
Chapter 10 Slides
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... Where they occur, barrels are surrounded by formations of other cells. One hypothesis is that barrel structures might form the nucleus of a functional column, with neurons located in between barrel locations possibly being dynamically transferable from one barrel to another as functional columns are ...
... Where they occur, barrels are surrounded by formations of other cells. One hypothesis is that barrel structures might form the nucleus of a functional column, with neurons located in between barrel locations possibly being dynamically transferable from one barrel to another as functional columns are ...
AP Biology Animal Physiology Study Guide
... called nephrons. When nephrons are damaged, other nephrons are able to take on the extra work for a while (which is why some people may live with kidney disease for years) but after continuing abuse or damage, they will stop working as well. After some time, the nephrons are not capable of filtering ...
... called nephrons. When nephrons are damaged, other nephrons are able to take on the extra work for a while (which is why some people may live with kidney disease for years) but after continuing abuse or damage, they will stop working as well. After some time, the nephrons are not capable of filtering ...
Brain and Nerve PowerPoint
... Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from adjacent neuron. Neurotransmitter generates electrical signal in neuron. Electrical signal travels down axon and axon terminals. Neurotransmitter is released by axon terminals. Neurotransmitter travels across synapse and is received by dendrites of next nerve ...
... Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from adjacent neuron. Neurotransmitter generates electrical signal in neuron. Electrical signal travels down axon and axon terminals. Neurotransmitter is released by axon terminals. Neurotransmitter travels across synapse and is received by dendrites of next nerve ...
Brain
... Brain Reflexes • Reflexes mediated by the brainstem • brain receives information and generates a response • ex. movements of the eyes while reading this sentence ...
... Brain Reflexes • Reflexes mediated by the brainstem • brain receives information and generates a response • ex. movements of the eyes while reading this sentence ...
08_NervousSystem
... cell membrane potential becomes more (-). (This is called hyperpolarization.) Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... cell membrane potential becomes more (-). (This is called hyperpolarization.) Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
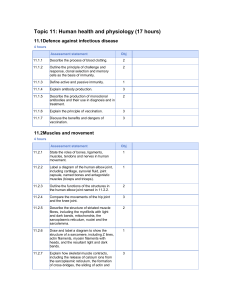
Topic 11: Human health and physiology (17 hours)
... penetration of the egg membrane by a sperm and the cortical reaction. ...
... penetration of the egg membrane by a sperm and the cortical reaction. ...
P312Ch11_Auditory III (Coding Frequency And Intensity
... Each hair cell is a frequency-specific receptor If a sound is composed of several frequencies, it will activate several receptors – one for each of the frequencies comprising the sound. Analogy: 100s of different cone types in the eye - a different type of cone for each wavelength of light. Since ea ...
... Each hair cell is a frequency-specific receptor If a sound is composed of several frequencies, it will activate several receptors – one for each of the frequencies comprising the sound. Analogy: 100s of different cone types in the eye - a different type of cone for each wavelength of light. Since ea ...
electrotherapy_part_1
... various sorts of incoming sensory information are integrated and correlated. The CNS is connected to sensory receptors, muscles, and glands in peripheral parts of the body by the PNS 2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes 12 pairs of cranial nerves that arise from the brain and 31 pairs of spin ...
... various sorts of incoming sensory information are integrated and correlated. The CNS is connected to sensory receptors, muscles, and glands in peripheral parts of the body by the PNS 2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes 12 pairs of cranial nerves that arise from the brain and 31 pairs of spin ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to Physiology of Perception
... – This negative charge of the neuron relative to its surroundings is the resting potential ...
... – This negative charge of the neuron relative to its surroundings is the resting potential ...
Introduction - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; anterior gray horns contain somatic motor nuclei. Lateral gray horns contain visceral motor neurons. Gray commissures contain the axons of interneurons that cross from one side of the cord to the other. ...
... Posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; anterior gray horns contain somatic motor nuclei. Lateral gray horns contain visceral motor neurons. Gray commissures contain the axons of interneurons that cross from one side of the cord to the other. ...
S06 Adaptation
... – body fluids form an internal environment that provides stable conditions to sustain life at the cellular level (a stability or “sameness”) – internal and external environments are independent of each other ...
... – body fluids form an internal environment that provides stable conditions to sustain life at the cellular level (a stability or “sameness”) – internal and external environments are independent of each other ...
Chapter 13
... Sensory receptor- distal end of sensory neuron (dendrite) or associated sensory structure *responds to internal or external stimuli ...
... Sensory receptor- distal end of sensory neuron (dendrite) or associated sensory structure *responds to internal or external stimuli ...
4 lesson_15.4
... The brain integrates and controls the activities of the nervous system. It is involved in emotions and all of your senses. The brain sits in the protective cavity formed by the bones of the skull. It is covered with layers of cranial meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. Both help protect ...
... The brain integrates and controls the activities of the nervous system. It is involved in emotions and all of your senses. The brain sits in the protective cavity formed by the bones of the skull. It is covered with layers of cranial meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. Both help protect ...
Untitled
... signals running along a complex, interconnected neural perception system genetically encoded to detect and respond to painful stimuli. The body detects and converts pain stimuli into electrical signals at the fine nerve endings of “nociceptors,” sensory neurons specialized to respond to pain. Their ...
... signals running along a complex, interconnected neural perception system genetically encoded to detect and respond to painful stimuli. The body detects and converts pain stimuli into electrical signals at the fine nerve endings of “nociceptors,” sensory neurons specialized to respond to pain. Their ...
Document
... b. cytosol/cytoplasm: The semi-fluid portion of the cytoplasm or intracellular fluid. a. Site of some chemical reactions (Anaerobic Phase of Cellular Respiration) b. Site where new substances are made for cellular use. c. Packaging of chemicals for transport to other parts of the body d. Facilitates ...
... b. cytosol/cytoplasm: The semi-fluid portion of the cytoplasm or intracellular fluid. a. Site of some chemical reactions (Anaerobic Phase of Cellular Respiration) b. Site where new substances are made for cellular use. c. Packaging of chemicals for transport to other parts of the body d. Facilitates ...
35 | the nervous system
... While glia are often thought of as the supporting cast of the nervous system, the number of glial cells in the brain actually outnumbers the number of neurons by a factor of ten. Neurons would be unable to function without the vital roles that are fulfilled by these glial cells. Glia guide developin ...
... While glia are often thought of as the supporting cast of the nervous system, the number of glial cells in the brain actually outnumbers the number of neurons by a factor of ten. Neurons would be unable to function without the vital roles that are fulfilled by these glial cells. Glia guide developin ...
6-Autonomic nervous system
... chain & join again the spinal nerve (via grey ramus communicans) to supply structures in head & thorax + blood vessels & sweat glands . ...
... chain & join again the spinal nerve (via grey ramus communicans) to supply structures in head & thorax + blood vessels & sweat glands . ...
5-Autonomic nervous system
... chain & join again the spinal nerve (via grey ramus communicans) to supply structures in head & thorax + blood vessels & sweat glands . ...
... chain & join again the spinal nerve (via grey ramus communicans) to supply structures in head & thorax + blood vessels & sweat glands . ...
What can cognitive psychology and sensory evaluation learn from
... retrieval of memories, the thalamus and the orbitofrontal cortex are involved in perception and cognition. How are odors coded at the level of the sensory cells? We currently believe that one olfactory cell expresses only one out of maybe one thousand odor receptors on the cilia which expand from it ...
... retrieval of memories, the thalamus and the orbitofrontal cortex are involved in perception and cognition. How are odors coded at the level of the sensory cells? We currently believe that one olfactory cell expresses only one out of maybe one thousand odor receptors on the cilia which expand from it ...
A22254 Touch [version 2.0 ].
... against the surface. Contact is experienced as light touch or pressure, or even pain, depending on how much force is exerted. When the stimulus moves on the skin, touch is perceived as stroking, tapping or vibration. Sensations of touch are often accompanied by temperature sensations of warmth or co ...
... against the surface. Contact is experienced as light touch or pressure, or even pain, depending on how much force is exerted. When the stimulus moves on the skin, touch is perceived as stroking, tapping or vibration. Sensations of touch are often accompanied by temperature sensations of warmth or co ...
[PPS]An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology
... Controls voluntary muscles and movement Autonomic Branch of the PNS Sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the ANS Regulates cardiovascular system & body temperature Also regulates the endocrine system and aids in digestion The Endocrine System Hormones ...
... Controls voluntary muscles and movement Autonomic Branch of the PNS Sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the ANS Regulates cardiovascular system & body temperature Also regulates the endocrine system and aids in digestion The Endocrine System Hormones ...
neural control of respiration
... while playing wind instruments, where the lungs serve as air reservoirs to be emptied at controlled rates. (2) Automatic control originates in lower brain centers, in the pons and the medulla. Impulses arising in this system also descend in the spinal cord to the motor neurons controlling respirator ...
... while playing wind instruments, where the lungs serve as air reservoirs to be emptied at controlled rates. (2) Automatic control originates in lower brain centers, in the pons and the medulla. Impulses arising in this system also descend in the spinal cord to the motor neurons controlling respirator ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.




















![A22254 Touch [version 2.0 ].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015818027_1-1fa81e941fb4f1ccea189d2b012bbb09-300x300.png)
![[PPS]An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003530395_1-516558861455cb703803779680da4c5d-300x300.png)
