It`s getting hot in here
... destructive. In many cases, these lava flows are slow and continuous but volcanoes can also erupt with unbelievable force and power. These types of eruptions can send lava, rock, and hot ash, known as pyroclastic material shooting outward for hundreds of square miles, in some cases, even sending up ...
... destructive. In many cases, these lava flows are slow and continuous but volcanoes can also erupt with unbelievable force and power. These types of eruptions can send lava, rock, and hot ash, known as pyroclastic material shooting outward for hundreds of square miles, in some cases, even sending up ...
7th Grade Science Chapter 9 Answers
... explosive eruptions. The volcano forms a steep slope with a narrow base. These volcanoes erode quickly because the pyroclastic material particles are not cemented by lava. Composite Volcano - Also known as Stratovolcano, are the most common type of volcano. Composite volcanoes are formed by explosiv ...
... explosive eruptions. The volcano forms a steep slope with a narrow base. These volcanoes erode quickly because the pyroclastic material particles are not cemented by lava. Composite Volcano - Also known as Stratovolcano, are the most common type of volcano. Composite volcanoes are formed by explosiv ...
Volcanoes
... 3 Transform (strike-slip) boundary - sliding mostly horizontally along faults (such as San Andreas Fault) - adjacent plates (usually microplates) slide past each other. The ocean floor spreading causes a symmetric age distribution of the ocean floor around the midoceanic ridge. The age and sediment ...
... 3 Transform (strike-slip) boundary - sliding mostly horizontally along faults (such as San Andreas Fault) - adjacent plates (usually microplates) slide past each other. The ocean floor spreading causes a symmetric age distribution of the ocean floor around the midoceanic ridge. The age and sediment ...
5- Volcanism
... Rather than being distributed randomly around the Earth, volcanoes occur in well-defined zones or belts. More than 60% of all active volcanoes are in the circum-Pacific belt that nearly encircles the margins of the Pacific Ocean basin (~ Figure 5-16). This belt includes the volcanoes along the west ...
... Rather than being distributed randomly around the Earth, volcanoes occur in well-defined zones or belts. More than 60% of all active volcanoes are in the circum-Pacific belt that nearly encircles the margins of the Pacific Ocean basin (~ Figure 5-16). This belt includes the volcanoes along the west ...
What Erupts from a Volcano?
... of volcanoes. One theory is that the mantle plume stays in the same spot while the tectonic plates move over it. • Other scientists think that hot spots are the result of cracks in the Earth’s crust. • The theory argues that hot-spot volcanoes occur in chains because they form along the cracks in th ...
... of volcanoes. One theory is that the mantle plume stays in the same spot while the tectonic plates move over it. • Other scientists think that hot spots are the result of cracks in the Earth’s crust. • The theory argues that hot-spot volcanoes occur in chains because they form along the cracks in th ...
Earthquakes
... Plate movements usually happen far below ground. The point beneath the Earth’s surface where the rocks break is called the focus – the origin of the earthquake. ...
... Plate movements usually happen far below ground. The point beneath the Earth’s surface where the rocks break is called the focus – the origin of the earthquake. ...
File
... – In the earliest stage of Earth’s history, internal thermal energy was generated from gravitational force, the decay of radioactive elements and extraterrestrial impacts. • Describe natural processes in which heat transfer in the Earth occurs by conduction, convection, and radiation. – Convection o ...
... – In the earliest stage of Earth’s history, internal thermal energy was generated from gravitational force, the decay of radioactive elements and extraterrestrial impacts. • Describe natural processes in which heat transfer in the Earth occurs by conduction, convection, and radiation. – Convection o ...
Causes of Volcanic Eruptions
... boundary, tectonic plates move away from each other. B. Mid-Ocean Ridges Form at Divergent Boundaries Most volcanic activity on Earth occurs at mid-ocean ridges. The next slide shows how magma forms at divergent boundaries such as those found along midocean ridges. ...
... boundary, tectonic plates move away from each other. B. Mid-Ocean Ridges Form at Divergent Boundaries Most volcanic activity on Earth occurs at mid-ocean ridges. The next slide shows how magma forms at divergent boundaries such as those found along midocean ridges. ...
Notes - Volcanoes
... • A volcano is a weak spot in the crust where molten material, magma, from the mantle comes to Earth’s surface. – Magma – a molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases and water. • When magma reaches the surface of Earth it is called ...
... • A volcano is a weak spot in the crust where molten material, magma, from the mantle comes to Earth’s surface. – Magma – a molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases and water. • When magma reaches the surface of Earth it is called ...
Plate tectonics theory
... several plates that drift upon the mantel. On the edge of the plates the plates move together and away from each other and by doing so they either push magma to the surface, creating new land, or push solid rock under the surface to sustain the circulation. This results in earthquakes, volcanic erup ...
... several plates that drift upon the mantel. On the edge of the plates the plates move together and away from each other and by doing so they either push magma to the surface, creating new land, or push solid rock under the surface to sustain the circulation. This results in earthquakes, volcanic erup ...
Inside the Earth, Why do the plates move?
... Plate Tectonics and Plate Boundaries The earth’s surface is divided up into plates or giant slabs like the pieces in a giant puzzle which are floating on the liquid mantle and moving around due to the convection currents. Sometimes the plates are moving apart and sometimes they move together. ...
... Plate Tectonics and Plate Boundaries The earth’s surface is divided up into plates or giant slabs like the pieces in a giant puzzle which are floating on the liquid mantle and moving around due to the convection currents. Sometimes the plates are moving apart and sometimes they move together. ...
revision-tectonic-landscapes-gcse
... What can be done to limit the effects of volcanic eruptions (6) 1- Hazard map: Three Zones have been defined in Montserrat after the first eruption in 1995 including an exclusion zone in the south with no admittance except for scientific monitoring and National Security Matters. 2- Three ways to di ...
... What can be done to limit the effects of volcanic eruptions (6) 1- Hazard map: Three Zones have been defined in Montserrat after the first eruption in 1995 including an exclusion zone in the south with no admittance except for scientific monitoring and National Security Matters. 2- Three ways to di ...
Easton
... I want to thank you for allowing me the opportunity to work on the Musical Plates Project. This project became more exciting and fun on a daily basis, as I was able to identify specific earthquake’s demonstrating more movement than other’s, from around the globe. The enclosed data represents the maj ...
... I want to thank you for allowing me the opportunity to work on the Musical Plates Project. This project became more exciting and fun on a daily basis, as I was able to identify specific earthquake’s demonstrating more movement than other’s, from around the globe. The enclosed data represents the maj ...
CHAPTER 9 STUDY GUIDE Test Date: 11/15
... tectonic plates scraping against each other causes the temperature and pressure to increase. This in turn causes the water to be released from the oceanic plate which lowers the melting point and allows the rock in the mantle to melt. This new body of magma can rise, because it is less dense than th ...
... tectonic plates scraping against each other causes the temperature and pressure to increase. This in turn causes the water to be released from the oceanic plate which lowers the melting point and allows the rock in the mantle to melt. This new body of magma can rise, because it is less dense than th ...
Unit 2: Plate Tectonics Test Review
... What are the 3 types of seismic waves that move through Earth when an earthquake occurs? ...
... What are the 3 types of seismic waves that move through Earth when an earthquake occurs? ...
Unit 2 Review
... What are the 3 types of seismic waves that move through Earth when an earthquake occurs? ...
... What are the 3 types of seismic waves that move through Earth when an earthquake occurs? ...
Ready Set Go for teachers
... 27. Where do a large number of volcanoes occur? Directly on tectonic plate ...
... 27. Where do a large number of volcanoes occur? Directly on tectonic plate ...
Volcanic landforms
... Task 1: Find the meaning of the underlined words and check the correct pronunciation. Task 2: Fill in the gaps in the text about Krakatau. Of all the earth processes, volcanic activity is certainly among the most powerful. By means of volcanic activity, people are able to witness the active transfer ...
... Task 1: Find the meaning of the underlined words and check the correct pronunciation. Task 2: Fill in the gaps in the text about Krakatau. Of all the earth processes, volcanic activity is certainly among the most powerful. By means of volcanic activity, people are able to witness the active transfer ...
Living in an Active Zone
... • The subduction of the oceanic crust creates a deep sea trench and earthquakes are formed at the subduction zone. • Fold mountains are created on the continental crust . • The subducted oceanic crust melts in the mantle rising up into the fold mountain to create composite volcanoes • E.g. Mount St ...
... • The subduction of the oceanic crust creates a deep sea trench and earthquakes are formed at the subduction zone. • Fold mountains are created on the continental crust . • The subducted oceanic crust melts in the mantle rising up into the fold mountain to create composite volcanoes • E.g. Mount St ...
Volcanos - High View School
... bowl or shield in the middle with long gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows. (Basalt lava is where magma contains partially melted rock). Lava domes are formed when erupting lava is too thick to flow and makes a steep-sided mound as the lava piles up near the volcanic vent. The eruption of Moun ...
... bowl or shield in the middle with long gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows. (Basalt lava is where magma contains partially melted rock). Lava domes are formed when erupting lava is too thick to flow and makes a steep-sided mound as the lava piles up near the volcanic vent. The eruption of Moun ...
Volcanoes
... Volcanic eruptions can develop into three different types of volcanic mountains, depending on the nature of the volcanic material. A shield cone is a volcanic mountain that is built almost entirely of lava flow. The slopes of a shield cone volcano are very gentle and rounded like a warrior's shield. ...
... Volcanic eruptions can develop into three different types of volcanic mountains, depending on the nature of the volcanic material. A shield cone is a volcanic mountain that is built almost entirely of lava flow. The slopes of a shield cone volcano are very gentle and rounded like a warrior's shield. ...
Volcanoes
... Volcanic eruptions can develop into three different types of volcanic mountains, depending on the nature of the volcanic material. A shield cone is a volcanic mountain that is built almost entirely of lava flow. The slopes of a shield cone volcano are very gentle and rounded like a warrior's shield. ...
... Volcanic eruptions can develop into three different types of volcanic mountains, depending on the nature of the volcanic material. A shield cone is a volcanic mountain that is built almost entirely of lava flow. The slopes of a shield cone volcano are very gentle and rounded like a warrior's shield. ...
Ring of Fire
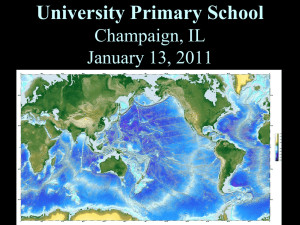
The Ring of Fire is an area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur. In a 40,000 km (25,000 mi) horseshoe shape, it is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and/or plate movements. It has 452 volcanoes and is home to over 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes. The Ring of Fire is sometimes called the circum-Pacific belt.About 90% of the world's earthquakes and 81% of the world's largest earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire. The next most seismically active region (5–6% of earthquakes and 17% of the world's largest earthquakes) is the Alpide belt, which extends from Java to the northern Atlantic Ocean via the Himalayas and southern Europe.All but 3 of the world's 25 largest volcanic eruptions of the last 11,700 years occurred at volcanoes in the Ring of Fire.The Ring of Fire is a direct result of plate tectonics and the movement and collisions of lithospheric plates. The eastern section of the ring is the result of the Nazca Plate and the Cocos Plate being subducted beneath the westward moving South American Plate. The Cocos Plate is being subducted beneath the Caribbean Plate, in Central America. A portion of the Pacific Plate along with the small Juan de Fuca Plate are being subducted beneath the North American Plate. Along the northern portion, the northwestward-moving Pacific plate is being subducted beneath the Aleutian Islands arc. Farther west, the Pacific plate is being subducted along the Kamchatka Peninsula arcs on south past Japan. The southern portion is more complex, with a number of smaller tectonic plates in collision with the Pacific plate from the Mariana Islands, the Philippines, Bougainville, Tonga, and New Zealand; this portion excludes Australia, since it lies in the center of its tectonic plate. Indonesia lies between the Ring of Fire along the northeastern islands adjacent to and including New Guinea and the Alpide belt along the south and west from Sumatra, Java, Bali, Flores, and Timor. The famous and very active San Andreas Fault zone of California is a transform fault which offsets a portion of the East Pacific Rise under southwestern United States and Mexico. The motion of the fault generates numerous small earthquakes, at multiple times a day, most of which are too small to be felt. The active Queen Charlotte Fault on the west coast of the Haida Gwaii, British Columbia, Canada, has generated three large earthquakes during the 20th century: a magnitude 7 event in 1929; a magnitude 8.1 in 1949 (Canada's largest recorded earthquake); and a magnitude 7.4 in 1970.