NERVOUS SYSTEM AND REFLEXES Introduction:
... eyes. When a bright light stimulates the retina of the eye, impulses are carried to the brain by sensory neurons. In the brain, the impulses are transmitted to interneurons which determine an appropriate response which is carried out by motor neurons that cause the muscles of the iris to contract. C ...
... eyes. When a bright light stimulates the retina of the eye, impulses are carried to the brain by sensory neurons. In the brain, the impulses are transmitted to interneurons which determine an appropriate response which is carried out by motor neurons that cause the muscles of the iris to contract. C ...
the original powerpoint file
... version of the wake-sleep algorithm • Replace the top layer of the causal network by an RBM – This eliminates explaining away at the top-level. – It is nice to have an associative memory at the top. • Replace the sleep phase by a top-down pass starting with the state of the RBM produced by the wake ...
... version of the wake-sleep algorithm • Replace the top layer of the causal network by an RBM – This eliminates explaining away at the top-level. – It is nice to have an associative memory at the top. • Replace the sleep phase by a top-down pass starting with the state of the RBM produced by the wake ...
Supplement: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... postsynaptic potentials in invertebrate preparations by depolarization of the presynaptic soma results from an increase in the probability of transmitter release16, perhaps through increases in tonic levels of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminals23 or through broadening of presynaptic action potentials ...
... postsynaptic potentials in invertebrate preparations by depolarization of the presynaptic soma results from an increase in the probability of transmitter release16, perhaps through increases in tonic levels of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminals23 or through broadening of presynaptic action potentials ...
Supplement to: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... postsynaptic potentials in invertebrate preparations by depolarization of the presynaptic soma results from an increase in the probability of transmitter release16, perhaps through increases in tonic levels of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminals23 or through broadening of presynaptic action potentials ...
... postsynaptic potentials in invertebrate preparations by depolarization of the presynaptic soma results from an increase in the probability of transmitter release16, perhaps through increases in tonic levels of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminals23 or through broadening of presynaptic action potentials ...
File - medicalfocus tanzania home of health professional
... A home heating system illustrates how a negative feedback mechanism works. You set the thermostat at, say, 68°F. This is the set point. The thermostat contains a thermometer, a sensor that detects when the room temperature falls below the set point. The thermostat is also the regulatory center; it t ...
... A home heating system illustrates how a negative feedback mechanism works. You set the thermostat at, say, 68°F. This is the set point. The thermostat contains a thermometer, a sensor that detects when the room temperature falls below the set point. The thermostat is also the regulatory center; it t ...
Distributed Processing of Sensory Information in
... Figure 4. Response of each type of motor neuron to single P cell stimulation. A, Average peak synaptic potential in millivolts in response to stimulation of a single PD (n 2 34). Each panel quadrant corresponds to the indicated quadrant of body surface (e.g., ipsilateral dorsal). The response of eac ...
... Figure 4. Response of each type of motor neuron to single P cell stimulation. A, Average peak synaptic potential in millivolts in response to stimulation of a single PD (n 2 34). Each panel quadrant corresponds to the indicated quadrant of body surface (e.g., ipsilateral dorsal). The response of eac ...
Modeling the role of mossy fiber input to CA3 objectives: extended model of Cerasti and Treves
... The entorhinal-hippocampal complex has been extensively studied in rodents. In one class of experiments, neural activity is monitored (typically through extracellular recordings) while a rodent performs a random foraging task, in which it runs around an environment (usually a box around 1 square met ...
... The entorhinal-hippocampal complex has been extensively studied in rodents. In one class of experiments, neural activity is monitored (typically through extracellular recordings) while a rodent performs a random foraging task, in which it runs around an environment (usually a box around 1 square met ...
Spinal Cord and the Peripheral Nervous System
... (acetylcholine; the neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction) into the synaptic cleft. • Ach binds to receptor sites on the muscle fiber (muscle cell) membrane. This opens up the Na+ channels so that sodium rushes into the cell. • When Na+ brings its positive charge to the inside of the cell, ...
... (acetylcholine; the neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction) into the synaptic cleft. • Ach binds to receptor sites on the muscle fiber (muscle cell) membrane. This opens up the Na+ channels so that sodium rushes into the cell. • When Na+ brings its positive charge to the inside of the cell, ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-30
... Lower Motor Neuron (LMN, alpha motor neuron): -Cell body in spinal cord (spinal nerve) or in brainstem (cranial nerve) -Axon terminates on muscles Upper Motor Neuron (UMN): -Cell body in brainstem or cortex -Synapses on lower motor neuron -Strong influence on lower motor neuron Reflex: 2 neurons and ...
... Lower Motor Neuron (LMN, alpha motor neuron): -Cell body in spinal cord (spinal nerve) or in brainstem (cranial nerve) -Axon terminates on muscles Upper Motor Neuron (UMN): -Cell body in brainstem or cortex -Synapses on lower motor neuron -Strong influence on lower motor neuron Reflex: 2 neurons and ...
Document
... Schwann cells– surround and myelinate axons of the PNS Satellite cells- surround neuron cell bodies within ganglia Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Schwann cells– surround and myelinate axons of the PNS Satellite cells- surround neuron cell bodies within ganglia Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Nervous System - The Beat@KUMC
... Sends signals between different parts of the body through neurons Coordinates and controls all the actions and senses in the body ...
... Sends signals between different parts of the body through neurons Coordinates and controls all the actions and senses in the body ...
Module 3 - yhernandez
... mechanical pressure and transform it into electrical signals – Signals are sent by the neuron’s axon to various areas in the spinal cord and brain – Brain interprets electrical signals as “pain” axon ...
... mechanical pressure and transform it into electrical signals – Signals are sent by the neuron’s axon to various areas in the spinal cord and brain – Brain interprets electrical signals as “pain” axon ...
Gnostic cells in the 21st century
... previously described by Horace Barlow and Lettvin himself in the 1950’s (Barlow 1953, Lettvin et al. 1959, Gross 2002). In the early 70’s, Barlow revisited Sherrington’s views and offered a more refined version of James’ pontifical cells (but far from Sherrington’s million-fold democracy), arguing t ...
... previously described by Horace Barlow and Lettvin himself in the 1950’s (Barlow 1953, Lettvin et al. 1959, Gross 2002). In the early 70’s, Barlow revisited Sherrington’s views and offered a more refined version of James’ pontifical cells (but far from Sherrington’s million-fold democracy), arguing t ...
Neurons and Glia
... fused together to form a continuous reticulum, or network, similar to the arteries and veins of the circulatory system. According to this reticular theory, the brain is an exception to the cell theory, which statesthar the individual cell is the elementary functional unit of all animal tissues. Caja ...
... fused together to form a continuous reticulum, or network, similar to the arteries and veins of the circulatory system. According to this reticular theory, the brain is an exception to the cell theory, which statesthar the individual cell is the elementary functional unit of all animal tissues. Caja ...
Slide ()
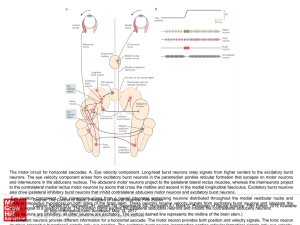
... of Gaze, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth comprising Editon nucleus prepositus hypoglossi on both sides of the brain stem. These neurons receive velocity signals from excitatory burst neurons and integrate this Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Prin ...
... of Gaze, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth comprising Editon nucleus prepositus hypoglossi on both sides of the brain stem. These neurons receive velocity signals from excitatory burst neurons and integrate this Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Prin ...
NEUROBIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOR
... • Pre-synaptic neuron: area of axon where neurotransmitters are stored. • Postsynaptic neuron: area of dendrite where receptor sites are located. ...
... • Pre-synaptic neuron: area of axon where neurotransmitters are stored. • Postsynaptic neuron: area of dendrite where receptor sites are located. ...
Olfactory network dynamics and the coding of multidimensional
... • Many olfactory problems are complex: they involve odours that are composed of multimolecular mixtures (sometimes containing hundreds of volatile components). • Odour perception tends to bind together rather than to segment the elements of a mixture; the olfactory system therefore recognizes odour ...
... • Many olfactory problems are complex: they involve odours that are composed of multimolecular mixtures (sometimes containing hundreds of volatile components). • Odour perception tends to bind together rather than to segment the elements of a mixture; the olfactory system therefore recognizes odour ...
IONIC BASES OF THE RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL
... since the membrane is negatively charged, potassium moves out more slowly than it moves in. Because of this, the two rate constants differ, depending on valence (charge), membrane potential as well as on concentration. It can be shown that: rin = p zV’/(ezV’-1) where z= valence (1), V’ = membrane po ...
... since the membrane is negatively charged, potassium moves out more slowly than it moves in. Because of this, the two rate constants differ, depending on valence (charge), membrane potential as well as on concentration. It can be shown that: rin = p zV’/(ezV’-1) where z= valence (1), V’ = membrane po ...
$doc.title
... • How can we (experimenters) process and understand the signals that we record from the brain? ...
... • How can we (experimenters) process and understand the signals that we record from the brain? ...
Class X: Control and Coordination Some movements are in fact the
... 19. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light? 20. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth. 21. Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin? 22. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain it ...
... 19. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light? 20. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth. 21. Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin? 22. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain it ...
ReinagelTutorial2000..
... information encoded by the firing rate of a neuron. We can then ask whether additional information is transmitted by other features of the neural response. The most striking lesson to emerge over the past decade is that the exact timing of action potentials is important in neural coding, particularl ...
... information encoded by the firing rate of a neuron. We can then ask whether additional information is transmitted by other features of the neural response. The most striking lesson to emerge over the past decade is that the exact timing of action potentials is important in neural coding, particularl ...
AND X 2
... Each neuron also has an axon goes out and splits into a number of strands to make a connection to other neurons The point at which neurons join other neurons is called a synapse ...
... Each neuron also has an axon goes out and splits into a number of strands to make a connection to other neurons The point at which neurons join other neurons is called a synapse ...
Nervous Tissue
... The cell membrane are very thin. The Nucleus has a thick nuclear membrane and clear nucleolus. The cytoplasm contains all cell organoids & inclusions but with no centrioles. The cytoplasm is rich in microtubules & nerofilaments. The cytoplasm is rich in Nissl granules or bodies. ...
... The cell membrane are very thin. The Nucleus has a thick nuclear membrane and clear nucleolus. The cytoplasm contains all cell organoids & inclusions but with no centrioles. The cytoplasm is rich in microtubules & nerofilaments. The cytoplasm is rich in Nissl granules or bodies. ...
cogsci200
... - how neurons can grow randomly and become organized. - that a large range of synaptic weights is not necessary. - how you can get a song stuck in your head. (You’re unable to reset regions of your cortex. One bar evokes the next…) - a model that can be viewed as implementing Paul Churchland’s “sema ...
... - how neurons can grow randomly and become organized. - that a large range of synaptic weights is not necessary. - how you can get a song stuck in your head. (You’re unable to reset regions of your cortex. One bar evokes the next…) - a model that can be viewed as implementing Paul Churchland’s “sema ...