CIS 265/506 Midterm Review
... 5. Comparing Strings: == vs. equals method; other String methods: charAt, compareTo, indexOf, concat, toUpper, toLower, substring (2 versions of this method). 6. Creating objects using new operator and constructor. 7. User-defined methods – methods have return type and parameters; primitive types ar ...
... 5. Comparing Strings: == vs. equals method; other String methods: charAt, compareTo, indexOf, concat, toUpper, toLower, substring (2 versions of this method). 6. Creating objects using new operator and constructor. 7. User-defined methods – methods have return type and parameters; primitive types ar ...
5 Exponential Functions - Arkansas Tech Faculty Web Sites
... The right-hand side is a percent rate. Thus, an exponential function is a function that changes at a constant percent rate. Example 5.2 Suppose you are offered a job at a starting salary of $40,000 per year. To strengthen the offer, the company promises annual raises of 6% per year for the first 10 ...
... The right-hand side is a percent rate. Thus, an exponential function is a function that changes at a constant percent rate. Example 5.2 Suppose you are offered a job at a starting salary of $40,000 per year. To strengthen the offer, the company promises annual raises of 6% per year for the first 10 ...
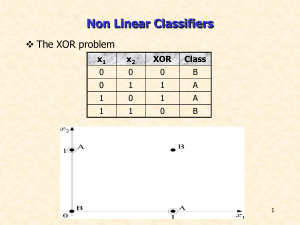
Machine Learning ICS 273A
... •The ability of a machine to improve its performance based on previous results. •The process by which computer systems can be directed to improve their performance over time. •Subspecialty of artificial intelligence concerned with developing methods for software to learn from experience or extract k ...
... •The ability of a machine to improve its performance based on previous results. •The process by which computer systems can be directed to improve their performance over time. •Subspecialty of artificial intelligence concerned with developing methods for software to learn from experience or extract k ...
Exhibit 8.1
... • The language barrier and literacy pose a major problem when doing a survey abroad. – It may be that exact translations do not exist for some survey questions. – The population may not have a high enough literacy rate to understand the survey. ...
... • The language barrier and literacy pose a major problem when doing a survey abroad. – It may be that exact translations do not exist for some survey questions. – The population may not have a high enough literacy rate to understand the survey. ...
CSCI 491/595: Mining Big Data Spring 2016
... This class will expose students to applications of data. Students will become functionally adept at data acquisition, data cleansing, feature selection, and data analysis. Though some time will be spent on the internals of popular algorithms for data mining, this discussion will be limited to develo ...
... This class will expose students to applications of data. Students will become functionally adept at data acquisition, data cleansing, feature selection, and data analysis. Though some time will be spent on the internals of popular algorithms for data mining, this discussion will be limited to develo ...
Document
... node is aware of only its neighbors but not the entire graph. Every node has a unique, unforgeable identity. • Problem: Assume that k among the n nodes are adversarial and the remaining (n-k) nodes are good nodes which follow a prescribed algorithm. For what values of k, can we get a distributed alg ...
... node is aware of only its neighbors but not the entire graph. Every node has a unique, unforgeable identity. • Problem: Assume that k among the n nodes are adversarial and the remaining (n-k) nodes are good nodes which follow a prescribed algorithm. For what values of k, can we get a distributed alg ...
Conversion_Webcast
... Multiple ways to filter the data – Decide what data types will be converted • Immunizations, allergies, medications, results, problems, documents, vitals, images – Not every data type may be present in the source system • If organization has no inbound results interface then there may not be results ...
... Multiple ways to filter the data – Decide what data types will be converted • Immunizations, allergies, medications, results, problems, documents, vitals, images – Not every data type may be present in the source system • If organization has no inbound results interface then there may not be results ...
X t
... This is an algorithmic procedure that computes the synaptic weights iteratively, so that an adopted cost function is minimized (optimized) In a large number of optimizing procedures, computation of derivatives are involved. ...
... This is an algorithmic procedure that computes the synaptic weights iteratively, so that an adopted cost function is minimized (optimized) In a large number of optimizing procedures, computation of derivatives are involved. ...
Recitation 1
... In a computer program a variable is a named storage location in the computer’s memory. Each variable has a type and a name A variable should be declared and initialized Variable Declaration: char a; char is the variable type and a is the variable name Variables must be declared before th ...
... In a computer program a variable is a named storage location in the computer’s memory. Each variable has a type and a name A variable should be declared and initialized Variable Declaration: char a; char is the variable type and a is the variable name Variables must be declared before th ...
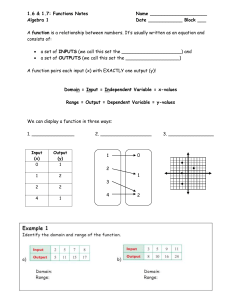
Algebra 1
... The Vertical Line Test The Vertical Line Test is a quick way to help you determine if a relation is a function. If all possible vertical lines cross the graph once or not at all, then the graph represents a function. The graph does not represent a function if you can draw even one vertical line tha ...
... The Vertical Line Test The Vertical Line Test is a quick way to help you determine if a relation is a function. If all possible vertical lines cross the graph once or not at all, then the graph represents a function. The graph does not represent a function if you can draw even one vertical line tha ...
Double Interpolation
... Two (independent) properties fix the state of a simple, pure substance. How many times have I made this point? Sometime in the future (hopefully near future) students of thermodynamics will rely exclusively on computerized thermodynamic property software to implement the two–property principle. Unti ...
... Two (independent) properties fix the state of a simple, pure substance. How many times have I made this point? Sometime in the future (hopefully near future) students of thermodynamics will rely exclusively on computerized thermodynamic property software to implement the two–property principle. Unti ...