PDF
... reward. The timing mechanism was implemented by representing each stimulus using a set of neurons, each of which was activated for a different duration (instead of the single prolonged inhibition in Barto’s model). The critic learning rule was modified to ensure that only the weight for the stimulus ...
... reward. The timing mechanism was implemented by representing each stimulus using a set of neurons, each of which was activated for a different duration (instead of the single prolonged inhibition in Barto’s model). The critic learning rule was modified to ensure that only the weight for the stimulus ...
Down - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... Fig. 5.15 (A) Estimate of mutual information between face stimuli and firing rate responses of C cells in the inferior-temporal cortex. The set of stimuli consisted 20 faces (stars). 8 faces (crosses), and 4 face(squares). (B) the information in the population of cells relative to the umber of stimu ...
... Fig. 5.15 (A) Estimate of mutual information between face stimuli and firing rate responses of C cells in the inferior-temporal cortex. The set of stimuli consisted 20 faces (stars). 8 faces (crosses), and 4 face(squares). (B) the information in the population of cells relative to the umber of stimu ...
29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems The
... 29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems • The spinal cord controls reflexes. – sensory neuron sends impulse to spinal cord – spinal cord directs impulse to motor neuron – does not involve the brain!!!! ...
... 29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems • The spinal cord controls reflexes. – sensory neuron sends impulse to spinal cord – spinal cord directs impulse to motor neuron – does not involve the brain!!!! ...
Down - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... Fig. 5.15 (A) Estimate of mutual information between face stimuli and firing rate responses of C cells in the inferior-temporal cortex. The set of stimuli consisted 20 faces (stars). 8 faces (crosses), and 4 face(squares). (B) the information in the population of cells relative to the umber of stimu ...
... Fig. 5.15 (A) Estimate of mutual information between face stimuli and firing rate responses of C cells in the inferior-temporal cortex. The set of stimuli consisted 20 faces (stars). 8 faces (crosses), and 4 face(squares). (B) the information in the population of cells relative to the umber of stimu ...
Chapter 48
... • The membrane potential of a cell can be measured APPLICATION Electrophysiologists use intracellular recording to measure the membrane potential of neurons and other cells. TECHNIQUE A microelectrode is made from a glass capillary tube filled with an electrically conductive salt solution. One end ...
... • The membrane potential of a cell can be measured APPLICATION Electrophysiologists use intracellular recording to measure the membrane potential of neurons and other cells. TECHNIQUE A microelectrode is made from a glass capillary tube filled with an electrically conductive salt solution. One end ...
52 Nerve Tissue
... A neuron has only one axon, which conducts impulses away from the parent neuron to other functionally related neurons or effector organs. The axon arises from the axon hillock, an elevation on the surface of the perikaryon that lacks Nissl substance. Occasionally, axons may arise from the base of a ...
... A neuron has only one axon, which conducts impulses away from the parent neuron to other functionally related neurons or effector organs. The axon arises from the axon hillock, an elevation on the surface of the perikaryon that lacks Nissl substance. Occasionally, axons may arise from the base of a ...
The Dynamics of Functional Brain Networks
... challenging 2-back trials within the N-back task using the EZ-diffusion model (Wagenmakers et al., 2007; Figure 3A). The diffusion model provides a decomposition of behavioral performance into cognitively relevant latent variables representing the speed and accuracy of information processing (drift ...
... challenging 2-back trials within the N-back task using the EZ-diffusion model (Wagenmakers et al., 2007; Figure 3A). The diffusion model provides a decomposition of behavioral performance into cognitively relevant latent variables representing the speed and accuracy of information processing (drift ...
EVOLUTIONARY AUTONOMOUS AGENTS: A NEUROSCIENCE
... on the basis of certain sensory stimuli16, and in particular, as in the EAA simulation, by food arousal17,18. This activity has been shown to control a variety of motor repertoires, mainly by inducing different activity patterns in the same network by modulating neuronal activity21,22 — again, in a ...
... on the basis of certain sensory stimuli16, and in particular, as in the EAA simulation, by food arousal17,18. This activity has been shown to control a variety of motor repertoires, mainly by inducing different activity patterns in the same network by modulating neuronal activity21,22 — again, in a ...
Ratio of Glia and Ne..
... Zooming in even further, her study counted 6.18 billion neurons and 8.68 billion glia in the gray matter of the cortex, vs. 1.29 billion neurons and 19.88 billion glia in the white matter. Gray matter is largely made up of the unmyelinated parts of neurons—neurons that are not sheathed by glial cell ...
... Zooming in even further, her study counted 6.18 billion neurons and 8.68 billion glia in the gray matter of the cortex, vs. 1.29 billion neurons and 19.88 billion glia in the white matter. Gray matter is largely made up of the unmyelinated parts of neurons—neurons that are not sheathed by glial cell ...
self-organising map
... •Only the winning neuron and neurons inside its neighbourhood have their weights adapted. All the other neurons have no change in their weights. •A method for deriving the weight update equations for the SOM model is based on a modified form of Hebbian learning. There is a forgetting term in the sta ...
... •Only the winning neuron and neurons inside its neighbourhood have their weights adapted. All the other neurons have no change in their weights. •A method for deriving the weight update equations for the SOM model is based on a modified form of Hebbian learning. There is a forgetting term in the sta ...
Maximum Likelihood
... The technique of maximum likelihood (ML) is a method to: (1) estimate the parameters of a model; and (2) test hypotheses about those parameters. There have been books written on the topic (a good one is Likelihood by A.W.F. Edwards, New York: Cambridge University Press, 1972), so this chapter will s ...
... The technique of maximum likelihood (ML) is a method to: (1) estimate the parameters of a model; and (2) test hypotheses about those parameters. There have been books written on the topic (a good one is Likelihood by A.W.F. Edwards, New York: Cambridge University Press, 1972), so this chapter will s ...
Author`s personal copy Computational models of motivated action
... James [1] noted, ‘selection is the keel on which our mental ship is built’. The connection between the BG and action selection has been studied intensively [2–5], with computational accounts initially and/or most prominently offered by Houk [6,7] and Barto [8], followed by Doya [9], Gurney [10], and ...
... James [1] noted, ‘selection is the keel on which our mental ship is built’. The connection between the BG and action selection has been studied intensively [2–5], with computational accounts initially and/or most prominently offered by Houk [6,7] and Barto [8], followed by Doya [9], Gurney [10], and ...
Biomorphic Circuits and Systems: Control of Robotic and Prosthetic Limbs
... that live in coastal waters, to cats [2]. Evidence of its presence has also been found in humans in different scenarios: in the spontaneous rhythmic movements made by some patients after spinal cord injury (SCI) [3], and from the evolution of EMG activity in the legs of patients with paraplegia who ...
... that live in coastal waters, to cats [2]. Evidence of its presence has also been found in humans in different scenarios: in the spontaneous rhythmic movements made by some patients after spinal cord injury (SCI) [3], and from the evolution of EMG activity in the legs of patients with paraplegia who ...
Document
... motor cortex synapse on lower motor neurons (ventral horn of spinal cord) also project to other control centers ...
... motor cortex synapse on lower motor neurons (ventral horn of spinal cord) also project to other control centers ...
Ch 48 Nervous System
... • In humans, the largest and most complex part of the brain – Is the cerebral cortex, where sensory information is analyzed, motor commands are issued, and language is generated ...
... • In humans, the largest and most complex part of the brain – Is the cerebral cortex, where sensory information is analyzed, motor commands are issued, and language is generated ...
Bi150 (2005)
... •The ‘mapping’ of these compounds probably occurs by matching to memory templates stored in the brain • A smell is categorized based on one’s previous experiences of it and on the other sensory stimuli correlated with its appearance. ...
... •The ‘mapping’ of these compounds probably occurs by matching to memory templates stored in the brain • A smell is categorized based on one’s previous experiences of it and on the other sensory stimuli correlated with its appearance. ...
(< 50 m) non-transfected neurons using laser scanning
... supplemented with 0.37 mM Nitroindolinyl (NI)-caged glutamate and 5 M CPP (Sigma-RBI). The cells in a pair were recorded sequentially. There were no differences in their basic membrane properties (resting potential, input resistance, capacitance; n = 4 animals, 9 cell pairs, P > 0.09, Wilcoxon rank ...
... supplemented with 0.37 mM Nitroindolinyl (NI)-caged glutamate and 5 M CPP (Sigma-RBI). The cells in a pair were recorded sequentially. There were no differences in their basic membrane properties (resting potential, input resistance, capacitance; n = 4 animals, 9 cell pairs, P > 0.09, Wilcoxon rank ...
Optic Glomeruli and Their Inputs inDrosophilaShare an
... Hemisection through the brain labeled with anti-␣-tubulin and anti-GFP, showing the ensemble of type Col A LCN neurons in the lobula Animal preparation. Our animal setup (Fig. with converging axons to its corresponding Col A glomerulus. This lies ventral and medial to a glomerulus receiving terminal ...
... Hemisection through the brain labeled with anti-␣-tubulin and anti-GFP, showing the ensemble of type Col A LCN neurons in the lobula Animal preparation. Our animal setup (Fig. with converging axons to its corresponding Col A glomerulus. This lies ventral and medial to a glomerulus receiving terminal ...
PRINCIPLES OF NEUROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 6
... neuron is about odor identity. The overlaps between these distributions are determined both by the means of the neuron’s responses and by response variability: distributions for less variable responses will be narrower and thus exhibit less overlap, and means that are further apart from each other w ...
... neuron is about odor identity. The overlaps between these distributions are determined both by the means of the neuron’s responses and by response variability: distributions for less variable responses will be narrower and thus exhibit less overlap, and means that are further apart from each other w ...
Monday, June 20, 2005
... electrophysiological methods. As examples, I introduce some of our applications of imaging techniques on evaluation of dynamics of neural functions modulated by intracellular Cl- as below. In individual neurons in brain slices in which Cl--sensitive fluorescent dye MEQ was injected from patch electr ...
... electrophysiological methods. As examples, I introduce some of our applications of imaging techniques on evaluation of dynamics of neural functions modulated by intracellular Cl- as below. In individual neurons in brain slices in which Cl--sensitive fluorescent dye MEQ was injected from patch electr ...
Coupling in Networks of Neuronal Oscillators (Spring 2015)
... Oscillators are ubiquitous in nature. From the pacemaker cells that keep our hearts beating to the predator-prey population interactions of wild animals, oscillators drive the natural world as we know it. An oscillator is any system that goes through various states cyclically and exhibits periodic b ...
... Oscillators are ubiquitous in nature. From the pacemaker cells that keep our hearts beating to the predator-prey population interactions of wild animals, oscillators drive the natural world as we know it. An oscillator is any system that goes through various states cyclically and exhibits periodic b ...
Nervous System
... Transient changes in the conductance of the postsynaptic plasma membrane to specific ions. Transient change in the membrane potential of the post synaptic cell (excitatory or inhibitory). Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Transient changes in the conductance of the postsynaptic plasma membrane to specific ions. Transient change in the membrane potential of the post synaptic cell (excitatory or inhibitory). Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
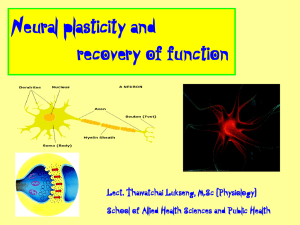
Neural plasticity and recovery of function
... • Plastic (adj.) = soft enough to be changed into a new shape • Neuroplasticity, brain plasticity or brain malleability • The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections • Neurons (nerve cells) in the brain to compensate for injury and disease and to adjust their activitie ...
... • Plastic (adj.) = soft enough to be changed into a new shape • Neuroplasticity, brain plasticity or brain malleability • The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections • Neurons (nerve cells) in the brain to compensate for injury and disease and to adjust their activitie ...
Chapter 3
... – Acetylcholine is broken down by acetylcholinesterase into acetate and choline. • Some serotonin and catecholamine molecules are converted into inactive chemicals: – COMT (catechol-o-methyltranferase)and MAO (monoamine oxidase) are enzymes that convert catecholamine transmitters into inactive chemi ...
... – Acetylcholine is broken down by acetylcholinesterase into acetate and choline. • Some serotonin and catecholamine molecules are converted into inactive chemicals: – COMT (catechol-o-methyltranferase)and MAO (monoamine oxidase) are enzymes that convert catecholamine transmitters into inactive chemi ...