CHAPTER NINE: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... iii. Mechanically gated channelopen and close in response to physical deformation of receptors b. When gated channels are _______ i. Ions diffuse quickly across the membrane along their electrochemical gradients 1. Chemical gradients go from high to low 2. Electrical gradients go from low to high ii ...
... iii. Mechanically gated channelopen and close in response to physical deformation of receptors b. When gated channels are _______ i. Ions diffuse quickly across the membrane along their electrochemical gradients 1. Chemical gradients go from high to low 2. Electrical gradients go from low to high ii ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
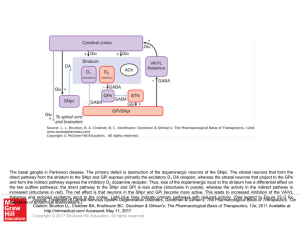
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
Central nervous system
... Two types of neural cells in the nervous system: Neurons Process, transfer, and store information Neuroglia – (also called “glial cells”) Support and protect neurons ...
... Two types of neural cells in the nervous system: Neurons Process, transfer, and store information Neuroglia – (also called “glial cells”) Support and protect neurons ...
Nervous System Guided Notes
... The ________________________________________, which consists of all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These receive stimuli and effect responses in muscles and glands. The peripheral nervous system can be further divided into: 1) _______________________________or sensory neurons - bring ...
... The ________________________________________, which consists of all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These receive stimuli and effect responses in muscles and glands. The peripheral nervous system can be further divided into: 1) _______________________________or sensory neurons - bring ...
Structure of the Brain PowerPoint Notes
... • GABA Keys – alcohol molecules so closely resemble those of the GABA neurotransmitter that alcohol can function like GABA keys and open GABA receptors – when GABA neurons are excited, they decrease neural activity REFLEX Reflex – unlearned, __________________reaction to some stimulus – neural conne ...
... • GABA Keys – alcohol molecules so closely resemble those of the GABA neurotransmitter that alcohol can function like GABA keys and open GABA receptors – when GABA neurons are excited, they decrease neural activity REFLEX Reflex – unlearned, __________________reaction to some stimulus – neural conne ...
Autonomic nervous system
... The longer they run, the more tired they get, of course; but at some point, the runners will “push through the wall” and “get their second wind.” ...
... The longer they run, the more tired they get, of course; but at some point, the runners will “push through the wall” and “get their second wind.” ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... The neurons are the nerve cells involved in the production and exchange of signals. They represent the functional unit of the nervous system. The majority of the neurons is characterized by 3 main areas: the cell body (also called soma), the dendrites and the axons. ...
... The neurons are the nerve cells involved in the production and exchange of signals. They represent the functional unit of the nervous system. The majority of the neurons is characterized by 3 main areas: the cell body (also called soma), the dendrites and the axons. ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 03 garber edited
... • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
Autonomic Nervous System Period 5 Jacquelene Hanein, Karina
... cerebrum with spinal cord o relay of motor/sensory signals between brain and spinal cord o Controls life supporting autonomic functions of PNS ● Spinal Cord ...
... cerebrum with spinal cord o relay of motor/sensory signals between brain and spinal cord o Controls life supporting autonomic functions of PNS ● Spinal Cord ...
File
... on a wide range of bodily functions and also impact emotions. When they act on the brain, they influence our interest in sex, food, and aggression. A special type of hormone called ...
... on a wide range of bodily functions and also impact emotions. When they act on the brain, they influence our interest in sex, food, and aggression. A special type of hormone called ...
Early Brain Development
... The brain has different sections, each section controls a specific function. One of the most important parts is the cortex. The cortex is the part of the brain that its growth permits more complex learning. Neurons in the baby’s brain are tiny messengers that transmit information in the brain and ne ...
... The brain has different sections, each section controls a specific function. One of the most important parts is the cortex. The cortex is the part of the brain that its growth permits more complex learning. Neurons in the baby’s brain are tiny messengers that transmit information in the brain and ne ...
CNS Autonomic NS
... within the receptor complex enables molecules to cross the cell membrane. Magnesium (Mg) blocks this channel. When Mg is removed from the channel and the receptor is activated, calcium (Ca++) and sodium (Na+) ions enter the cell and potassium ions (K+) leave. ...
... within the receptor complex enables molecules to cross the cell membrane. Magnesium (Mg) blocks this channel. When Mg is removed from the channel and the receptor is activated, calcium (Ca++) and sodium (Na+) ions enter the cell and potassium ions (K+) leave. ...
Motor Neuron
... • Central nervous system (CNS) – Brain – Spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – Nerves outside the brain and spinal cord ...
... • Central nervous system (CNS) – Brain – Spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – Nerves outside the brain and spinal cord ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... In the central nervous system • Gray matter – cell bodies and unmylenated fibers • Nuclei – clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system In the peripheral nervous system: ...
... In the central nervous system • Gray matter – cell bodies and unmylenated fibers • Nuclei – clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system In the peripheral nervous system: ...
Document
... The nervous system is one of the 2 control systems in our body. The nervous system is designed for fast action. It coordinates fast or rapid activities, such as muscle movement. Signaling is by electrical impulses, these are rapid, specific and produce an almost immediate response. ...
... The nervous system is one of the 2 control systems in our body. The nervous system is designed for fast action. It coordinates fast or rapid activities, such as muscle movement. Signaling is by electrical impulses, these are rapid, specific and produce an almost immediate response. ...
Peripheral Nerve Repair
... Central & Peripheral Nervous System •Allows the Brain to control the body •crucial for human movement and function • Highway for information processing and response •Sensory Neurons- send stimulation information from senses to the brain. • Motor Neurons- send commands from the brain to muscles or ot ...
... Central & Peripheral Nervous System •Allows the Brain to control the body •crucial for human movement and function • Highway for information processing and response •Sensory Neurons- send stimulation information from senses to the brain. • Motor Neurons- send commands from the brain to muscles or ot ...
HORMONES AND BEHAVIOR 1. The Neuroendocrine System: Sum
... 2. ___________________: coordinates motor responses involved in feeding behaviors; 3. ______________: receives signals from leptin & insulin, and project to paraventricular nucleus and lateral hypothalamus to • or ↓ feeding. ...
... 2. ___________________: coordinates motor responses involved in feeding behaviors; 3. ______________: receives signals from leptin & insulin, and project to paraventricular nucleus and lateral hypothalamus to • or ↓ feeding. ...
Central Nervous System
... Frontal lobe – voluntary motor activity (primary motor cortex), speaking, thought ...
... Frontal lobe – voluntary motor activity (primary motor cortex), speaking, thought ...
Review questions: Neuroanatomy
... 1. Describe the neural organisation of the autonomic nervous system and the differences in the two divisions. 2. What are the three sympathetic ganglionic groups and where would you find them? 3. What's so special about the adrenal medulla? 4. Compare and contrast activation of the sympathetic and p ...
... 1. Describe the neural organisation of the autonomic nervous system and the differences in the two divisions. 2. What are the three sympathetic ganglionic groups and where would you find them? 3. What's so special about the adrenal medulla? 4. Compare and contrast activation of the sympathetic and p ...
spinal cord
... control and coordination of life functions and activities 2 systems involved: 1. nervous- electrical system, brain,spine and nerves found in multicellular organisms 2. endocrine- chemical system, hormones found in all organisms Nervous System: definitions: a. stimulus- change in the internal or ex ...
... control and coordination of life functions and activities 2 systems involved: 1. nervous- electrical system, brain,spine and nerves found in multicellular organisms 2. endocrine- chemical system, hormones found in all organisms Nervous System: definitions: a. stimulus- change in the internal or ex ...
Document
... visceral organs, glands, and blood vessels • Autonomic reflex activity influenced by hypothalamus and higher brain centers • Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions influence activities of enteric nervous system through autonomic reflexes – Enteric nervous system can function independently of CNS ...
... visceral organs, glands, and blood vessels • Autonomic reflex activity influenced by hypothalamus and higher brain centers • Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions influence activities of enteric nervous system through autonomic reflexes – Enteric nervous system can function independently of CNS ...
Note: This hypothesis is mainly concerned with peripheral neurons
... In vitro assays have shown that NTs enhance both axonal and dendritic growth In vivo, the situation is more difficult to study Why? In standard knockouts, it is difficult to separate the survival effects of NTs from their effects on the morphology of neurons. This problem has begun to be addressed ...
... In vitro assays have shown that NTs enhance both axonal and dendritic growth In vivo, the situation is more difficult to study Why? In standard knockouts, it is difficult to separate the survival effects of NTs from their effects on the morphology of neurons. This problem has begun to be addressed ...
Anatomy of the Nervous System
... – Functional units of nervous system (conduct electricity) • Sensory neurons – “afferent neurons” – Sense and relay info (stimuli) from environment to CNS » (ex// photoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, etc.) » Ganglia: clusters of sensory receptors. ...
... – Functional units of nervous system (conduct electricity) • Sensory neurons – “afferent neurons” – Sense and relay info (stimuli) from environment to CNS » (ex// photoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, etc.) » Ganglia: clusters of sensory receptors. ...