Drug Targets
... Comprehensive set of tag SNPs for all druggable targets – Efficacy targets of approved drugs (small mol, mAb and other protein therapeutic) – drug repurposing – Efficacy targets of clinical candidates – target validation, drug trial support and stratification – ADME associated proteins (transporters ...
... Comprehensive set of tag SNPs for all druggable targets – Efficacy targets of approved drugs (small mol, mAb and other protein therapeutic) – drug repurposing – Efficacy targets of clinical candidates – target validation, drug trial support and stratification – ADME associated proteins (transporters ...
CHEMOTHERAPY
... Accelerated drug elimination as in patient with cystic fibrosis or during pregnancy may result in rapid clearance or large volume of distribution resulting in low serum concentrations as with aminoglycosides. Inactivation of antimicrobial agents by another drug. Poor penetration into the site of inf ...
... Accelerated drug elimination as in patient with cystic fibrosis or during pregnancy may result in rapid clearance or large volume of distribution resulting in low serum concentrations as with aminoglycosides. Inactivation of antimicrobial agents by another drug. Poor penetration into the site of inf ...
What happens when things don`t work out like they were supposed to?
... warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solu ...
... warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solu ...
Recent advances in ocular drug delivery
... Creation and use of materials and devices at the size scale of intracellular structures and molecules, and involves systems and constructs in the order of <100 nm. General principles: 1- Bio-mimicry: direct molecules to the proper cells 2- Pseudo-intelligence 3- Feedback control: control dosage prec ...
... Creation and use of materials and devices at the size scale of intracellular structures and molecules, and involves systems and constructs in the order of <100 nm. General principles: 1- Bio-mimicry: direct molecules to the proper cells 2- Pseudo-intelligence 3- Feedback control: control dosage prec ...
PHARMACOKINETICS: What the body does to a drug
... Plasma half-life-time taken to decline to half of a drug’s previous level. Only useful when first order kinetics apply Steady state-usually reached in dosing after 5 half-lives of the drug have elapsed (note with depots steady state depends on drug release not removal) Tolerance-this occurs when dos ...
... Plasma half-life-time taken to decline to half of a drug’s previous level. Only useful when first order kinetics apply Steady state-usually reached in dosing after 5 half-lives of the drug have elapsed (note with depots steady state depends on drug release not removal) Tolerance-this occurs when dos ...
Medicinal and Recreational drugs
... the primary intention to alter the state of consciousness (through alteration of the central nervous system) in order to create positive emotions and feelings. Examples: Adol –for kids Aspren –for head aces Caffeine ...
... the primary intention to alter the state of consciousness (through alteration of the central nervous system) in order to create positive emotions and feelings. Examples: Adol –for kids Aspren –for head aces Caffeine ...
How to Make Your Drug Cards
... How to Make Your Drug Cards Each week make drug cards from the list or location provided. Drug cards must be hand written. You may use both sides and large note cards if necessary. You are welcome to use a nursing drug guide to complete your cards! ...
... How to Make Your Drug Cards Each week make drug cards from the list or location provided. Drug cards must be hand written. You may use both sides and large note cards if necessary. You are welcome to use a nursing drug guide to complete your cards! ...
Lacosamide (Vimpat) Drug Monitoring
... severe kidney impairment • Lacosamide should not be used in patients with o Severe liver impairment o Cardiac disease or cardiac conduction abnormalities Drug can cause dose-dependent PR-interval prolongation, increasing risk for atrioventricular block • Lacosamide use can result in abnormal resul ...
... severe kidney impairment • Lacosamide should not be used in patients with o Severe liver impairment o Cardiac disease or cardiac conduction abnormalities Drug can cause dose-dependent PR-interval prolongation, increasing risk for atrioventricular block • Lacosamide use can result in abnormal resul ...
Soft Drug
... • The three-dimensional structure of a protein can be determined using methods such as X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance ...
... • The three-dimensional structure of a protein can be determined using methods such as X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance ...
SMU-DDE-Assignments-Scheme of Evaluation PROGRAM Bachelor
... The actions of the drug on the body are termed as pharmacodynamics. The effect of a drug present at the site of action is determined by that drug’s binding with a receptor. However, at the molecular level, drug binding is only the first among a complex set of events. Types of drug – receptor interac ...
... The actions of the drug on the body are termed as pharmacodynamics. The effect of a drug present at the site of action is determined by that drug’s binding with a receptor. However, at the molecular level, drug binding is only the first among a complex set of events. Types of drug – receptor interac ...
The possible role of somatropin derivatives as a theranostic in
... S-2-(4-isothiocyanatobenzyl)-1,4,7triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid (NOTA) allows the incorporation of radiometals for SPECT/PET-diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. However, because somatropin has nine potential binding sites (Lys) for NOTA, analytical characterization of the heterogeneous prod ...
... S-2-(4-isothiocyanatobenzyl)-1,4,7triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid (NOTA) allows the incorporation of radiometals for SPECT/PET-diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. However, because somatropin has nine potential binding sites (Lys) for NOTA, analytical characterization of the heterogeneous prod ...
2.exilam details
... 7. It is without doubt that Etizolam is currently one of the most popular research chemicals available on the market. It easily ranks in popularity with compounds like Methoxetamine (MXE) and many bath salt compounds. 8. Etizolam is a sedative, and should never be mixed with other Sedatives or Depre ...
... 7. It is without doubt that Etizolam is currently one of the most popular research chemicals available on the market. It easily ranks in popularity with compounds like Methoxetamine (MXE) and many bath salt compounds. 8. Etizolam is a sedative, and should never be mixed with other Sedatives or Depre ...
1. An introduction to drugs, their action and discovery
... referred to as a ligand, to a receptor sets in motion a series of biochemical events that result in a biological or physiological effect. • Stereoelectronic structure: Both as regards molecular shape and electron distribution, is complementary with the stereoelectronic structure of the receptor resp ...
... referred to as a ligand, to a receptor sets in motion a series of biochemical events that result in a biological or physiological effect. • Stereoelectronic structure: Both as regards molecular shape and electron distribution, is complementary with the stereoelectronic structure of the receptor resp ...
Lecture Resource ()
... In screening modified compounds, it is possible to find a compound with completely different pharmacological activity than the lead compound ...
... In screening modified compounds, it is possible to find a compound with completely different pharmacological activity than the lead compound ...
Basics of Drug Testing Many factors influence the length of time
... Basics of Drug Testing Many factors influence the length of time required for drugs to be metabolized and excreted through the urine. The most important of these is the half-life of the drug. Half-life refers to the amount of time the body requires to reduce the amount of a given drug to undetectabl ...
... Basics of Drug Testing Many factors influence the length of time required for drugs to be metabolized and excreted through the urine. The most important of these is the half-life of the drug. Half-life refers to the amount of time the body requires to reduce the amount of a given drug to undetectabl ...
Document
... Drugs may bind to both their desired target and to other molecules in an organism. If interactions with other targets are negligible then a drug is said to be specific. In most cases drugs will show a non-exclusive preference for their target - selective. The interaction with both their inte ...
... Drugs may bind to both their desired target and to other molecules in an organism. If interactions with other targets are negligible then a drug is said to be specific. In most cases drugs will show a non-exclusive preference for their target - selective. The interaction with both their inte ...
PHT 415 HomeWork
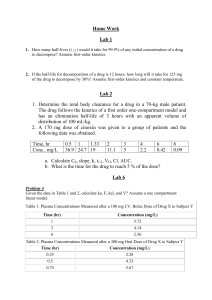
... 2. If the half-life for decomposition of a drug is 12 hours, how long will it take for 125 mg of the drug to decompose by 30%? Assume first-order kinetics and constant temperature. ...
... 2. If the half-life for decomposition of a drug is 12 hours, how long will it take for 125 mg of the drug to decompose by 30%? Assume first-order kinetics and constant temperature. ...
Synthetic Chemistry and Medicine
... relate it to applied synthetic chemistry • Medicinal chemistry—a definition—the use of synthetic organic chemistry to create molecules that will alter in a useful way some disease process in a living system. -D. Lednicer ...
... relate it to applied synthetic chemistry • Medicinal chemistry—a definition—the use of synthetic organic chemistry to create molecules that will alter in a useful way some disease process in a living system. -D. Lednicer ...
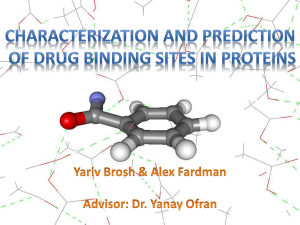
Characterization and prediction of drug binding sites in proteins
... • Proteins – organic compounds that constitute the basic functional and computational unit in the cell. They are able to bind other molecules specifically and tightly. ...
... • Proteins – organic compounds that constitute the basic functional and computational unit in the cell. They are able to bind other molecules specifically and tightly. ...
patrick_ch09_p1-1
... Selectivity between different enzymes, receptors etc. Selectivity between receptor types and subtypes Selectivity between isozymes Organ selectivity ...
... Selectivity between different enzymes, receptors etc. Selectivity between receptor types and subtypes Selectivity between isozymes Organ selectivity ...
FINDING A LEAD Part 1: Sections 9.1-9.3
... Selectivity between different enzymes, receptors etc. Selectivity between receptor types and subtypes Selectivity between isozymes Organ selectivity ...
... Selectivity between different enzymes, receptors etc. Selectivity between receptor types and subtypes Selectivity between isozymes Organ selectivity ...
Collecting Data --- Experiments Example: testing of new
... • Clinical trial: Double blinded, placebo controlled, randomized. • recruit volunteers that met specific requirements (have certain conditions). Statistician will decide how much subjects is enough. (usually 100 to 1000, depending on what you are looking for, what is the budget, how certain the res ...
... • Clinical trial: Double blinded, placebo controlled, randomized. • recruit volunteers that met specific requirements (have certain conditions). Statistician will decide how much subjects is enough. (usually 100 to 1000, depending on what you are looking for, what is the budget, how certain the res ...
Substance Jeopardy - Lake Park High School
... to remove particles from structures in the respiratory system ...
... to remove particles from structures in the respiratory system ...
Drug design
Drug design, sometimes referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is often referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.The phrase ""drug design"" is to some extent a misnomer. A more accurate term is ligand design (i.e., design of a molecule that will bind tightly to its target). Although design techniques for prediction of binding affinity are reasonably successful, there are many other properties, such as bioavailability, metabolic half-life, side effects, etc., that first must be optimized before a ligand can become a safe and efficacious drug. These other characteristics are often difficult to predict with rational design techniques. Nevertheless, due to high attrition rates, especially during clinical phases of drug development, more attention is being focused early in the drug design process on selecting candidate drugs whose physicochemical properties are predicted to result in fewer complications during development and hence more likely to lead to an approved, marketed drug. Furthermore, in vitro experiments complemented with computation methods are increasingly used in early drug discovery to select compounds with more favorable ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) and toxicological profiles.