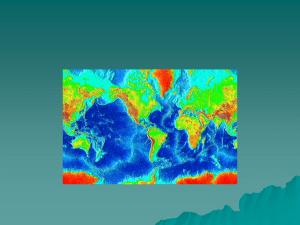
Ocean Crust Ages Lecture Tutorial
... Africa. Would you fund this project? Use the age of the ocean crust to support your answer. ...
... Africa. Would you fund this project? Use the age of the ocean crust to support your answer. ...
Chapter_2_Section_2_NOTES
... Forces that wear down and __break apart _____ the Earth’s crust. a. Weathering: _the process that breaks rocks down into tiny pieces Caused by: _water, ice, and living things (lichens) Helps create: ___soil ___ b. Erosion: __removal of small pieces of rock by water, ice, and wind. Creates ___new lan ...
... Forces that wear down and __break apart _____ the Earth’s crust. a. Weathering: _the process that breaks rocks down into tiny pieces Caused by: _water, ice, and living things (lichens) Helps create: ___soil ___ b. Erosion: __removal of small pieces of rock by water, ice, and wind. Creates ___new lan ...
Sea-Floor Spreading
... by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle. ...
... by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle. ...
Discovery Education: Earth`s Spheres interactive text
... where life can exist. It forms a narrow layer ranging from approximately 11 km beneath the ocean’s surface to 9 km in the air. It extends from the equator to the polar ice caps. Thus, the biosphere consists of parts of the geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Why does life exist where it does on ...
... where life can exist. It forms a narrow layer ranging from approximately 11 km beneath the ocean’s surface to 9 km in the air. It extends from the equator to the polar ice caps. Thus, the biosphere consists of parts of the geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Why does life exist where it does on ...
Continental Margins and Ocean Basins
... More than 0.6 miles high Many form at hotspots, but others have formed at spreading centers Movement of the plates has moved them away from their original location About 10,000 occur in the Pacific Ocean ...
... More than 0.6 miles high Many form at hotspots, but others have formed at spreading centers Movement of the plates has moved them away from their original location About 10,000 occur in the Pacific Ocean ...
File
... In the 1960’s Princeton professor H.H. Hess came up with the concept of convection cells – moving mantle patterns that pushed magma up for form ...
... In the 1960’s Princeton professor H.H. Hess came up with the concept of convection cells – moving mantle patterns that pushed magma up for form ...
Windsor High School Katers Earth and Space Science A Windsor
... C1. Name the major gases, and their percent C2. Describe physical properties of atmospheric gases C3. Name the layers of the atmosphere, from Earth up, and explain how the layers are determined C4. Describe the importance of the troposphere to the formation of weather C5. Describe air pressure and i ...
... C1. Name the major gases, and their percent C2. Describe physical properties of atmospheric gases C3. Name the layers of the atmosphere, from Earth up, and explain how the layers are determined C4. Describe the importance of the troposphere to the formation of weather C5. Describe air pressure and i ...
Landforms - Rankin County School District / Homepage
... • Geology- the study of Earth’s physical structures and the processes that have created them • Forces below Earth’s surface are key to shaping landforms • Four important zones in Earth’s Interior – Core-Center: like a nuclear furnace, divided into inner(solid) and outer core (dense liquid metal) – M ...
... • Geology- the study of Earth’s physical structures and the processes that have created them • Forces below Earth’s surface are key to shaping landforms • Four important zones in Earth’s Interior – Core-Center: like a nuclear furnace, divided into inner(solid) and outer core (dense liquid metal) – M ...
Unit 3 : Oceans
... At deeper levels, ocean mixing is caused by differences in density between colder, saltier water and warmer, fresher water. Because the density of water increases as it becomes colder and saltier, it sinks at high latitudes and is replaced by warm water flowing northward from the tropics. (This pat ...
... At deeper levels, ocean mixing is caused by differences in density between colder, saltier water and warmer, fresher water. Because the density of water increases as it becomes colder and saltier, it sinks at high latitudes and is replaced by warm water flowing northward from the tropics. (This pat ...
Life on the sea floor - National Oceanography Centre
... cracks in the Earth’s crust where very hot water escapes after being heated in the rocks below. These vents are most often found along mid ocean ridges where the plates of the Earth’s crust are slowly being pulled apart and molten lava from below forms new crust. The first hydrothermal vent was disc ...
... cracks in the Earth’s crust where very hot water escapes after being heated in the rocks below. These vents are most often found along mid ocean ridges where the plates of the Earth’s crust are slowly being pulled apart and molten lava from below forms new crust. The first hydrothermal vent was disc ...
deep ocean/high seas resource use: understanding the legal issues
... Webinar on “The Legal Implications of Deep Ocean Resource Exploration and Extraction” 31 March 2017 27 March 2017 The World Ocean Council (WOC) continues to provide information to the ocean business community on the legal and policy aspects of ocean sustainable development. The WOC is pleased to ann ...
... Webinar on “The Legal Implications of Deep Ocean Resource Exploration and Extraction” 31 March 2017 27 March 2017 The World Ocean Council (WOC) continues to provide information to the ocean business community on the legal and policy aspects of ocean sustainable development. The WOC is pleased to ann ...
Plate Tectonics
... Plate tectonics=The Earth's surface is made up of moving plates According to this theory, the Earth's crust….. is made up of about a dozen plates, some are little and others ...
... Plate tectonics=The Earth's surface is made up of moving plates According to this theory, the Earth's crust….. is made up of about a dozen plates, some are little and others ...
to Ch. 14, 16 Notes
... 21. ocean current: mass of ocean water that flows from one place to another 22. surface current: movement of water that flows horizontally in the upper part of the ocean’s surface 23. gyre: the large circular surface current pattern found in each ocean 24. Coriolis Effect: the apparent deflection of ...
... 21. ocean current: mass of ocean water that flows from one place to another 22. surface current: movement of water that flows horizontally in the upper part of the ocean’s surface 23. gyre: the large circular surface current pattern found in each ocean 24. Coriolis Effect: the apparent deflection of ...
Do You Know Where You Are - New York Geographic Alliance
... learning “location words,” such as “next to,” “inside of,” and “in between.” Then you can progress to directional words (“north” and “southeast”). The maps included in this lesson and in the Atlas of New York: Legacies of the Erie Canal should help develop these important geographic skills. 1. World ...
... learning “location words,” such as “next to,” “inside of,” and “in between.” Then you can progress to directional words (“north” and “southeast”). The maps included in this lesson and in the Atlas of New York: Legacies of the Erie Canal should help develop these important geographic skills. 1. World ...
Thursday 1-31 ps - elyceum-beta
... • Age of ocean rock vs continental rock Max age of ocean crust 175 million, max age of continental crust around 4 billion • The existence of ridges in the middle of the oceans ...
... • Age of ocean rock vs continental rock Max age of ocean crust 175 million, max age of continental crust around 4 billion • The existence of ridges in the middle of the oceans ...
GEOSPHERE The geosphere is the Earth itself, the rocks, minerals
... Additionally, advances in geothermal technology will enable us to harness greater amounts of heat energy within the crust, which can be converted to electricity at the surface. ...
... Additionally, advances in geothermal technology will enable us to harness greater amounts of heat energy within the crust, which can be converted to electricity at the surface. ...
- Catalyst
... temperature curve has a steeper slope compared to the geothermal gradient. The outer core is liquid because the actual temperature is greater than the melting temperature of iron-nickel for this depth (pressure). The opposite is true for the inner core. You can use a similar example for the partial ...
... temperature curve has a steeper slope compared to the geothermal gradient. The outer core is liquid because the actual temperature is greater than the melting temperature of iron-nickel for this depth (pressure). The opposite is true for the inner core. You can use a similar example for the partial ...
Earth`s Oceans Power Point
... currents are caused mainly by differences in water density. The cold, salty water, that is more dense, flowing from the polar regions moves under the less dense water away from the polar regions. Most deep currents flow in the opposite direction from surface currents. ...
... currents are caused mainly by differences in water density. The cold, salty water, that is more dense, flowing from the polar regions moves under the less dense water away from the polar regions. Most deep currents flow in the opposite direction from surface currents. ...
Practice Final Exam – Oceanography – Spring 2011 Part A – The
... 77) The area of the ocean that produces the largest standing stock of commercial fish is in the: A) coastal areas. B) epipelagic zone. C) mesopelagic zone. D) tropical areas. E) upwelling areas. 78) The term by-catch refers to: A) krill and other shellfish. B) non-target species that are caught alon ...
... 77) The area of the ocean that produces the largest standing stock of commercial fish is in the: A) coastal areas. B) epipelagic zone. C) mesopelagic zone. D) tropical areas. E) upwelling areas. 78) The term by-catch refers to: A) krill and other shellfish. B) non-target species that are caught alon ...
Volcanoes
... 13. Compare the planets of Venus and Mars to Earth. Venus is hot, VERY HOT 100s of degrees hot – Too much CO2 (greenhouse gasses) Mars is a cold dry rock – lacks CO2 (greenhouse gasses) 14. What crisis did our planet face about 700 million years ago? What is its nickname? The Earth was completely fr ...
... 13. Compare the planets of Venus and Mars to Earth. Venus is hot, VERY HOT 100s of degrees hot – Too much CO2 (greenhouse gasses) Mars is a cold dry rock – lacks CO2 (greenhouse gasses) 14. What crisis did our planet face about 700 million years ago? What is its nickname? The Earth was completely fr ...
Glossary for Plate tectonics and associated hazards
... Surface seismic waves which cause the round to move up and down the average period of time between earthquakes in a seismic region A scale to measure the magnitude of earthquakes. It is a logarithmic scale where 6.0 is ten times greater than 5.0 Forms where two parallel down faults have formed a tro ...
... Surface seismic waves which cause the round to move up and down the average period of time between earthquakes in a seismic region A scale to measure the magnitude of earthquakes. It is a logarithmic scale where 6.0 is ten times greater than 5.0 Forms where two parallel down faults have formed a tro ...
Earth Science 16.1 Ocean Circulation
... density of water in the world. This cold salty water sinks to the sea floor, where it moves throughout the ocean basins in slow currents. After sinking from the surface of the ocean, deep waters will not reappear at the surface for an average of 500 to 2000 years. ...
... density of water in the world. This cold salty water sinks to the sea floor, where it moves throughout the ocean basins in slow currents. After sinking from the surface of the ocean, deep waters will not reappear at the surface for an average of 500 to 2000 years. ...
Ocean

An ocean (from Ancient Greek Ὠκεανός, transc. Okeanós, the sea of classical antiquity) is a body of saline water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere. On Earth, an ocean is one of the major conventional divisions of the World Ocean, which covers almost 71% of its surface. These are, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. The word sea is often used interchangeably with ""ocean"" in American English but, strictly speaking, a sea is a body of saline water (generally a division of the world ocean) partly or fully enclosed by land.Saline water covers approximately 72% of the planet's surface (~3.6×108 km2) and is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas, with the ocean covering approximately 71% of Earth's surface. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water, and oceanographers have stated that only 5% of the World Ocean has been explored. The total volume is approximately 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (320 million cu mi) with an average depth of nearly 3,700 meters (12,100 ft).As it is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, the world ocean is integral to all known life, forms part of the carbon cycle, and influences climate and weather patterns. It is the habitat of 230,000 known species, although much of the oceans depths remain unexplored, and over two million marine species are estimated to exist. The origin of Earth's oceans remains unknown; oceans are thought to have formed in the Hadean period and may have been the impetus for the emergence of life.Extraterrestrial oceans may be composed of water or other elements and compounds. The only confirmed large stable bodies of extraterrestrial surface liquids are the lakes of Titan, although there is evidence for the existence of oceans elsewhere in the Solar System. Early in their geologic histories, Mars and Venus are theorized to have had large water oceans. The Mars ocean hypothesis suggests that nearly a third of the surface of Mars was once covered by water, and a runaway greenhouse effect may have boiled away the global ocean of Venus. Compounds such as salts and ammonia dissolved in water lower its freezing point, so that water might exist in large quantities in extraterrestrial environments as brine or convecting ice. Unconfirmed oceans are speculated beneath the surface of many dwarf planets and natural satellites; notably, the ocean of Europa is estimated to have over twice the water volume of Earth. The Solar System's giant planets are also thought to have liquid atmospheric layers of yet to be confirmed compositions. Oceans may also exist on exoplanets and exomoons, including surface oceans of liquid water within a circumstellar habitable zone. Ocean planets are a hypothetical type of planet with a surface completely covered with liquid.