development of an artificial neural network for monitoring
... A neural network is a massively parallel distributed processor made up of simple processing units, which has a natural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. The knowledge is acquired by the networks from its environment through a learning process which is bas ...
... A neural network is a massively parallel distributed processor made up of simple processing units, which has a natural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. The knowledge is acquired by the networks from its environment through a learning process which is bas ...
EN Sokolov`s Neural Model of Stimuli as Neuro
... important elements of attention that respond to the first stimulus presentation [9]. Novelty neurons are used to distinguish new signals. As their distinct feature, their background impulses increase under the influence of new stimuli of different modalities. These neurons are connected through mult ...
... important elements of attention that respond to the first stimulus presentation [9]. Novelty neurons are used to distinguish new signals. As their distinct feature, their background impulses increase under the influence of new stimuli of different modalities. These neurons are connected through mult ...
Biochemistry of Nerve Transmission - I-GaP
... repolarization to take place; this step, hydrolysis, is carried out by the enzyme, acetylcholinesterase. The acetylcholinesterase found at nerve endings is anchored to the plasma membrane through a glycolipid. ACh receptors are ligandgated cation channels composed of four different polypeptide subun ...
... repolarization to take place; this step, hydrolysis, is carried out by the enzyme, acetylcholinesterase. The acetylcholinesterase found at nerve endings is anchored to the plasma membrane through a glycolipid. ACh receptors are ligandgated cation channels composed of four different polypeptide subun ...
Insights from models of rhythmic motor systems
... the motor pattern, which tends to deviate from the intrinsic oscillation frequency of the isolated neural circuit and to approach the natural frequency of the body part [7]. Furthermore, a closed loop between a neuronal oscillator and a mechanical system can lead to the emergence of modes of oscilla ...
... the motor pattern, which tends to deviate from the intrinsic oscillation frequency of the isolated neural circuit and to approach the natural frequency of the body part [7]. Furthermore, a closed loop between a neuronal oscillator and a mechanical system can lead to the emergence of modes of oscilla ...
news and views - Cortical Plasticity
... Because zero-valued synaptic weights translate into ineffectual connections, this implies that most neighboring pairs of neurons should not be connected. This finding helps explain why many neighboring neurons do not connect with functional synapses even though they are so close that their axons and ...
... Because zero-valued synaptic weights translate into ineffectual connections, this implies that most neighboring pairs of neurons should not be connected. This finding helps explain why many neighboring neurons do not connect with functional synapses even though they are so close that their axons and ...
VI. The vertebrate nervous system is a hierarchy of structural and
... • The undershoot phase is a time when the membrane potential is temporarily more negative than the resting state (hyperpolarized); sodium channels remain closed but potassium channels remain open since the inactivation gates have not had time to respond to repolarization of the membrane. A refractor ...
... • The undershoot phase is a time when the membrane potential is temporarily more negative than the resting state (hyperpolarized); sodium channels remain closed but potassium channels remain open since the inactivation gates have not had time to respond to repolarization of the membrane. A refractor ...
Nervous System
... • travels down axon one small segment at a time • As soon as action potential moves on, the previous section undergoes refractory period – Sodium gates cannot reopen – Prevents retrograde transmission – During this time sodium-potassium pump restores ions to original positions ...
... • travels down axon one small segment at a time • As soon as action potential moves on, the previous section undergoes refractory period – Sodium gates cannot reopen – Prevents retrograde transmission – During this time sodium-potassium pump restores ions to original positions ...
Membrane Potential Fluctuations in Neural Integrator
... have to be integrated into position signals by a neural integrator. Lesion experiment and analysis of neural activity patterns suggest that the fixation and VOR subsystems share the same integrator [45]. As angular rotation is an analog process, the ocular motor integrator must possess graded persis ...
... have to be integrated into position signals by a neural integrator. Lesion experiment and analysis of neural activity patterns suggest that the fixation and VOR subsystems share the same integrator [45]. As angular rotation is an analog process, the ocular motor integrator must possess graded persis ...
Pattern Vision and Natural Scenes
... To return to eye design implications. Saccade lengths tend to be larger than decorrelation distances ( the distance over which contrast is correlated) in natural scenes. The arrow indicates the average decorrelation distance in natural outdoor scenes. We have measured saccade lengths in search expe ...
... To return to eye design implications. Saccade lengths tend to be larger than decorrelation distances ( the distance over which contrast is correlated) in natural scenes. The arrow indicates the average decorrelation distance in natural outdoor scenes. We have measured saccade lengths in search expe ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... a stimulus in the receptive field. In the left panels themonkey is fixating and a stable stimulus is in the receptive field. The neuron has low firing rate. In the center panel the monkey receives a cue instructing him to make a saccade to the receptive field. The neuron gradually increases its resp ...
... a stimulus in the receptive field. In the left panels themonkey is fixating and a stable stimulus is in the receptive field. The neuron has low firing rate. In the center panel the monkey receives a cue instructing him to make a saccade to the receptive field. The neuron gradually increases its resp ...
Bio 103 Lecture Outline:
... * environmental changes affect the membrane potential by opening a gated ion channel ...
... * environmental changes affect the membrane potential by opening a gated ion channel ...
Bio 103 Lecture Outline:
... * environmental changes affect the membrane potential by opening a gated ion channel ...
... * environmental changes affect the membrane potential by opening a gated ion channel ...
simple cyclic movements as a distinct autism
... of Mental Disorders, DSM) define the whole Autism Spectrum of Disorders (ASD) rather than just autism. Currently, most researchers agree that ASD is a developmental and behavioral disease with multiple etiologies, including genetic mutations as well as metabolic and immune system deregulation leading ...
... of Mental Disorders, DSM) define the whole Autism Spectrum of Disorders (ASD) rather than just autism. Currently, most researchers agree that ASD is a developmental and behavioral disease with multiple etiologies, including genetic mutations as well as metabolic and immune system deregulation leading ...
1 - Wsfcs
... axon; action potential ___ 14. The difference between neuron A, which picks up information about a mad dog running toward you, and neuron B, which picks up information about the smell of food cooking in the restaurant next door, is the presence of A) myelin around neuron A but not neuron B. B) myeli ...
... axon; action potential ___ 14. The difference between neuron A, which picks up information about a mad dog running toward you, and neuron B, which picks up information about the smell of food cooking in the restaurant next door, is the presence of A) myelin around neuron A but not neuron B. B) myeli ...
Slide ()
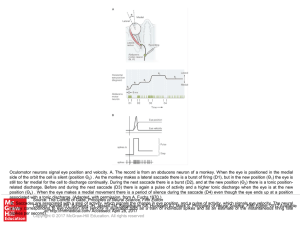
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
lgn - cinpla
... feedback from the visual cortex. One would therefore expect the LGN to be more heavily influenced by visual cortex and the response not so similar to the input from retina. The role of this massive feedback has not been clearly identified, and the functional role of the LGN is therefore poorly under ...
... feedback from the visual cortex. One would therefore expect the LGN to be more heavily influenced by visual cortex and the response not so similar to the input from retina. The role of this massive feedback has not been clearly identified, and the functional role of the LGN is therefore poorly under ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... Afferent neurons: The afferent neurons (fibers) of the autonomic nervous system are important in the reflexregulation of this system (for example, by sensing pressure in the carotid sinus and aortic arch) and signaling theCNS to influence the efferent branch of the system to respond Sympathetic neur ...
... Afferent neurons: The afferent neurons (fibers) of the autonomic nervous system are important in the reflexregulation of this system (for example, by sensing pressure in the carotid sinus and aortic arch) and signaling theCNS to influence the efferent branch of the system to respond Sympathetic neur ...
Autism and Computational Simulations
... hippocampus elucidated synchronization processes and showed the influence of various chemicals. Very high 200-600 Hz (phi) frequencies observed in some form of epilepsy cannot be generated by “normal” chemical synapses. Fast electrical nonsynaptic communication is possible through gap junctions fill ...
... hippocampus elucidated synchronization processes and showed the influence of various chemicals. Very high 200-600 Hz (phi) frequencies observed in some form of epilepsy cannot be generated by “normal” chemical synapses. Fast electrical nonsynaptic communication is possible through gap junctions fill ...
Linking Genetically Defined Neurons to Behavior through a Broadly
... of GFPtox from RC::PFtox requires removal of two stop cassettes, a loxP-flanked cassette excisable by Cre recombinase and an FRT-flanked cassette, by Flpe (Figures 1A–1C). GFPtox action, therefore, should restrict to just those cells having expressed both Cre and Flpe recombinase. Requiring two reco ...
... of GFPtox from RC::PFtox requires removal of two stop cassettes, a loxP-flanked cassette excisable by Cre recombinase and an FRT-flanked cassette, by Flpe (Figures 1A–1C). GFPtox action, therefore, should restrict to just those cells having expressed both Cre and Flpe recombinase. Requiring two reco ...
Ch. 7 - Nervous System
... VI Abducens nerve—motor fibers to eye muscles VII Facial nerve—sensory for taste; motor fibers to the face VIII Vestibulocochlear nerve—sensory for balance and hearing IX Glossopharyngeal nerve—sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx X Vagus nerves—sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx ...
... VI Abducens nerve—motor fibers to eye muscles VII Facial nerve—sensory for taste; motor fibers to the face VIII Vestibulocochlear nerve—sensory for balance and hearing IX Glossopharyngeal nerve—sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx X Vagus nerves—sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx ...
Note
... Estimating the discriminability of two stimuli from the neural responses proceeds by calculating the distribution of responses to the two stimuli P(n|v) from data (where n = NT , the number of spikes); the stimuli v are noise (n) and tone plus noise (t). The discrimination task is to detect the ton ...
... Estimating the discriminability of two stimuli from the neural responses proceeds by calculating the distribution of responses to the two stimuli P(n|v) from data (where n = NT , the number of spikes); the stimuli v are noise (n) and tone plus noise (t). The discrimination task is to detect the ton ...
Myotatic Reflex
... — panniculus reflex: pricking skin triggers contraction of cutaneus trunci (panniculus) m. — myotatic reflex: muscle stretch is resisted by reflex contraction of the muscle — withdrawal reflex: limb flexes to withdraw from a noxious stimulus ...
... — panniculus reflex: pricking skin triggers contraction of cutaneus trunci (panniculus) m. — myotatic reflex: muscle stretch is resisted by reflex contraction of the muscle — withdrawal reflex: limb flexes to withdraw from a noxious stimulus ...
Models and Selection Criteria for Regression and Classification x, y
... for this task. In particular, we examine a spe cial class of models, which we call Bayesian regression/classification (BRC) models, that can be factored into independent conditional (ylx) and input ( x ) models. These mod els are convenient, because the conditional model (the portion of the full m ...
... for this task. In particular, we examine a spe cial class of models, which we call Bayesian regression/classification (BRC) models, that can be factored into independent conditional (ylx) and input ( x ) models. These mod els are convenient, because the conditional model (the portion of the full m ...