Cold War Hot Spots Maps and Pictures
... • Domino theory prompts US involvement against communist rebels, Viet Cong, and North Vietnam in 1960 under President Kennedy • Peak troop deployment in 1968 under President Johnson – over 500,000 American personnel were in Vietnam ...
... • Domino theory prompts US involvement against communist rebels, Viet Cong, and North Vietnam in 1960 under President Kennedy • Peak troop deployment in 1968 under President Johnson – over 500,000 American personnel were in Vietnam ...
Study Guide Overview
... that reflected the divisions created by Cold War tensions and hostilities. The tension between the free world and the communist world caused divisiveness at home and abroad. ...
... that reflected the divisions created by Cold War tensions and hostilities. The tension between the free world and the communist world caused divisiveness at home and abroad. ...
The Aftermath of World War II
... The United States detonated the first nuclear weapon in the year 1)___________, causing a power shift that made the United States the first superpower. The 2) __________ _________ was second. It took the 2) __________ _________ four years to detonate their own nuclear weapon; they detonated an atomi ...
... The United States detonated the first nuclear weapon in the year 1)___________, causing a power shift that made the United States the first superpower. The 2) __________ _________ was second. It took the 2) __________ _________ four years to detonate their own nuclear weapon; they detonated an atomi ...
Spread of The cold War
... As a result of lack of U.S. support, Britain, France, and Israel were forced to withdraw its troops. ...
... As a result of lack of U.S. support, Britain, France, and Israel were forced to withdraw its troops. ...
File - Ms. Nancy K. Ware`s US History Classes
... countries of Greece and Turkey stop Soviet expansion into their countries. Truman’s foreign policy stated the United States would help any country that opposed communism (foreshadow!!) ...
... countries of Greece and Turkey stop Soviet expansion into their countries. Truman’s foreign policy stated the United States would help any country that opposed communism (foreshadow!!) ...
Spread of The cold War
... As a result of lack of U.S. support, Britain, France, and Israel were forced to withdraw its troops. ...
... As a result of lack of U.S. support, Britain, France, and Israel were forced to withdraw its troops. ...
CHAPTER 38 AP WORLD QUESTIONS
... 13. The struggle between the U.S. and the Soviet Union led to the creation of two military blocs: the _________________________ founded in 1949 and the ________________established as a response to the rearming of West Germany. 14. Where did hostilities break out in the summer of 1950? __________ It ...
... 13. The struggle between the U.S. and the Soviet Union led to the creation of two military blocs: the _________________________ founded in 1949 and the ________________established as a response to the rearming of West Germany. 14. Where did hostilities break out in the summer of 1950? __________ It ...
Dealing with Russia
... subtle and was replaced by Paul Nitze. NSC document 68 proposed a rapid build-up of political, economic and military strength of the free world.4 In Kissinger’s analysis, US strategy on the Soviet Union began with containment, which already under Truman drew the country into peripheral actions. Eise ...
... subtle and was replaced by Paul Nitze. NSC document 68 proposed a rapid build-up of political, economic and military strength of the free world.4 In Kissinger’s analysis, US strategy on the Soviet Union began with containment, which already under Truman drew the country into peripheral actions. Eise ...
NEWL54FalloftheUSSR
... would have returned hard line communists to power in Russia. “shock therapy”: Yeltsin advocated a rapid transition from state planning to a market economy while simultaneously introducing democracy to Russia. “Shock therapy” caused inflation and unemployment. ...
... would have returned hard line communists to power in Russia. “shock therapy”: Yeltsin advocated a rapid transition from state planning to a market economy while simultaneously introducing democracy to Russia. “Shock therapy” caused inflation and unemployment. ...
File - Mrs. Argus
... "The German ultimatum ordering the Dutch commander of Rotterdam to cease fire was delivered to him at 10:30 a.m. on May 14, 1940. At 1:22 p.m., German bombers set the whole inner city of Rotterdam ablaze, killing 800-900 of its inhabitants.” * Aerial view of the ruins of Rotterdam. ...
... "The German ultimatum ordering the Dutch commander of Rotterdam to cease fire was delivered to him at 10:30 a.m. on May 14, 1940. At 1:22 p.m., German bombers set the whole inner city of Rotterdam ablaze, killing 800-900 of its inhabitants.” * Aerial view of the ruins of Rotterdam. ...
Grade 11: Virginia and United States History
... VUS.12: The student will demonstrate knowledge of United States foreign policy since World War II. Following a visit to the Museum, students will be able to answer these SOL Essential Questions: o What were the political, economic, and social consequences of World War II? o How did the U.S. respo ...
... VUS.12: The student will demonstrate knowledge of United States foreign policy since World War II. Following a visit to the Museum, students will be able to answer these SOL Essential Questions: o What were the political, economic, and social consequences of World War II? o How did the U.S. respo ...
Chapter 35 The End of the Cold War and the Shape of a New Era
... The fall of the USSR gave way to new independent states in eastern Europe. Yeltsen was replaced by Vladimir Putin after economic problems in Russia. ...
... The fall of the USSR gave way to new independent states in eastern Europe. Yeltsen was replaced by Vladimir Putin after economic problems in Russia. ...
Ch 20 Foreign Policy
... conflicts. OPEC controls the price of oil and amount its members produce and sell. ...
... conflicts. OPEC controls the price of oil and amount its members produce and sell. ...
Rise of the Cold War - Plain Local Schools
... immediately after World War II? They A. adopted democratic reforms in their political systems. B. became satellite states of the Soviet Union. C. became dependent on aid provided by the Marshall Plan. D. emerged as world economic ...
... immediately after World War II? They A. adopted democratic reforms in their political systems. B. became satellite states of the Soviet Union. C. became dependent on aid provided by the Marshall Plan. D. emerged as world economic ...
Marshall Plan poster of ship
... Cold War Germany This map shows how Germany and Berlin were divided into occupation zones. Meant as temporary divisions, they became permanent, transformed by the Cold War into East and West Germany. In 1948, with the Berlin airlift, and again in 1961, with the erection of the Berlin Wall, Berlin be ...
... Cold War Germany This map shows how Germany and Berlin were divided into occupation zones. Meant as temporary divisions, they became permanent, transformed by the Cold War into East and West Germany. In 1948, with the Berlin airlift, and again in 1961, with the erection of the Berlin Wall, Berlin be ...
Unit 12: The Cold War
... President Kennedy, a World War II veteran, was assassinated in _________ in _______________ in an event that shook the nation’s confidence and began a period of internal strife and divisiveness, especially spurred by divisions over United States involvement in ______________ Unlike veterans of W ...
... President Kennedy, a World War II veteran, was assassinated in _________ in _______________ in an event that shook the nation’s confidence and began a period of internal strife and divisiveness, especially spurred by divisions over United States involvement in ______________ Unlike veterans of W ...
Chapter 17 - cloudfront.net
... military power and ideological influence, create a free-market global economy, and build an international security system. A. ...
... military power and ideological influence, create a free-market global economy, and build an international security system. A. ...
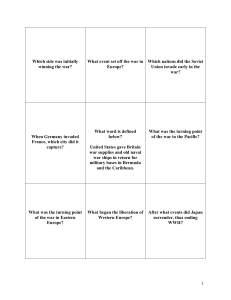
Which side was initially winning the war
... Which Cold War conflict ended in the Soviet Union removing its missiles in response to a U.S. blockade? ...
... Which Cold War conflict ended in the Soviet Union removing its missiles in response to a U.S. blockade? ...
1945
... National Defense and Education Act (NDEA) Creation of NASA 2nd Berlin Crisis Nixon attacked in Venezuela US aid for Civil War in Lebanon ...
... National Defense and Education Act (NDEA) Creation of NASA 2nd Berlin Crisis Nixon attacked in Venezuela US aid for Civil War in Lebanon ...
Document
... Truman, Stalin, and Churchill – the three agree on post-war boundaries 1945 Truman okays bombing of Japanese cities (Hiroshima and Nagasaki), leading to Japan’s surrender. ...
... Truman, Stalin, and Churchill – the three agree on post-war boundaries 1945 Truman okays bombing of Japanese cities (Hiroshima and Nagasaki), leading to Japan’s surrender. ...
Impact of the Cold War at home
... United States and American ideals of democracy and freedom ultimately prevailed in the Cold War struggle with Soviet communism. ...
... United States and American ideals of democracy and freedom ultimately prevailed in the Cold War struggle with Soviet communism. ...
Cold War PPT.
... War. The US and USSR saw their leaders change, and with that, some were more determined than ever to prove their countries military superiority over the others—two leaders to the point that they signed a treaty called M.A.D. (Mutually Assured Destruction)—I think this speaks for itself on its meanin ...
... War. The US and USSR saw their leaders change, and with that, some were more determined than ever to prove their countries military superiority over the others—two leaders to the point that they signed a treaty called M.A.D. (Mutually Assured Destruction)—I think this speaks for itself on its meanin ...
Containment

Containment is a military strategy to stop the expansion of an enemy. It is best known as the Cold War policy of the United States and its allies to prevent the spread of communism abroad. A component of the Cold War, this policy was a response to a series of moves by the Soviet Union to enlarge communist influence in Eastern Europe, China, Korea, Africa, and Vietnam. Containment represented a middle-ground position between detente and rollback, but it let the opponent choose the place and time of any confrontation.The basis of the doctrine was articulated in a 1946 cable by U.S. diplomat George F. Kennan during the post-WWII administration of U.S. President Harry Truman. As a description of U.S. foreign policy, the word originated in a report Kennan submitted to U.S. Defense Secretary James Forrestal in 1947, a report that was later used in a magazine article. It is a translation of the French cordon sanitaire, used to describe Western policy toward the Soviet Union in the 1920s.