unit deals with the basic aspects of the geology of the sea floor and points out its relevance to marine biology. The basic structural features of the ocean basins and the earth are described. The theory of plate tectonics is discussed as the mechanism for the creation of the sea floor and the ...
THE BIG EVENT Oceans Fact Sheet
... Vast in scope and size, there is only one true ocean on Earth. This connected body of water surrounds the continents and is divided into five major regions: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern oceans. Taken together, the oceans cover more than 70 percent of the Earth's surface and gi ...
... Vast in scope and size, there is only one true ocean on Earth. This connected body of water surrounds the continents and is divided into five major regions: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern oceans. Taken together, the oceans cover more than 70 percent of the Earth's surface and gi ...
Impact of ocean stratification on small
... Physical forcing of the surface ocean includes a variety of energetic processes, ranging from internal wave (IW) to submesoscale and mesoscale. Recent works based on acoustic data showed that, off Peru, the vertical displacements of the oxycline depth provide a robust proxy of isopycnals displacemen ...
... Physical forcing of the surface ocean includes a variety of energetic processes, ranging from internal wave (IW) to submesoscale and mesoscale. Recent works based on acoustic data showed that, off Peru, the vertical displacements of the oxycline depth provide a robust proxy of isopycnals displacemen ...
Plate Tectonics Chapter 1 Study Guide Section 1 Earth`s Interior In
... How does the temperature change as you go from the surface toward the center of the Earth? ________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ waves ...
... How does the temperature change as you go from the surface toward the center of the Earth? ________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ waves ...
Eighth Grade Field Trip Worksheet
... Zone and Deep Reef. Draw these animals and write where you're likely to see them and why. ...
... Zone and Deep Reef. Draw these animals and write where you're likely to see them and why. ...
El Niño and La Niña events
... El Niño and La Niña events are a natural part of the global climate system. They occur when the Pacific Ocean and the atmosphere above it change from their neutral ('normal') state for several seasons. El Niño events are associated with a warming of the central and eastern tropical Pacific, while L ...
... El Niño and La Niña events are a natural part of the global climate system. They occur when the Pacific Ocean and the atmosphere above it change from their neutral ('normal') state for several seasons. El Niño events are associated with a warming of the central and eastern tropical Pacific, while L ...
Worksheet 11.1 Oceans: Environment for Life
... 22. What are two roles that dissolved carbon dioxide gas plays in the ocean? 23. Plant live is restricted to the ______________ zone, which has a depth of about ____________ in clear ocean water. 24. Would you expect the photic zone to be deeper at the equator or the high latitudes near the poles if ...
... 22. What are two roles that dissolved carbon dioxide gas plays in the ocean? 23. Plant live is restricted to the ______________ zone, which has a depth of about ____________ in clear ocean water. 24. Would you expect the photic zone to be deeper at the equator or the high latitudes near the poles if ...
The Hadean Eon
... Oldest moon rocks = 4.5 Ga and 3.9 Ga • moon formed shortly after the Earth • lunar surface records events from the Hadean • intense meteoric bombardment from 4.0 to 3.9 Ga - Late Heavy Bombardment. ...
... Oldest moon rocks = 4.5 Ga and 3.9 Ga • moon formed shortly after the Earth • lunar surface records events from the Hadean • intense meteoric bombardment from 4.0 to 3.9 Ga - Late Heavy Bombardment. ...
Unit 3 - Jeopardy Physical Geography
... the Earth, (2) latitude and the size of the land mass to be heated and (3) volume of atmosphere heat must pass through to reach Earth is greater at North Pole? ...
... the Earth, (2) latitude and the size of the land mass to be heated and (3) volume of atmosphere heat must pass through to reach Earth is greater at North Pole? ...
The Structure and Origin of the Ocean Basins The water Planet
... Shouldn’t our planet be called “Water” rather than “Earth”? If you look at a world map in an atlas, you will see that there is more water than land. • The oceans cover about 71% of the earth's surface. They are not distributed equally with respect to the Equator. • Southern Hemisphere: ~ 80% is ocea ...
... Shouldn’t our planet be called “Water” rather than “Earth”? If you look at a world map in an atlas, you will see that there is more water than land. • The oceans cover about 71% of the earth's surface. They are not distributed equally with respect to the Equator. • Southern Hemisphere: ~ 80% is ocea ...
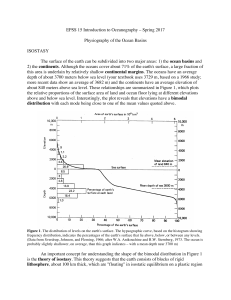
EPSS 15 Introduction to Oceanography – Spring 2017 Physiography
... Submarine canyons are steep-walled, V-shaped valleys that incise into continental shelves and slopes and open out at depth onto the continental rise. Most submarine canyons are associated with the mouths of large rivers. Although their origin is still debated, submarine canyons are important here be ...
... Submarine canyons are steep-walled, V-shaped valleys that incise into continental shelves and slopes and open out at depth onto the continental rise. Most submarine canyons are associated with the mouths of large rivers. Although their origin is still debated, submarine canyons are important here be ...
Continental Drift
... • The north magnetic pole had clearly wandered over time. • More surprisingly, the path it seemed to have followed was different in Europe than in North America. ...
... • The north magnetic pole had clearly wandered over time. • More surprisingly, the path it seemed to have followed was different in Europe than in North America. ...
EARTH, ATMOSPHERIC, OCEAN AND PLANETARY SCIENCES
... The mixing time of deep ocean water is about 1000 years. Therefore, elements such Na, Mg, P and Si having residence limits significantly longer than 1000 years should be homogeneously distributed in the ocean. Which one of the following sets of elements is non homogeneously distributed ...
... The mixing time of deep ocean water is about 1000 years. Therefore, elements such Na, Mg, P and Si having residence limits significantly longer than 1000 years should be homogeneously distributed in the ocean. Which one of the following sets of elements is non homogeneously distributed ...
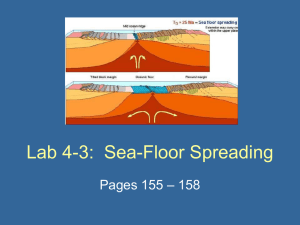
Lab 4-3: Sea-Floor Spreading
... Vocab • Sea-Floor Spreading: – Ocean crust is created at a divergent boundary as plates pull apart and molten material rises from deep within the Earth. ...
... Vocab • Sea-Floor Spreading: – Ocean crust is created at a divergent boundary as plates pull apart and molten material rises from deep within the Earth. ...
Earth Science Chapter 20
... continental shelf is a steeper slope called the continental slope. • Boundary between the continental crust and the oceanic crust is found at the base of the continental slope. • Continental shelf & continental slope may be cut by deep V-shaped valleys. ...
... continental shelf is a steeper slope called the continental slope. • Boundary between the continental crust and the oceanic crust is found at the base of the continental slope. • Continental shelf & continental slope may be cut by deep V-shaped valleys. ...
Evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading
... process of sea-floor spreading? • At the mid-ocean ridge, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. • Over tens of millions of years, the process continues until the oldest ocean floor collides with the cont ...
... process of sea-floor spreading? • At the mid-ocean ridge, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. • Over tens of millions of years, the process continues until the oldest ocean floor collides with the cont ...
To change the ocean water density we can: provide heating/cooling
... Water mass transformation by surface density flux Integration in space and time of the density flux gives the transformation rate of waters at given density, F(ρ), which represents the time average over a period T (generally one year) of the density change of a unit water volume of density ρ which ...
... Water mass transformation by surface density flux Integration in space and time of the density flux gives the transformation rate of waters at given density, F(ρ), which represents the time average over a period T (generally one year) of the density change of a unit water volume of density ρ which ...
Ocean

An ocean (from Ancient Greek Ὠκεανός, transc. Okeanós, the sea of classical antiquity) is a body of saline water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere. On Earth, an ocean is one of the major conventional divisions of the World Ocean, which covers almost 71% of its surface. These are, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. The word sea is often used interchangeably with ""ocean"" in American English but, strictly speaking, a sea is a body of saline water (generally a division of the world ocean) partly or fully enclosed by land.Saline water covers approximately 72% of the planet's surface (~3.6×108 km2) and is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas, with the ocean covering approximately 71% of Earth's surface. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water, and oceanographers have stated that only 5% of the World Ocean has been explored. The total volume is approximately 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (320 million cu mi) with an average depth of nearly 3,700 meters (12,100 ft).As it is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, the world ocean is integral to all known life, forms part of the carbon cycle, and influences climate and weather patterns. It is the habitat of 230,000 known species, although much of the oceans depths remain unexplored, and over two million marine species are estimated to exist. The origin of Earth's oceans remains unknown; oceans are thought to have formed in the Hadean period and may have been the impetus for the emergence of life.Extraterrestrial oceans may be composed of water or other elements and compounds. The only confirmed large stable bodies of extraterrestrial surface liquids are the lakes of Titan, although there is evidence for the existence of oceans elsewhere in the Solar System. Early in their geologic histories, Mars and Venus are theorized to have had large water oceans. The Mars ocean hypothesis suggests that nearly a third of the surface of Mars was once covered by water, and a runaway greenhouse effect may have boiled away the global ocean of Venus. Compounds such as salts and ammonia dissolved in water lower its freezing point, so that water might exist in large quantities in extraterrestrial environments as brine or convecting ice. Unconfirmed oceans are speculated beneath the surface of many dwarf planets and natural satellites; notably, the ocean of Europa is estimated to have over twice the water volume of Earth. The Solar System's giant planets are also thought to have liquid atmospheric layers of yet to be confirmed compositions. Oceans may also exist on exoplanets and exomoons, including surface oceans of liquid water within a circumstellar habitable zone. Ocean planets are a hypothetical type of planet with a surface completely covered with liquid.