The Peripheral Nervous System The P.N.S.
... cells which are folded together in order to fit inside the cranium. 3) What are the 3 major structures of the ...
... cells which are folded together in order to fit inside the cranium. 3) What are the 3 major structures of the ...
Benefits of Massage - Carolinas Natural Health Center
... Massage is known to increase the circulation of blood and flow of lymph. The direct mechanical effect of rhythmically applied manual pressure and movement used in massage can dramatically increase the rate of blood flow. Also, the stimulation of nerve receptors causes the blood vessels to dilate, wh ...
... Massage is known to increase the circulation of blood and flow of lymph. The direct mechanical effect of rhythmically applied manual pressure and movement used in massage can dramatically increase the rate of blood flow. Also, the stimulation of nerve receptors causes the blood vessels to dilate, wh ...
2d Unit II Cells of the Body
... muscle appears to have alternating bands of light and dark striations. The skeletal muscle cells are also multinucleated. Smooth muscle tissue lines the walls of the digestive tract and some blood vessels in the circulatory system. Smooth muscle tissue is spindle shaped and the cells contain only on ...
... muscle appears to have alternating bands of light and dark striations. The skeletal muscle cells are also multinucleated. Smooth muscle tissue lines the walls of the digestive tract and some blood vessels in the circulatory system. Smooth muscle tissue is spindle shaped and the cells contain only on ...
Inotropes - GEOCITIES.ws
... Catecholamines • Most frequently used inotropic agent in ICU • All act on adrenergic receptors ...
... Catecholamines • Most frequently used inotropic agent in ICU • All act on adrenergic receptors ...
SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COMPLETION 1. The
... A. if only 1, 2 and 3 are correct B. if only 1 and 3 are correct C. if only 2 and 4 are Correct D. if only 4 is correct E. if all are correct 40. Hair cells of the vestibular system (1) release transmitter even when not stimulated (2) do not generate action potentials (3) have only one kinocilium pe ...
... A. if only 1, 2 and 3 are correct B. if only 1 and 3 are correct C. if only 2 and 4 are Correct D. if only 4 is correct E. if all are correct 40. Hair cells of the vestibular system (1) release transmitter even when not stimulated (2) do not generate action potentials (3) have only one kinocilium pe ...
Plant Growth and Development
... the root cap and all other cell types in the root. There are several zones in the root: Root cap: protects the meristem as it pushes through the soil. Zone of elongation: most cells stop dividing but increase in length. Phloem matures and xylem starts to form. Zone of cell division: cells fo ...
... the root cap and all other cell types in the root. There are several zones in the root: Root cap: protects the meristem as it pushes through the soil. Zone of elongation: most cells stop dividing but increase in length. Phloem matures and xylem starts to form. Zone of cell division: cells fo ...
Click here to get the file
... Intuitive Definition: Maps are a (scaled) depiction of a certain area. Location (x,y) is directly mapped to a piece of paper. Additional information such as topographical, geographical, political can be added as colors or symbols. Important: A map is always a reduction in complexity. It is a REDUCED ...
... Intuitive Definition: Maps are a (scaled) depiction of a certain area. Location (x,y) is directly mapped to a piece of paper. Additional information such as topographical, geographical, political can be added as colors or symbols. Important: A map is always a reduction in complexity. It is a REDUCED ...
PowerPoint Chapter 33
... c. Bones form when cells called osteoblasts secrete chemicals that cause cartilage to harden. 1). Process called calcification 2). Bones grow from their ends ...
... c. Bones form when cells called osteoblasts secrete chemicals that cause cartilage to harden. 1). Process called calcification 2). Bones grow from their ends ...
Supplementary material 4 – Unified probability of spike
... hemisphere. Each cell’s radial distance, and hence SNR as well as maximum deflection amplitude, can be calculated as shown earlier. ...
... hemisphere. Each cell’s radial distance, and hence SNR as well as maximum deflection amplitude, can be calculated as shown earlier. ...
Handout - personal.kent.edu
... Dollard & Miller (& Hull) Habit refers to a learned association between stimulus and response that makes them occur together frequently – can be learned & unlearned (temporary) Drive is a strong stimulation producing discomfort Æ hunger ...
... Dollard & Miller (& Hull) Habit refers to a learned association between stimulus and response that makes them occur together frequently – can be learned & unlearned (temporary) Drive is a strong stimulation producing discomfort Æ hunger ...
sion to superior salivatory neurons in rats
... The GABAergic excitatory action induced Ca2+ entry into neurons via NMDA receptors and voltagedependent Ca2+ channels. This Ca2+ influx is thought to be important in the regulation of various transcription factors which are involved in synapse development. The GABA-induced excitation may have a func ...
... The GABAergic excitatory action induced Ca2+ entry into neurons via NMDA receptors and voltagedependent Ca2+ channels. This Ca2+ influx is thought to be important in the regulation of various transcription factors which are involved in synapse development. The GABA-induced excitation may have a func ...
CNS Cellular Components - Johns Hopkins Medicine
... biochemical changes in the neuronal cell body following axonal damage. They include retraction of dendrites, cellular swelling and dispersion of Nissl bodies (chromatolysis), and accumulation of intermediate filaments. In the PNS, but not in the CNS, axonal regeneration and restoration of normal neu ...
... biochemical changes in the neuronal cell body following axonal damage. They include retraction of dendrites, cellular swelling and dispersion of Nissl bodies (chromatolysis), and accumulation of intermediate filaments. In the PNS, but not in the CNS, axonal regeneration and restoration of normal neu ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... • A) There was no difference between the enriched-environment rats and the rats raised in bare cages. • B) Enriched-environment rats showed more stress and aggression. • C) Enriched-environment rats were able to ...
... • A) There was no difference between the enriched-environment rats and the rats raised in bare cages. • B) Enriched-environment rats showed more stress and aggression. • C) Enriched-environment rats were able to ...
primary visual cortex
... Comprise all layers of the primary visual cortex, except lower layer IV. Characterized by rectangular receptive fields. These fields are comprised of excitatory areas and inhibitory areas separated by straight lines. ...
... Comprise all layers of the primary visual cortex, except lower layer IV. Characterized by rectangular receptive fields. These fields are comprised of excitatory areas and inhibitory areas separated by straight lines. ...
Central Nervous System
... schwann cells-these cells myelinate PNS axons. All cells-even the unmyelinated ones- in the PNS are surrounded by schwann cells. ...
... schwann cells-these cells myelinate PNS axons. All cells-even the unmyelinated ones- in the PNS are surrounded by schwann cells. ...
Ch. 8 - personal.kent.edu
... pattern. The dog’s first reactions to shock in the shuttle box were much the same as those of a naïve dog: it ran around frantically for about thirty seconds. But then, it stopped moving; to our surprise, it lay down and quietly whined . . on the next trial, the dog did it again . . . on all succeed ...
... pattern. The dog’s first reactions to shock in the shuttle box were much the same as those of a naïve dog: it ran around frantically for about thirty seconds. But then, it stopped moving; to our surprise, it lay down and quietly whined . . on the next trial, the dog did it again . . . on all succeed ...
CHANGES OF THE CELL BODY OF NEURONS IN CENTRAL
... To assess the relationship of behavioral and morphological and functional status of the neurons of the brain and spinal cord of different lines of mice with the "cuprizone" model of demyelination. Adult mouse of lines C57Bl/6, 129/Sv and FVB daily for three weeks received "cuprizone" with food. The ...
... To assess the relationship of behavioral and morphological and functional status of the neurons of the brain and spinal cord of different lines of mice with the "cuprizone" model of demyelination. Adult mouse of lines C57Bl/6, 129/Sv and FVB daily for three weeks received "cuprizone" with food. The ...
36.3 – The Integumentary System
... During cell division, cells fill with keratin and produce a plate-like nail that covers and protects the fingertips and toes. ...
... During cell division, cells fill with keratin and produce a plate-like nail that covers and protects the fingertips and toes. ...
Slide ()
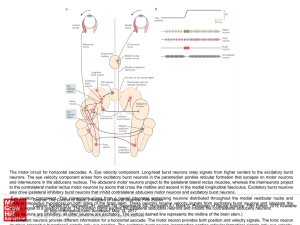
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
reflex
... the afferent neuron in the PNS. The afferent neuron then transmits an impulse to the spinal cord. The impulse will transmit through the ganglion then to the gray matter in the spinal cord. (Ganglion is a structure containing a number of nerve cell bodies). ...
... the afferent neuron in the PNS. The afferent neuron then transmits an impulse to the spinal cord. The impulse will transmit through the ganglion then to the gray matter in the spinal cord. (Ganglion is a structure containing a number of nerve cell bodies). ...
Nervous Tissues
... Located in certain nervous organs (brain, spinal cord and nerve ganglia. From these organs nerves extend to different tissues. The cytons differ in size and shape, some few microns and other hundreds microns in diameter. May be round, ovoid, spindle, star-shaped ...
... Located in certain nervous organs (brain, spinal cord and nerve ganglia. From these organs nerves extend to different tissues. The cytons differ in size and shape, some few microns and other hundreds microns in diameter. May be round, ovoid, spindle, star-shaped ...
Slide 1
... The Nerve Action Potential Nerve action potentials are the electrical signals sent out by the body to control bodily processes such as muscular movement. They are controlled by ions and their concentrations around the nerve cell. They propagate uniformly along the nerve cell and are governed by the ...
... The Nerve Action Potential Nerve action potentials are the electrical signals sent out by the body to control bodily processes such as muscular movement. They are controlled by ions and their concentrations around the nerve cell. They propagate uniformly along the nerve cell and are governed by the ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.