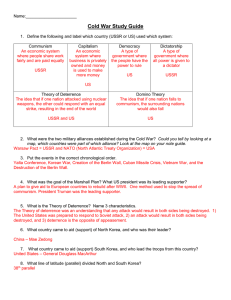
Ch.19, Sec.1- Origins of the Cold War
... Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Member nations agreed that an armed attack against one or more of them shall be considered an attack against them all. This principle of mutual military assistance is called collective security. • In 1955, the Soviet Union responded to the formation of NATO by cr ...
... Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Member nations agreed that an armed attack against one or more of them shall be considered an attack against them all. This principle of mutual military assistance is called collective security. • In 1955, the Soviet Union responded to the formation of NATO by cr ...
Origins of the Cold War
... Cold War Conflicts The Cold War and the danger of nuclear war define international affairs, especially after the Korean War. Fear of communism in the U.S. leads to accusations against innocent citizens. ...
... Cold War Conflicts The Cold War and the danger of nuclear war define international affairs, especially after the Korean War. Fear of communism in the U.S. leads to accusations against innocent citizens. ...
Cabinet memorandum by the Foreign Secretary, E. Bevin
... into two opposing camps which were in conflict. It called on Communists everywhere to close their ranks, not to underestimate their strength, and to intensify the struggle. It denounced the “Truman-Marshall Plan as a component part of the general policy of the United States and Great Britain for “st ...
... into two opposing camps which were in conflict. It called on Communists everywhere to close their ranks, not to underestimate their strength, and to intensify the struggle. It denounced the “Truman-Marshall Plan as a component part of the general policy of the United States and Great Britain for “st ...
VUS.13
... The Cold War lasted from the end of World War II until the collapse of the Soviet Union. The United States and the Soviet Union represented starkly different fundamental values. The United States represented democratic political institutions and a generally free market economic system. The Sovie ...
... The Cold War lasted from the end of World War II until the collapse of the Soviet Union. The United States and the Soviet Union represented starkly different fundamental values. The United States represented democratic political institutions and a generally free market economic system. The Sovie ...
Soviet union`s use of Peaceful Coexistence
... the Soviet Union at various points during the Cold War in the context of primarily Marxist–Leninist foreign policy and was adopted by Soviet-influenced "Socialist states" that they could peacefully coexist with the capitalist bloc.This was in contrast to the antagonistic contradiction principle that ...
... the Soviet Union at various points during the Cold War in the context of primarily Marxist–Leninist foreign policy and was adopted by Soviet-influenced "Socialist states" that they could peacefully coexist with the capitalist bloc.This was in contrast to the antagonistic contradiction principle that ...
Causes - Glen Innes High School
... • At the Tehran Conference (1943) Stalin and Churchill clashed over how much control Stalin would have over the countries of eastern Europe. However, the 'Big Three' - especially President Roosevelt - knew that they had to stay allied until the end of the war, so they managed to patch up these diffe ...
... • At the Tehran Conference (1943) Stalin and Churchill clashed over how much control Stalin would have over the countries of eastern Europe. However, the 'Big Three' - especially President Roosevelt - knew that they had to stay allied until the end of the war, so they managed to patch up these diffe ...
Chapter 17, Section 3: Guide to the Essentials
... it later became a sions”—that improved relations with the however. In the 1800s it began leader in world Soviet Union and China. expanding its territory. By winaffairs. The end of the cold war began when ning the Spanish-American War Mikhail Gorbachev became the leader of in 1898, the United States ...
... it later became a sions”—that improved relations with the however. In the 1800s it began leader in world Soviet Union and China. expanding its territory. By winaffairs. The end of the cold war began when ning the Spanish-American War Mikhail Gorbachev became the leader of in 1898, the United States ...
File
... In 1948, the Soviet Union blockaded West Germany. They wanted the west to surrender it. If that happened, Stalin would have shown that Communism couldn’t be contained. President Truman used airplanes from all over the world to supply West Berlin and save it from Communism. The Berlin Airlift was a v ...
... In 1948, the Soviet Union blockaded West Germany. They wanted the west to surrender it. If that happened, Stalin would have shown that Communism couldn’t be contained. President Truman used airplanes from all over the world to supply West Berlin and save it from Communism. The Berlin Airlift was a v ...
26-cold war conflicts - Wood
... As a result they felt justified in their claim to Eastern Europe Furthermore, they felt they needed Eastern Europe as a buffer against future German aggression ...
... As a result they felt justified in their claim to Eastern Europe Furthermore, they felt they needed Eastern Europe as a buffer against future German aggression ...
The Origins of the Cold War
... George Kennan and the “Long Telegram • Argued that the Soviet Union was intent on expansion. • Unless the United States stopped them, they wouldn’t be content until they had obtained worldwide domination. • Leads to doctrine of Containment- stopping the spread of Communism worldwide ...
... George Kennan and the “Long Telegram • Argued that the Soviet Union was intent on expansion. • Unless the United States stopped them, they wouldn’t be content until they had obtained worldwide domination. • Leads to doctrine of Containment- stopping the spread of Communism worldwide ...
GCSE History mapping grid: Using Pearson`s Edexcel GCSE History
... Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty 1968 is covered on p.47, which is separate from the existing content on the consequences of the ...
... Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty 1968 is covered on p.47, which is separate from the existing content on the consequences of the ...
Cold War
... 2. After World War II, the United States signed several treaties with foreign countries. These treaties called for the nations that signed them to protect each other, even if an enemy attacked only one of them. Which factor caused the United States to sign the treaties? a. the growing sense of trust ...
... 2. After World War II, the United States signed several treaties with foreign countries. These treaties called for the nations that signed them to protect each other, even if an enemy attacked only one of them. Which factor caused the United States to sign the treaties? a. the growing sense of trust ...
Chapter 25, The Cold War Begins 2013-2014
... ____ 12. Why did the United States not share the plan to develop the atomic bomb with the Soviet Union during World War II? a. The Soviet Union already had an atomic bomb. b. The United States did not trust the Soviet Union. c. The Allies would have been against its development on moral grounds. d. ...
... ____ 12. Why did the United States not share the plan to develop the atomic bomb with the Soviet Union during World War II? a. The Soviet Union already had an atomic bomb. b. The United States did not trust the Soviet Union. c. The Allies would have been against its development on moral grounds. d. ...
CHAPTER 28 THE ONSET OF THE COLD WAR
... Europe, American troops occupied western Europe Soviet Union sought eastern European buffer U.S. demanded national selfdetermination through free elections throughout Europe Stalin converted eastern Europe into a system of satellite nations ...
... Europe, American troops occupied western Europe Soviet Union sought eastern European buffer U.S. demanded national selfdetermination through free elections throughout Europe Stalin converted eastern Europe into a system of satellite nations ...
Activity V
... client states in Eastern Europe into the Warsaw Pact in May 1955. The heart of NATO beat around the military and financial muscle of the United States. However, because the post-war Soviet threat was perceived to be against Western Europe, the headquarters of NATO was based in Brussels, Belgium. ...
... client states in Eastern Europe into the Warsaw Pact in May 1955. The heart of NATO beat around the military and financial muscle of the United States. However, because the post-war Soviet threat was perceived to be against Western Europe, the headquarters of NATO was based in Brussels, Belgium. ...
end of the Cold War
... • His campaign team, “CRP,” (Committee to Re-Elect the President) is determined to discredit the Democratic Party • 5 men break in to the Democratic Headquarters at the Watergate Building Complex – plan to steal documents & ...
... • His campaign team, “CRP,” (Committee to Re-Elect the President) is determined to discredit the Democratic Party • 5 men break in to the Democratic Headquarters at the Watergate Building Complex – plan to steal documents & ...
1970 at a glance
... Détente and the SALT I agreement With the United States suddenly in friendly negotiations with China, their biggest rivals, the Soviet Union, was ready to negotiate towards peace with the US. After weeks of meetings and talks, Nixon and Soviet premier Leonid Breznev announced that they had agreed to ...
... Détente and the SALT I agreement With the United States suddenly in friendly negotiations with China, their biggest rivals, the Soviet Union, was ready to negotiate towards peace with the US. After weeks of meetings and talks, Nixon and Soviet premier Leonid Breznev announced that they had agreed to ...
The End of World War II
... • This begins the idea that those who commit “crimes against humanity” (atrocities), in time of war or peace, should be brought to justice…. –the International Criminal Court (ICC): ...
... • This begins the idea that those who commit “crimes against humanity” (atrocities), in time of war or peace, should be brought to justice…. –the International Criminal Court (ICC): ...
Collapse of Communism
... political changes did Gorbachev want to occur in Soviet society? • 1) Less government control over the economy; 2) Some private ...
... political changes did Gorbachev want to occur in Soviet society? • 1) Less government control over the economy; 2) Some private ...
Collapse of Communism
... political changes did Gorbachev want to occur in Soviet society? • 1) Less government control over the economy; 2) Some private ...
... political changes did Gorbachev want to occur in Soviet society? • 1) Less government control over the economy; 2) Some private ...
Name
... 19. What leader rose to power in North Vietnam in 1950 and what other country supported North Vietnam? Ho Chi Minh led North Vietnam and was supported by the USSR and China. 20. What other country supported South Vietnam? The United States 21. Describe both events. Gulf of Tonkin Resolution ...
... 19. What leader rose to power in North Vietnam in 1950 and what other country supported North Vietnam? Ho Chi Minh led North Vietnam and was supported by the USSR and China. 20. What other country supported South Vietnam? The United States 21. Describe both events. Gulf of Tonkin Resolution ...
Cold War and Global Hegemony, 1945-1991
... officials worried that their occupation of Japan might fail and that the Japanese might seek to enhance their own interests by looking to the Soviets or the communist Chinese as future economic partners. In 1948, U.S. policymakers turned their attention from reforming Japanese social and political ...
... officials worried that their occupation of Japan might fail and that the Japanese might seek to enhance their own interests by looking to the Soviets or the communist Chinese as future economic partners. In 1948, U.S. policymakers turned their attention from reforming Japanese social and political ...
Cold War

The Cold War was a state of political and military tension after World War II between powers in the Western Bloc (the United States, its NATO allies and others) and powers in the Eastern Bloc (the Soviet Union and its allies in the Warsaw Pact).Historians have not fully agreed on the dates, but 1947–1991 is common. It was termed as ""cold"" because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two sides, although there were major regional wars, known as proxy wars, in Korea, Vietnam and Afghanistan that the two sides supported. The Cold War split the temporary wartime alliance against Nazi Germany, leaving the USSR and the US as two superpowers with profound economic and political differences: the former being a single-party Marxist–Leninist state operating planned economy and controlled press while professing state atheism and owning exclusively the right to establish and govern communities, and the latter being a capitalist state with generally free elections and press, which also granted freedom of religion and freedom of association to its citizens. A self-proclaimed neutral bloc arose with the Non-Aligned Movement founded by Egypt, India, Indonesia and Yugoslavia; this faction rejected association with either the US-led West or the Soviet-led East. The two superpowers never engaged directly in full-scale armed combat but they each armed heavily in preparation for a possible all-out nuclear world war. Each side had a nuclear deterrent that deterred an attack by the other side, on the basis that such an attack would lead to total destruction of the attacker: the doctrine of mutually assured destruction (MAD). Aside from the development of the two sides' nuclear arsenals, and deployment of conventional military forces, the struggle for dominance was expressed via proxy wars around the globe, psychological warfare, massive propaganda campaigns and espionage, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race.The first phase of the Cold War began in the first two years after the end of the Second World War in 1945. The USSR consolidated its control over the states of the Eastern Bloc while the United States began a strategy of global containment to challenge Soviet power, extending military and financial aid to the countries of Western Europe (for example, supporting the anti-Communist side in the Greek Civil War) and creating the NATO alliance. The Berlin Blockade (1948–49) was the first major crisis of the Cold War.With victory of the Communist side in the Chinese Civil War and the outbreak of the Korean War (1950–53), the conflict expanded. The USSR and USA competed for influence in Latin America and decolonizing states of Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. Meanwhile, the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 was stopped by the Soviets. The expansion and escalation sparked more crises, such as the Suez Crisis (1956), the Berlin Crisis of 1961, and the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962. Following this last crisis a new phase began that saw the Sino-Soviet split complicate relations within the Communist sphere while US allies, particularly France, demonstrated greater independence of action. The USSR crushed the 1968 Prague Spring liberalization program in Czechoslovakia, and the Vietnam War (1955–1975) ended with a defeat of the US-backed Republic of South Vietnam, prompting further adjustments.By the 1970s, both sides had become interested in accommodations to create a more stable and predictable international system, inaugurating a period of détente that saw Strategic Arms Limitation Talks and the US opening relations with the People's Republic of China as a strategic counterweight to the Soviet Union. Détente collapsed at the end of the decade with the Soviet war in Afghanistan beginning in 1979.The early 1980s were another period of elevated tension, with the Soviet downing of Korean Air Lines Flight 007 (1983), and the ""Able Archer"" NATO military exercises (1983). The United States increased diplomatic, military, and economic pressures on the Soviet Union, at a time when the communist state was already suffering from economic stagnation. In the mid-1980s, the new Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced the liberalizing reforms of perestroika (""reorganization"", 1987) and glasnost (""openness"", c. 1985) and ended Soviet involvement in Afghanistan. Pressures for national independence grew stronger in Eastern Europe, especially Poland. Gorbachev meanwhile refused to use Soviet troops to bolster the faltering Warsaw Pact regimes as had occurred in the past. The result in 1989 was a wave of revolutions that peacefully (with the exception of the Romanian Revolution) overthrew all of the Communist regimes of Central and Eastern Europe. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union itself lost control and was banned following an abortive coup attempt in August 1991. This in turn led to the formal dissolution of the USSR in December 1991 and the collapse of Communist regimes in other countries such as Mongolia, Cambodia and South Yemen. The United States remained as the world's only superpower.The Cold War and its events have left a significant legacy, and it is often referred to in popular culture, especially in media featuring themes of espionage (such as the internationally successful James Bond film series) and the threat of nuclear warfare.